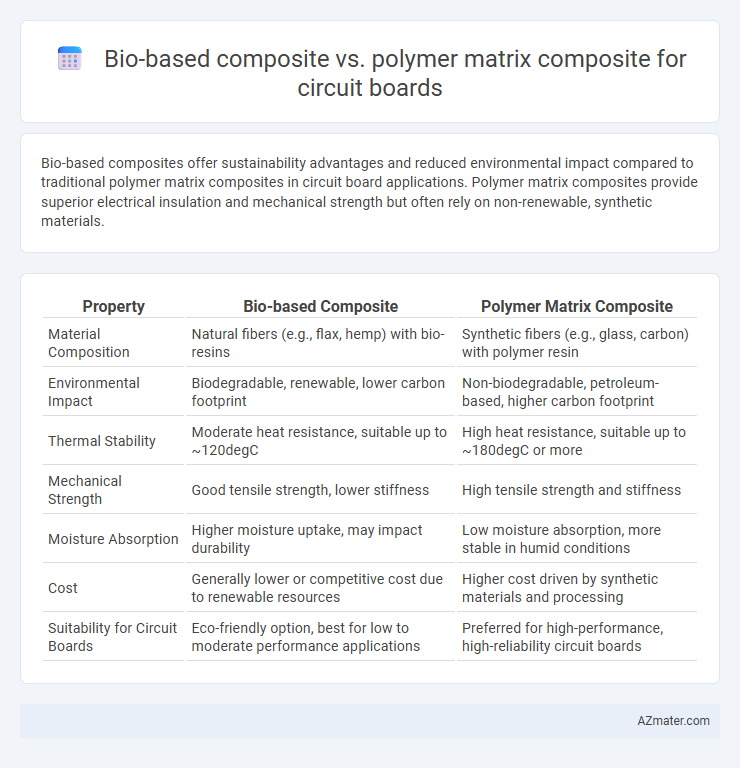
Bio-based composites offer sustainability advantages and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional polymer matrix composites in circuit board applications. Polymer matrix composites provide superior electrical insulation and mechanical strength but often rely on non-renewable, synthetic materials.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bio-based Composite | Polymer Matrix Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural fibers (e.g., flax, hemp) with bio-resins | Synthetic fibers (e.g., glass, carbon) with polymer resin |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable, lower carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based, higher carbon footprint |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate heat resistance, suitable up to ~120degC | High heat resistance, suitable up to ~180degC or more |
| Mechanical Strength | Good tensile strength, lower stiffness | High tensile strength and stiffness |
| Moisture Absorption | Higher moisture uptake, may impact durability | Low moisture absorption, more stable in humid conditions |
| Cost | Generally lower or competitive cost due to renewable resources | Higher cost driven by synthetic materials and processing |
| Suitability for Circuit Boards | Eco-friendly option, best for low to moderate performance applications | Preferred for high-performance, high-reliability circuit boards |
Introduction to Circuit Board Material Technologies
Bio-based composites for circuit boards utilize renewable natural fibers combined with biodegradable resins, promoting environmental sustainability and reducing electronic waste. Polymer matrix composites, commonly made from epoxy or phenolic resins reinforced with glass or carbon fibers, offer superior mechanical strength, thermal stability, and electrical insulation critical for reliable circuit performance. Advancements in bio-based materials are narrowing the performance gap, making them viable alternatives for green electronics without compromising essential material properties.
Overview of Bio-based Composites
Bio-based composites for circuit boards utilize natural fibers combined with bio-derived resins, offering improved sustainability and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional polymer matrix composites. These materials provide adequate mechanical strength, thermal stability, and electrical insulation properties necessary for electronic applications while significantly lowering carbon footprint. Advances in bio-resin formulations and fiber treatments enhance durability and moisture resistance, positioning bio-based composites as viable alternatives in eco-friendly electronics manufacturing.
