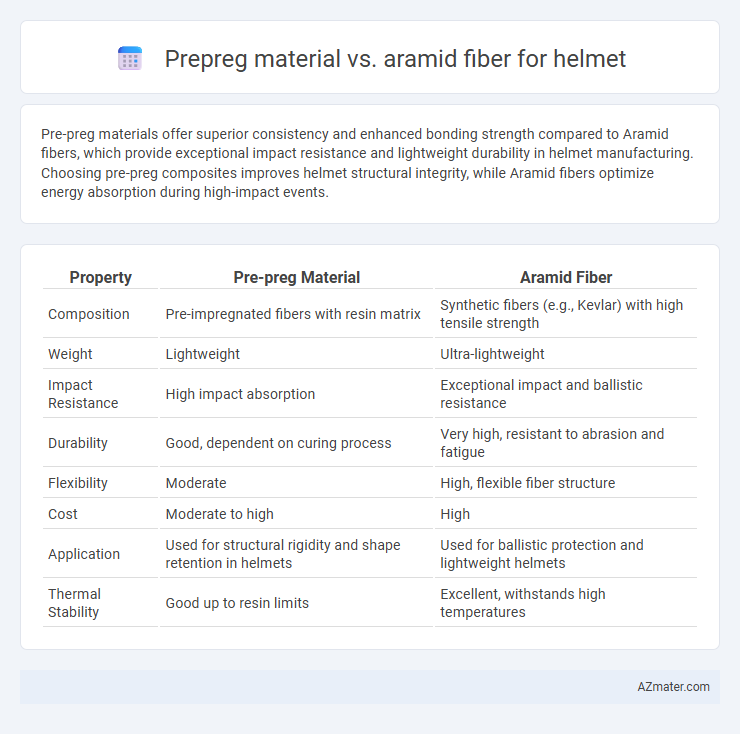
Pre-preg materials offer superior consistency and enhanced bonding strength compared to Aramid fibers, which provide exceptional impact resistance and lightweight durability in helmet manufacturing. Choosing pre-preg composites improves helmet structural integrity, while Aramid fibers optimize energy absorption during high-impact events.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Pre-preg Material | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pre-impregnated fibers with resin matrix | Synthetic fibers (e.g., Kevlar) with high tensile strength |
| Weight | Lightweight | Ultra-lightweight |
| Impact Resistance | High impact absorption | Exceptional impact and ballistic resistance |
| Durability | Good, dependent on curing process | Very high, resistant to abrasion and fatigue |
| Flexibility | Moderate | High, flexible fiber structure |
| Cost | Moderate to high | High |
| Application | Used for structural rigidity and shape retention in helmets | Used for ballistic protection and lightweight helmets |
| Thermal Stability | Good up to resin limits | Excellent, withstands high temperatures |
Introduction to Helmet Materials
Pre-preg materials consist of resin-impregnated fibers that provide controlled resin content and uniform distribution, enhancing helmet strength and durability. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer exceptional impact resistance and high tensile strength, making them ideal for energy absorption in helmets. Combining pre-preg technology with aramid fibers results in lightweight, high-performance helmets with superior protection and long-lasting structural integrity.
Overview of Pre-Preg Materials
Pre-preg materials consist of fibers pre-impregnated with a resin system, offering precise resin-to-fiber ratios that enhance consistency and mechanical properties in helmet manufacturing. These materials provide superior strength-to-weight ratios and improved impact resistance compared to traditional methods, resulting in helmets with optimized durability and comfort. The controlled curing process of pre-pregs ensures uniform structural performance, making them ideal for advanced protective gear applications.
Understanding Aramid Fiber
Aramid fiber, a synthetic fiber known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and high thermal resistance, is widely used in helmet manufacturing to enhance impact protection and durability. Unlike pre-preg materials, which combine reinforcing fibers with resin for precise curing control, aramid fibers provide lightweight ballistic resistance and excellent energy absorption in helmets. The inherent toughness and flexibility of aramid fiber contribute to superior helmet performance in military, law enforcement, and extreme sports applications.
Key Differences Between Pre-Preg and Aramid Fiber
Pre-preg materials are composite fabrics pre-impregnated with resin, offering superior moldability and consistent resin distribution, crucial for manufacturing helmets with precise shapes and high structural integrity. Aramid fiber, known for its exceptional toughness and impact resistance, serves as a reinforcement fiber within composites but lacks inherent resin content, requiring separate resin infusion during the helmet fabrication process. Key differences include pre-preg's ready-to-use resin content enhancing manufacturing efficiency and uniform quality, while aramid fiber's primary role is to provide ballistic protection and energy absorption through its high tensile strength and flexibility.
Strength and Impact Resistance Comparison
Pre-preg materials, often composed of carbon fiber or fiberglass infused with epoxy resin, provide superior tensile strength and consistent fiber alignment, enhancing helmet durability. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, excels in impact resistance and energy absorption due to its high toughness and flexibility, making it ideal for blast and penetration protection. Comparing strength and impact resistance, pre-preg composites deliver higher rigidity and structural integrity, while aramid fibers offer excellent multi-hit capability and deformation resistance under dynamic impacts.
Weight and Comfort Factors
Pre-preg materials used in helmet manufacturing offer superior weight reduction due to their precise fiber-resin ratios, enhancing overall comfort without compromising structural integrity. Aramid fiber, known for its high tensile strength and impact resistance, provides lightweight protection but often results in a slightly bulkier and stiffer helmet compared to pre-preg composites. The combination of pre-preg technology with aramid fiber can optimize helmet weight and comfort, making it ideal for prolonged wear and high-performance applications.
Durability and Longevity
Pre-preg materials, composed of epoxy-impregnated fibers cured under controlled heat and pressure, offer superior durability and consistent performance in helmet applications by enhancing fiber-matrix bonding and reducing voids. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide excellent impact resistance and flexibility but are more susceptible to environmental degradation like UV exposure and moisture, which can reduce their longevity. Helmets utilizing pre-preg composites generally achieve longer service life and sustained structural integrity compared to those relying solely on aramid fibers.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Pre-preg materials offer superior consistency and ease of handling in helmet manufacturing but tend to have higher initial costs due to specialized processing and storage requirements. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, provides cost-effective raw material options with excellent impact resistance, although it requires more labor-intensive lamination processes that can increase production time. Manufacturers must balance the premium cost of pre-preg composites against the lower raw material cost but higher labor expenses of aramid fiber to optimize helmet performance and production efficiency.
Applications in Helmet Design
Pre-preg materials, composed of resin-impregnated fibers like carbon or fiberglass, offer precise control over fiber orientation and resin content, resulting in helmets with superior impact resistance and lightweight properties. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide exceptional tensile strength and excellent energy absorption, making them ideal for ballistic and high-impact helmet applications. Combining pre-preg composites with aramid fibers enhances helmet performance by optimizing durability, flexibility, and protection for military and sports helmet designs.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Helmet
Pre-preg materials offer superior consistency and enhanced strength-to-weight ratios, making them ideal for high-performance helmets requiring precise manufacturing control. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide excellent impact resistance and energy absorption, which are critical for protective helmet applications. Choosing the right helmet material depends on balancing factors like durability, weight, impact protection, and manufacturing complexity to meet specific safety standards and usage scenarios.
Infographic: Pre-preg material vs Aramid fiber for Helmet
 azmater.com
azmater.com