Fiberglass, a composite material made from glass fibers embedded in resin, offers superior strength, durability, and corrosion resistance for boat hulls compared to standard glass fiber used alone. Its enhanced mechanical properties and lightweight nature make fiberglass the preferred choice for high-performance and long-lasting marine applications.
Table of Comparison
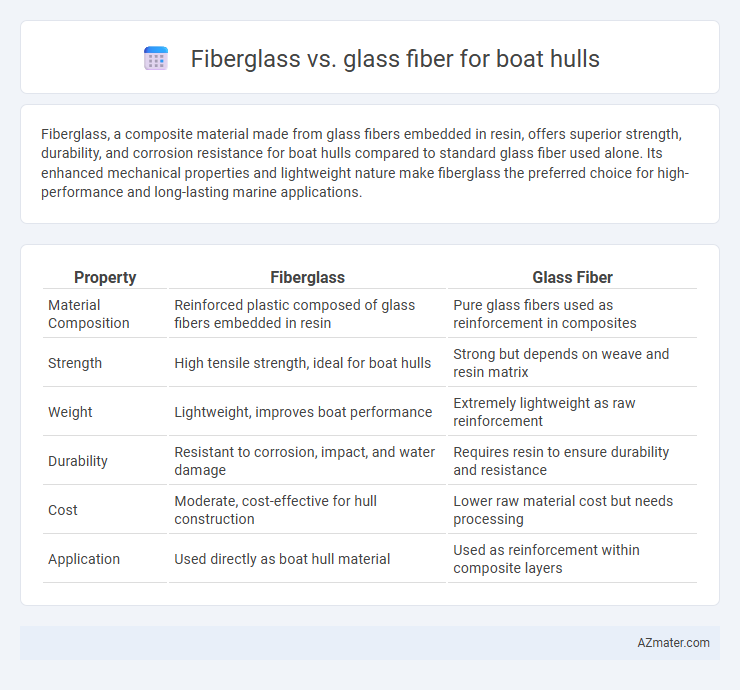
| Property | Fiberglass | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Reinforced plastic composed of glass fibers embedded in resin | Pure glass fibers used as reinforcement in composites |
| Strength | High tensile strength, ideal for boat hulls | Strong but depends on weave and resin matrix |
| Weight | Lightweight, improves boat performance | Extremely lightweight as raw reinforcement |
| Durability | Resistant to corrosion, impact, and water damage | Requires resin to ensure durability and resistance |
| Cost | Moderate, cost-effective for hull construction | Lower raw material cost but needs processing |
| Application | Used directly as boat hull material | Used as reinforcement within composite layers |
Introduction to Boat Hull Materials
Fiberglass, composed of glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix, is the most widely used material for boat hulls due to its strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion. Glass fiber specifically refers to the reinforcing fibers within the composite structure, providing tensile strength and flexibility to the hull. Choosing fiberglass for boat hull construction ensures a lightweight, low-maintenance, and cost-effective solution essential for performance and longevity in marine environments.
What is Fiberglass?
Fiberglass, a composite material made from fine glass fibers embedded in resin, is widely used in boat hull construction due to its strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion. Unlike glass fiber, which refers simply to the raw glass strands, fiberglass combines these fibers with a polymer matrix to create a rigid, lightweight material ideal for marine applications. This composite structure enhances impact resistance and flexibility, making fiberglass the preferred choice for modern boat hulls.
Understanding Glass Fiber
Glass fiber, a key material in boat hull construction, offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for marine environments. Unlike generic fiberglass, glass fiber specifically refers to fine strands of glass woven into fabrics, enhancing structural integrity and flexibility critical for hull durability. Its composition provides superior tensile strength and impact resistance, ensuring long-lasting protection against water damage and mechanical stress.
Key Differences Between Fiberglass and Glass Fiber
Fiberglass and glass fiber differ primarily in structure and application; fiberglass is a composite material made by weaving glass fibers into mats or fabrics and embedding them in resin, while glass fiber refers solely to the fine fibers produced from molten glass. Boat hull construction favors fiberglass due to its enhanced strength, durability, and resistance to water absorption, providing superior impact resistance and longevity compared to raw glass fiber. The resin matrix in fiberglass composites also offers improved chemical resistance and ease of fabrication, making it the preferred choice for marine environments.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Fiberglass and glass fiber are often used interchangeably in boat hull construction, but fiberglass refers to the composite material made by embedding glass fibers in a resin matrix, offering superior strength and durability. Glass fiber alone provides high tensile strength and flexibility, but when combined with resins, it forms a rigid and impact-resistant hull structure that withstands marine environments better. The composite nature of fiberglass enhances resistance to water absorption, UV damage, and fatigue, making it the preferred choice for long-lasting, strong boat hulls.
Weight and Performance Factors
Fiberglass composite materials used for boat hulls vary primarily in weight and performance, with glass fiber offering higher tensile strength and durability while maintaining moderate weight. Fiberglass, often referring to a polyester or vinylester resin matrix combined with glass fiber reinforcement, provides a lightweight hull that balances strength and flexibility, crucial for hydrodynamic efficiency and fuel economy. The choice between these materials affects overall vessel weight, impacting speed, maneuverability, and resistance to impact, with glass fiber-reinforced composites favored in high-performance applications due to superior strength-to-weight ratios.
Cost Analysis: Fiberglass vs Glass Fiber
Fiberglass and glass fiber are often used interchangeably but differ in structure and cost implications for boat hull construction. Fiberglass, a composite material made by embedding glass fibers in a resin matrix, generally offers better durability and a smoother finish but comes at a higher price due to processing and resin quality. Glass fiber alone is less expensive as a raw reinforcement but requires additional resin and labor, often resulting in higher overall costs when factoring in manufacturing and long-term maintenance expenses.
Maintenance and Longevity
Fiberglass boat hulls, composed of resin and glass fibers, offer superior durability and require less maintenance due to their resistance to corrosion, rot, and UV damage compared to traditional glass fiber hulls. Glass fiber hulls, being lighter and more flexible, may be prone to delamination and require more frequent inspections and repairs to prevent water intrusion and structural weakening. Over time, fiberglass hulls provide enhanced longevity with minimal upkeep, making them a preferred choice for boat owners seeking a long-lasting and low-maintenance solution.
Suitability for Different Boat Types
Fiberglass, composed of woven glass fibers embedded in resin, offers superior strength and flexibility suitable for recreational boats, kayaks, and small to medium-sized motorboats requiring smooth finishes and durability in varied water conditions. Glass fiber, specifically referring to the raw fiber material, is often used in custom or industrial boat construction where tailored reinforcement is necessary for larger vessels like fishing boats or commercial ships demanding high impact resistance and structural integrity. Selecting between fiberglass and glass fiber depends on the boat type's size, expected usage, and specific performance criteria such as weight, stiffness, and maintenance needs.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Your Boat Hull
Fiberglass, composed of fine glass fibers embedded in resin, offers excellent strength, durability, and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for boat hulls subjected to harsh marine environments. Glass fiber, while similar, often refers specifically to the reinforcing fibers themselves and may vary in weave and weight, influencing the hull's overall performance and flexibility. Selecting the right material depends on balancing factors like weight, strength, cost, and maintenance requirements to ensure optimal longevity and performance of the boat hull.
Infographic: Fiberglass vs Glass fiber for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com