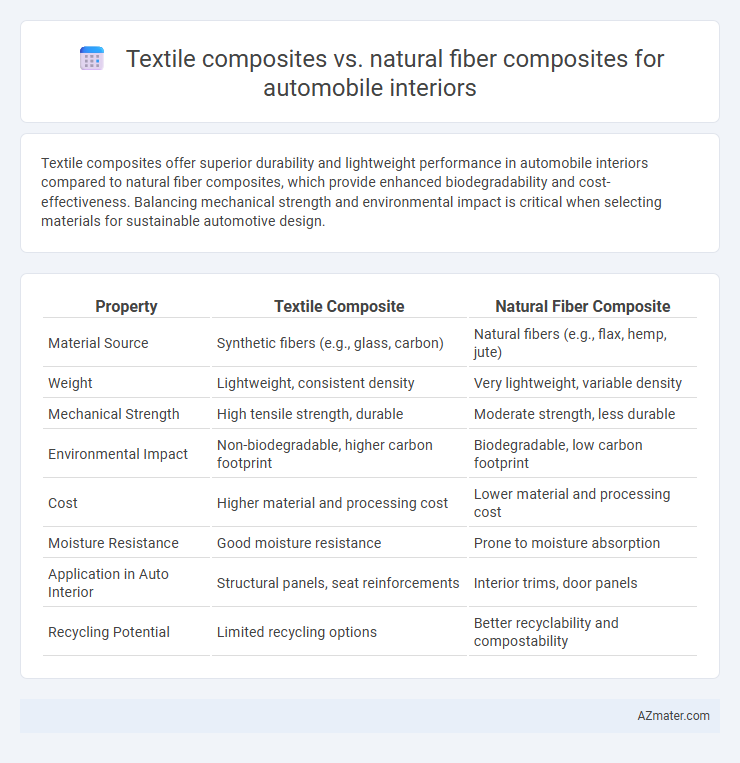
Textile composites offer superior durability and lightweight performance in automobile interiors compared to natural fiber composites, which provide enhanced biodegradability and cost-effectiveness. Balancing mechanical strength and environmental impact is critical when selecting materials for sustainable automotive design.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Textile Composite | Natural Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Synthetic fibers (e.g., glass, carbon) | Natural fibers (e.g., flax, hemp, jute) |
| Weight | Lightweight, consistent density | Very lightweight, variable density |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, durable | Moderate strength, less durable |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, higher carbon footprint | Biodegradable, low carbon footprint |
| Cost | Higher material and processing cost | Lower material and processing cost |
| Moisture Resistance | Good moisture resistance | Prone to moisture absorption |
| Application in Auto Interior | Structural panels, seat reinforcements | Interior trims, door panels |
| Recycling Potential | Limited recycling options | Better recyclability and compostability |
Introduction to Automotive Interior Materials
Textile composites and natural fiber composites play crucial roles in automotive interior materials, offering versatility, lightweight properties, and sustainability. Textile composites, often made from synthetic fibers like carbon or glass, provide superior durability and design flexibility, catering to high-performance needs. Natural fiber composites utilize renewable fibers such as flax or hemp, reducing environmental impact and improving recyclability while meeting safety and comfort standards in automotive interiors.
Overview: Textile Composites in Automotive Industry
Textile composites in the automotive industry offer enhanced strength-to-weight ratios and superior durability compared to natural fiber composites, making them ideal for high-performance interior components. These composites are engineered using synthetic fibers like carbon and glass combined with polymer matrices, providing consistent quality and resistance to moisture and wear. Their ability to be precisely tailored for specific mechanical properties supports improved safety, comfort, and design flexibility in vehicle interiors.
Natural Fiber Composites: Definition and Applications
Natural fiber composites in automobile interiors consist of plant-based fibers such as flax, jute, and hemp embedded in polymer matrices, offering sustainable alternatives to traditional materials. These composites provide advantages including reduced weight, enhanced biodegradability, and improved acoustic insulation, making them ideal for door panels, dashboards, and seat backs. The adoption of natural fiber composites contributes to lower carbon footprints and compliance with eco-friendly automotive manufacturing standards.
Material Properties: Strength, Weight, and Flexibility
Textile composites used in automobile interiors exhibit high tensile strength and excellent impact resistance, making them suitable for structural applications requiring durability. Natural fiber composites provide a lightweight alternative, reducing overall vehicle weight and improving fuel efficiency while maintaining moderate strength levels. The flexibility of natural fiber composites often surpasses that of textile composites, allowing for complex shapes and designs, although they may require additional treatment to enhance moisture resistance and mechanical performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Textile composites made from synthetic fibers offer high durability and lightweight properties but often involve energy-intensive production and non-biodegradable waste, raising environmental concerns. Natural fiber composites, such as those using hemp or flax, provide significant sustainability advantages through biodegradability, reduced carbon footprint, and renewable sourcing, aligning with green automotive initiatives. Lifecycle assessments demonstrate that natural fiber composites contribute to lower greenhouse gas emissions and improved recyclability in automobile interior applications.
Cost Analysis: Production and Lifecycle Expenses
Textile composites generally involve higher initial production costs due to complex manufacturing processes and synthetic material prices, whereas natural fiber composites benefit from lower raw material expenses and simpler processing techniques. Lifecycle expenses favor natural fiber composites because of their biodegradability, reduced environmental impact, and potential for cost savings in disposal and recycling. Cost analysis in automobile interiors reveals natural fiber composites as economically advantageous in both production and end-of-life management.
Manufacturing Processes and Complexity
Textile composites for automobile interiors typically involve complex manufacturing processes such as resin transfer molding (RTM) and vacuum infusion, which provide high precision and consistency in part quality. Natural fiber composites, often produced through simpler compression molding or manual lay-up techniques, offer advantages in biodegradability and cost but demand careful moisture control and variability management in raw materials. Both composites require tailored processing parameters, but textile composites generally exhibit higher manufacturing complexity due to the need for precise fiber orientation and resin impregnation.
Aesthetic and Functional Performance
Textile composites in automobile interiors offer superior aesthetic versatility with customizable textures and color options, enhancing visual appeal and luxury perception. Natural fiber composites provide excellent functional performance through lightweight strength, improved vibration damping, and eco-friendly sustainability, reducing vehicle weight and emissions. Balancing these materials enables automotive designers to achieve both high aesthetic quality and robust functional durability in interior components.
Industry Trends: Adoption and Innovations
Textile composites are increasingly favored in automobile interiors due to their superior durability, lightweight properties, and design flexibility, driving innovation in high-performance synthetic fibers and advanced weaving techniques. Natural fiber composites gain traction for sustainability, incorporating materials like flax, hemp, and kenaf to reduce environmental impact while meeting regulatory demands for eco-friendly vehicles. Industry trends highlight a hybrid approach combining textile and natural fibers to optimize cost, performance, and recyclability in automotive interior components.
Conclusion: Future Prospects for Automotive Interiors
Textile composites offer superior strength, durability, and design flexibility, making them ideal for high-performance automotive interiors, while natural fiber composites provide sustainability benefits through biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint. The future of automotive interior materials lies in hybrid solutions that integrate textile composites with natural fibers to balance mechanical performance and environmental impact. Advancements in bio-based resins and enhanced fiber-matrix bonding will drive the adoption of these composites, promoting lighter, eco-friendly, and customizable car interiors.
Infographic: Textile composite vs Natural fiber composite for Automobile interior
 azmater.com
azmater.com