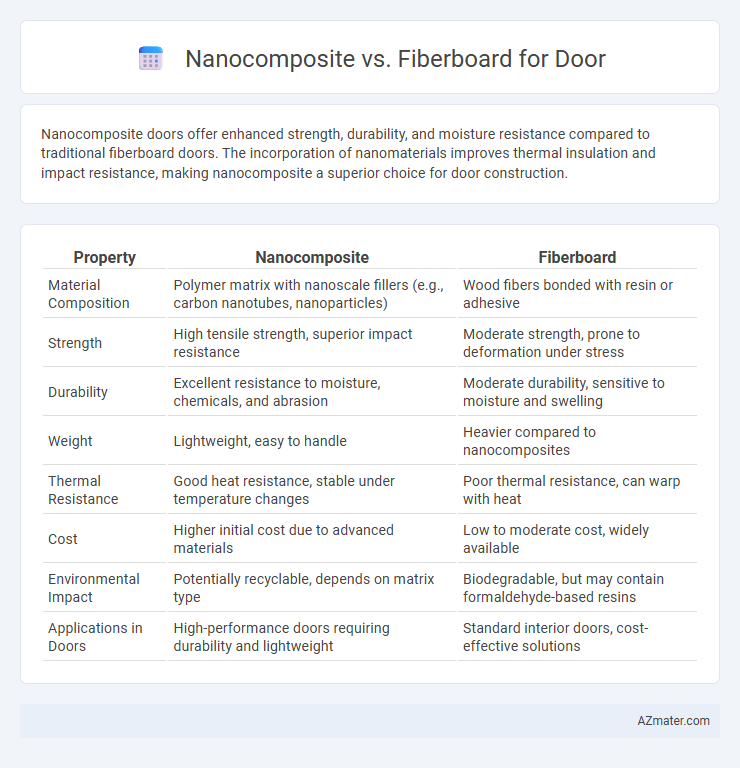
Nanocomposite doors offer enhanced strength, durability, and moisture resistance compared to traditional fiberboard doors. The incorporation of nanomaterials improves thermal insulation and impact resistance, making nanocomposite a superior choice for door construction.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nanocomposite | Fiberboard |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Polymer matrix with nanoscale fillers (e.g., carbon nanotubes, nanoparticles) | Wood fibers bonded with resin or adhesive |
| Strength | High tensile strength, superior impact resistance | Moderate strength, prone to deformation under stress |
| Durability | Excellent resistance to moisture, chemicals, and abrasion | Moderate durability, sensitive to moisture and swelling |
| Weight | Lightweight, easy to handle | Heavier compared to nanocomposites |
| Thermal Resistance | Good heat resistance, stable under temperature changes | Poor thermal resistance, can warp with heat |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to advanced materials | Low to moderate cost, widely available |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially recyclable, depends on matrix type | Biodegradable, but may contain formaldehyde-based resins |
| Applications in Doors | High-performance doors requiring durability and lightweight | Standard interior doors, cost-effective solutions |
Introduction to Nanocomposite and Fiberboard Doors
Nanocomposite doors incorporate nanoparticles into a matrix material, enhancing strength, durability, and resistance to moisture and environmental factors. Fiberboard doors, made from compressed wood fibers bonded with resin, offer affordability, smooth surfaces, and ease of customization but may lack the enhanced mechanical properties of nanocomposites. Comparing nanocomposite and fiberboard doors highlights differences in material composition, performance under stress, and long-term resilience.
Material Composition and Structure
Nanocomposite doors utilize advanced materials combining nanoparticles with polymers or resins, resulting in enhanced mechanical strength, durability, and resistance to moisture and impact. Fiberboard doors consist mainly of wood fibers bonded under heat and pressure, offering uniform density but lower resistance to water and mechanical stress compared to nanocomposites. The nanoscale reinforcement within nanocomposites significantly improves structural integrity and durability over the relatively homogenous structure of fiberboard.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Nanocomposite doors exhibit superior strength and durability compared to fiberboard due to their enhanced material composition, which integrates nanoparticles that increase resistance to impact, moisture, and warping. Fiberboard, primarily composed of compressed wood fibers, is more prone to swelling, cracking, and deformation under prolonged exposure to humidity and mechanical stress. The nanocomposite's improved structural integrity and longevity make it a more reliable choice for heavy-use or adverse environmental conditions.
Resistance to Moisture and Environmental Factors
Nanocomposite doors exhibit superior resistance to moisture and environmental factors compared to fiberboard doors due to their advanced material composition, which includes nanoparticles that enhance durability and reduce water absorption. Fiberboard, primarily made from compressed wood fibers, tends to absorb moisture, leading to swelling, warping, and reduced structural integrity over time in humid conditions. The enhanced moisture resistance of nanocomposite doors makes them ideal for exterior and high-humidity environments, providing long-term stability and reduced maintenance costs.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Properties
Nanocomposite doors exhibit superior thermal insulation due to their enhanced molecular structure, reducing heat transfer more effectively than fiberboard doors. Their dense, engineered matrix also provides better acoustic insulation by absorbing and dampening sound waves, outperforming conventional fiberboard materials. Fiberboard doors, while cost-effective and moderately insulating, lack the advanced noise reduction and thermal efficiency characteristics found in nanocomposite alternatives.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Options
Nanocomposite doors offer superior design flexibility and aesthetic options compared to fiberboard, allowing for intricate patterns and smooth finishes unattainable with traditional materials. The advanced composition of nanocomposites enables customization in color, texture, and shapes, making them ideal for modern architectural styles. Fiberboard doors, while cost-effective, typically provide limited design versatility and fewer visual choices, often resulting in more uniform and less dynamic appearances.
Manufacturing Process and Sustainability
Nanocomposite doors involve the integration of nanoscale materials like carbon nanotubes or nanoclays into polymer matrices, enhancing mechanical strength and durability through advanced dispersion techniques during manufacturing. Fiberboard doors, typically made from wood fibers bonded with resins under heat and pressure, rely on traditional composite panel production methods that are energy-intensive but utilize recycled wood waste. Nanocomposite manufacturing reduces material usage and waste due to improved performance at lower thicknesses, offering superior sustainability compared to fiberboard doors, which, while recyclable, often contain formaldehyde-based adhesives impacting indoor air quality.
Cost Analysis: Nanocomposite vs Fiberboard
Nanocomposite doors typically have a higher initial cost compared to fiberboard doors due to advanced material technology and enhanced durability. Fiberboard doors offer a more budget-friendly option with lower upfront expenses but may incur additional maintenance and replacement costs over time. Evaluating long-term value requires balancing the upfront investment of nanocomposites against the potentially higher lifecycle costs associated with fiberboard.
Applications and Use Cases in Door Manufacturing
Nanocomposites offer enhanced mechanical strength, thermal stability, and moisture resistance, making them ideal for high-performance, lightweight door applications in commercial and industrial buildings. Fiberboard, especially medium-density fiberboard (MDF), is widely used in interior door manufacturing due to its smooth surface suitable for painting and cost-effectiveness in residential settings. Nanocomposite doors excel in environments requiring durability and weather resistance, while fiberboard doors are preferred for budget-friendly, decorative interior designs.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Door Material
Nanocomposite doors offer superior durability, moisture resistance, and enhanced strength compared to traditional fiberboard doors, making them ideal for high-traffic or humid environments. Fiberboard doors provide an economical choice with decent sound insulation and a smooth finish suitable for interior use in low-moisture areas. Selecting the right door material depends on balancing factors like budget, environmental conditions, and long-term performance requirements.
Infographic: Nanocomposite vs Fiberboard for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com