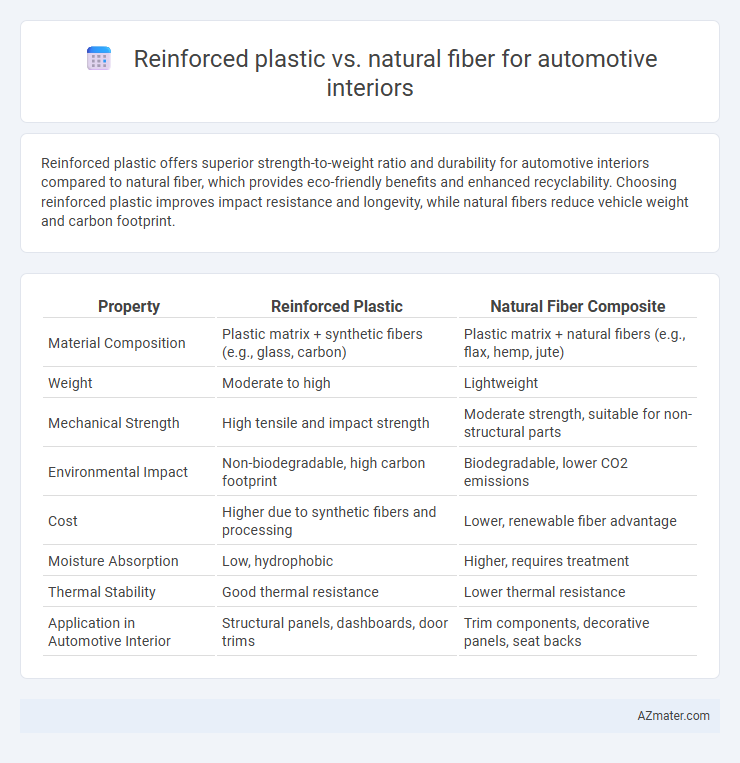
Reinforced plastic offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and durability for automotive interiors compared to natural fiber, which provides eco-friendly benefits and enhanced recyclability. Choosing reinforced plastic improves impact resistance and longevity, while natural fibers reduce vehicle weight and carbon footprint.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Reinforced Plastic | Natural Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Plastic matrix + synthetic fibers (e.g., glass, carbon) | Plastic matrix + natural fibers (e.g., flax, hemp, jute) |
| Weight | Moderate to high | Lightweight |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile and impact strength | Moderate strength, suitable for non-structural parts |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, high carbon footprint | Biodegradable, lower CO2 emissions |
| Cost | Higher due to synthetic fibers and processing | Lower, renewable fiber advantage |
| Moisture Absorption | Low, hydrophobic | Higher, requires treatment |
| Thermal Stability | Good thermal resistance | Lower thermal resistance |
| Application in Automotive Interior | Structural panels, dashboards, door trims | Trim components, decorative panels, seat backs |
Introduction to Automotive Interior Materials
Automotive interior materials increasingly balance durability, weight, and sustainability, with reinforced plastics and natural fibers emerging as key contenders. Reinforced plastics offer high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent resistance to wear, making them ideal for structural and decorative components. Natural fibers provide eco-friendly alternatives that reduce vehicle weight and improve biodegradability while maintaining adequate mechanical properties for interior panels and trim.
Overview of Reinforced Plastics
Reinforced plastics in automotive interiors combine polymers with fibers such as glass or carbon to enhance strength, durability, and lightweight properties. These composites offer superior mechanical performance, impact resistance, and design flexibility compared to traditional materials. Their ability to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions makes them a preferred choice for modern vehicle interior components.
Overview of Natural Fiber Composites
Natural fiber composites, made from renewable resources like flax, hemp, and jute, offer lightweight and eco-friendly alternatives to traditional reinforced plastics in automotive interiors. These materials provide favorable mechanical properties such as good tensile strength and impact resistance, while significantly reducing vehicle weight and enhancing sustainability. Increased use of natural fibers helps lower carbon emissions and supports circular economy principles within the automotive manufacturing industry.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Reinforced plastics offer superior tensile strength, stiffness, and impact resistance compared to natural fibers, making them ideal for high-demand automotive interior applications. Natural fibers, such as flax or hemp, provide lower density and improved vibration damping but exhibit reduced mechanical durability and lower resistance to moisture and UV exposure. Advanced hybrid composites combining reinforced plastics and natural fibers are increasingly developed to optimize mechanical performance while reducing environmental impact.
Weight and Fuel Efficiency Implications
Reinforced plastics in automotive interiors offer significant weight reduction compared to traditional materials, enhancing fuel efficiency by lowering vehicle mass. Natural fiber composites provide a sustainable alternative with comparable weight savings, contributing to reduced fuel consumption and emissions. Lightweight reinforced plastics and natural fibers both improve vehicle performance through decreased energy demand during operation.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Reinforced plastics, primarily made from synthetic polymers and glass fibers, present challenges in environmental impact due to non-biodegradability and energy-intensive manufacturing, whereas natural fiber composites derived from flax, hemp, or kenaf offer significant sustainability benefits through biodegradability and lower carbon footprints. The use of natural fibers reduces vehicle weight, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and reduced greenhouse gas emissions throughout the automotive lifecycle. Recyclability of reinforced plastics remains limited compared to the renewable sourcing and end-of-life composting potential of natural fiber materials, positioning the latter as a more eco-friendly solution for automotive interiors.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Reinforced plastics in automotive interiors offer higher durability and consistent quality but come with increased raw material and processing costs compared to natural fibers such as hemp or flax, which provide cost-effective, lightweight alternatives with growing market availability. Natural fibers benefit from renewable sourcing and lower environmental impact, attracting automotive manufacturers focused on sustainability, though their market penetration remains limited due to variability and performance constraints in high-stress applications. Cost analysis reveals that while reinforced plastics dominate established segments due to scalability and mechanical properties, the expanding demand for eco-friendly, affordable materials is driving broader availability and adoption of natural fiber composites in mid-range vehicle interiors.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Options
Reinforced plastics offer superior design flexibility for automotive interiors with customizable shapes, intricate textures, and diverse color options that enhance aesthetic appeal. Natural fibers provide unique textures and eco-friendly aesthetics but are limited in molding complexity and color variation. Advanced composite techniques now blend reinforced plastics with natural fibers, achieving a balance between innovative design flexibility and sustainable interior finishes.
Processing and Manufacturing Considerations
Reinforced plastics offer consistent quality and easier moldability in automotive interior manufacturing due to their thermoset or thermoplastic matrices, enabling precise control over part geometry and surface finish. Natural fibers, while environmentally sustainable, present challenges such as moisture absorption and variability in fiber length, requiring specialized treatment and drying processes to ensure compatibility with polymer matrices and maintain dimensional stability. Processing natural fiber composites often demands adjustments in extrusion and injection molding parameters to prevent fiber degradation and achieve optimal mechanical properties in automotive interiors.
Future Trends in Automotive Interior Materials
Reinforced plastics offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced durability, driving their growing adoption in automotive interiors to improve fuel efficiency and safety. Natural fibers, such as hemp and flax, are gaining attention due to their sustainability, biodegradability, and potential to reduce carbon footprint in vehicle manufacturing. Emerging trends emphasize hybrid composites combining reinforced plastics with natural fibers to optimize performance, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness in next-generation automotive interiors.
Infographic: Reinforced plastic vs Natural fiber for Automotive interior
 azmater.com
azmater.com