Essentials of Polymer Matrix Composites
Polymer matrix composites (PMCs) used in circuit boards consist of a polymer resin reinforced with fibers, offering high mechanical strength, thermal stability, and electrical insulation crucial for electronic performance. Bio-based composites integrate natural fibers and biodegradable polymers, enhancing sustainability while maintaining adequate dielectric properties and reducing environmental impact. Essential PMC properties for circuit boards include excellent heat resistance, flame retardance, and dimensional stability to ensure reliability under operational stresses.
Environmental Impact: Bio-based vs Polymer Matrix
Bio-based composites for circuit boards significantly reduce environmental impact by utilizing renewable natural fibers and biodegradable resins, leading to lower carbon emissions and enhanced recyclability compared to traditional polymer matrix composites made from non-renewable petrochemical sources. Life cycle assessments reveal bio-based composites generate less hazardous waste and consume less energy during production and disposal phases. These sustainable materials contribute to minimizing electronic waste accumulation and promote circular economy principles within the electronics industry.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Bio-based composites for circuit boards demonstrate superior environmental sustainability with comparable tensile strength and flexural modulus to traditional polymer matrix composites (PMCs), which typically offer higher impact resistance and thermal stability. These bio-composites leverage natural fibers such as flax or hemp, enhancing stiffness and reducing weight, whereas PMCs utilize synthetic fibers like glass or carbon, providing enhanced durability and consistent mechanical performance under thermal cycling. Mechanical property optimization in bio-based composites aims to close the gap in interlaminar shear strength and moisture resistance found in conventional PMCs used for high-performance electronic substrates.
Electrical Performance and Suitability
Bio-based composites for circuit boards offer enhanced sustainability with comparable electrical insulation and thermal stability to traditional polymer matrix composites, making them suitable for eco-friendly electronic applications. Polymer matrix composites provide superior dielectric properties, low moisture absorption, and consistent electrical conductivity, ensuring reliability in high-performance circuits. The choice between bio-based and polymer matrix composites depends on balancing environmental impact with specific electrical performance requirements and application conditions.
Manufacturing Processes and Scalability
Bio-based composites for circuit boards utilize natural fibers combined with bio-resins, offering eco-friendly manufacturing processes that often require lower energy consumption and less toxic chemical usage compared to polymer matrix composites (PMCs). Polymer matrix composites, typically made from synthetic resins and reinforcement fibers, benefit from well-established, highly scalable manufacturing techniques such as automated lay-up and resin transfer molding, enabling consistent high-volume production. Scalability challenges in bio-based composites arise due to variability in raw material quality and less mature processing technologies, whereas PMCs provide predictable material properties and processes optimized for industrial-scale circuit board fabrication.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Bio-based composites for circuit boards offer a cost advantage due to the use of renewable materials like cellulose and lignin, which reduce raw material expenses compared to traditional polymer matrix composites (PMCs) that rely on petroleum-based resins such as epoxy or phenolic resins. Market availability of bio-based composites is growing but remains limited, with niche suppliers and higher production costs impacting scalability, whereas PMCs have well-established global manufacturing infrastructure, extensive supplier networks, and lower per-unit costs due to mass production. Cost analysis reveals bio-based composites can achieve competitive pricing when environmental regulations or sustainability demands increase, but current market dominance and widespread availability of PMCs maintain their preference in mainstream circuit board manufacturing.
Future Trends in Circuit Board Materials
Future trends in circuit board materials emphasize sustainability, with bio-based composites offering eco-friendly alternatives to traditional polymer matrix composites. Bio-based composites utilize renewable resources, reducing environmental impact while maintaining comparable mechanical and thermal properties essential for circuit board performance. Advancements in bio-based resin formulations and fiber reinforcements aim to enhance durability and electrical insulation, positioning them as viable candidates for next-generation flexible and rigid circuit boards.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Composite
Selecting between bio-based composites and polymer matrix composites for circuit boards depends on environmental impact, mechanical performance, and application requirements. Bio-based composites offer enhanced sustainability with lower carbon footprints and biodegradability, making them ideal for eco-friendly electronics. Polymer matrix composites provide superior electrical insulation and thermal stability, crucial for high-performance circuit boards in demanding industrial applications.
Infographic: Bio-based composite vs Polymer matrix composite for Circuit board
 azmater.com
azmater.com