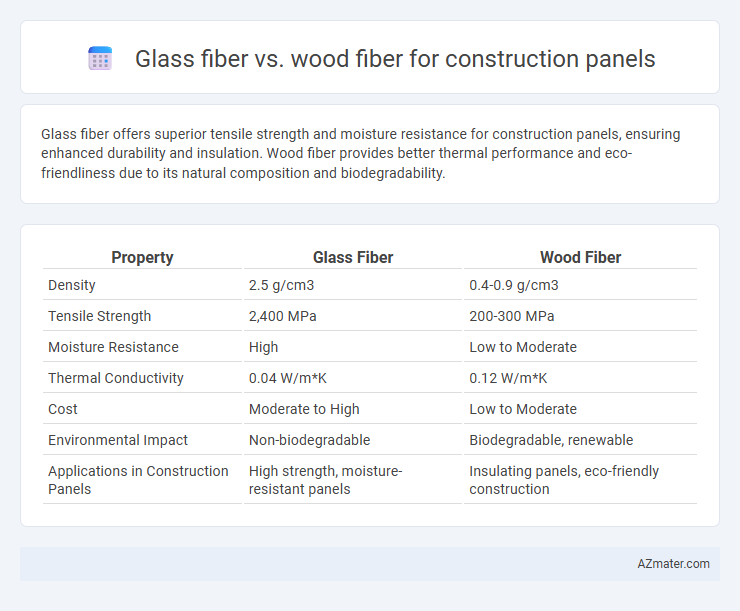
Glass fiber offers superior tensile strength and moisture resistance for construction panels, ensuring enhanced durability and insulation. Wood fiber provides better thermal performance and eco-friendliness due to its natural composition and biodegradability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass Fiber | Wood Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 2.5 g/cm3 | 0.4-0.9 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 2,400 MPa | 200-300 MPa |
| Moisture Resistance | High | Low to Moderate |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.04 W/m*K | 0.12 W/m*K |
| Cost | Moderate to High | Low to Moderate |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable | Biodegradable, renewable |
| Applications in Construction Panels | High strength, moisture-resistant panels | Insulating panels, eco-friendly construction |
Introduction to Construction Panel Materials
Glass fiber and wood fiber are two prominent materials used in construction panels, each offering unique properties. Glass fiber panels provide superior strength, moisture resistance, and durability, making them ideal for high-performance applications in exterior walls and roofing. Wood fiber panels offer natural insulation, breathability, and eco-friendly benefits, often preferred for interior walls and sustainable building projects.
Overview of Glass Fiber Panels
Glass fiber panels offer superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced moisture resistance compared to wood fiber panels, making them ideal for high-performance construction applications. Their non-porous structure improves insulation and fire resistance, contributing to durability and energy efficiency in building envelopes. These panels provide dimensional stability and resistance to decay, pests, and mold, outperforming traditional wood fiber alternatives in longevity and maintenance.
Overview of Wood Fiber Panels
Wood fiber panels are engineered from natural wood strands or fibers bonded with resins, offering excellent insulation, sound absorption, and environmental sustainability through renewable resources. These panels provide superior breathability and moisture regulation compared to glass fiber, enhancing indoor air quality and preventing mold growth. Commonly used in wall sheathing, flooring, and roofing applications, wood fiber panels also exhibit good thermal performance and mechanical strength, making them a popular choice for eco-friendly construction projects.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Glass fiber construction panels exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to wood fiber panels, offering higher tensile and flexural strength essential for load-bearing applications. The inherent stiffness and durability of glass fibers enhance impact resistance and structural integrity under varying stress conditions. Wood fiber panels provide moderate strength but are less resistant to deformation and environmental factors, making glass fiber panels a more robust choice for demanding construction needs.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Properties
Glass fiber offers superior thermal insulation with an R-value typically ranging from 2.2 to 2.7 per inch, effectively reducing heat transfer in construction panels. Wood fiber insulation panels provide excellent acoustic dampening due to their dense and fibrous structure, absorbing sound waves more efficiently for noise reduction. Combining glass fiber's low thermal conductivity and wood fiber's sound absorption capabilities results in enhanced overall insulation performance for building applications.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Glass fiber panels offer superior durability and weather resistance compared to wood fiber boards, as glass fibers are less prone to moisture absorption, rot, and insect damage. Wood fiber panels tend to degrade faster when exposed to prolonged humidity and extreme weather conditions, reducing their lifespan in outdoor applications. The non-porous nature of glass fiber enhances structural integrity and maintains insulation properties under harsh environmental stresses, making it ideal for long-term construction use.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Glass fiber panels have a higher embedded energy and carbon footprint compared to wood fiber panels, which are derived from renewable timber sources with lower processing emissions. Wood fiber panels offer better biodegradability and contribute to carbon sequestration, enhancing their sustainability profile in construction. The recycling potential of glass fiber is limited, whereas wood fiber panels can often be recycled or composted, minimizing landfill waste.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Glass fiber panels typically have a higher upfront cost compared to wood fiber panels due to the energy-intensive manufacturing process and raw material expenses. Wood fiber panels offer a cost-effective solution with lower production costs and renewable resource benefits, which can reduce long-term economic impact. Evaluating life-cycle costs, including durability, maintenance, and insulation properties, is essential for accurate economic considerations in construction projects.
Ease of Installation and Workability
Glass fiber panels offer superior ease of installation due to their lightweight nature and flexibility, making them easier to cut, shape, and handle on-site compared to wood fiber panels. Wood fiber panels are heavier and more rigid, often requiring specialized tools and increased labor time for precise fitting and fastening. The enhanced workability of glass fiber enhances construction efficiency, reducing labor costs and installation time.
Applications and Suitability Recommendations
Glass fiber panels excel in applications requiring high durability, moisture resistance, and thermal insulation, making them ideal for exterior cladding, roofing, and industrial environments. Wood fiber panels are better suited for interior applications such as wall sheathing and flooring due to their natural insulation properties and eco-friendly composition. For moisture-prone areas or exposure to harsh weather, glass fiber panels are recommended, whereas wood fiber panels work well in dry, controlled environments emphasizing sustainability and sound absorption.
Infographic: Glass fiber vs Wood fiber for Construction panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com