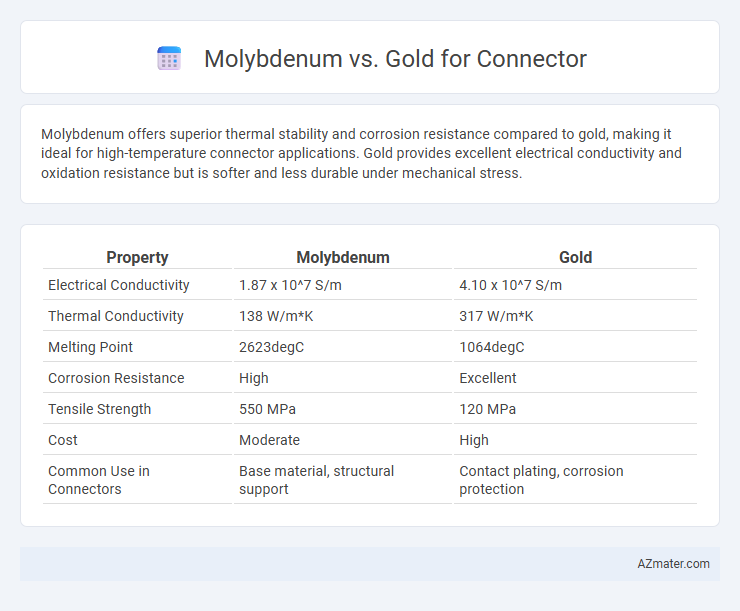
Molybdenum offers superior thermal stability and corrosion resistance compared to gold, making it ideal for high-temperature connector applications. Gold provides excellent electrical conductivity and oxidation resistance but is softer and less durable under mechanical stress.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Molybdenum | Gold |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 1.87 x 10^7 S/m | 4.10 x 10^7 S/m |
| Thermal Conductivity | 138 W/m*K | 317 W/m*K |
| Melting Point | 2623degC | 1064degC |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | Excellent |
| Tensile Strength | 550 MPa | 120 MPa |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
| Common Use in Connectors | Base material, structural support | Contact plating, corrosion protection |
Introduction to Connector Materials
Molybdenum and gold are prominent materials used in connector manufacturing due to their distinct properties influencing performance and durability. Molybdenum offers high tensile strength, excellent thermal stability, and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for harsh environments and applications requiring robust mechanical support. Gold provides superior electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and reliable contact performance, commonly employed in high-precision connectors where signal integrity is critical.
Overview of Molybdenum and Gold
Molybdenum is a high-strength, corrosion-resistant metal commonly used in connectors due to its excellent thermal conductivity and stability under extreme conditions. Gold, renowned for its superior electrical conductivity and resistance to oxidation, is often employed as a thin plating on connectors to enhance signal reliability and prevent corrosion. Choosing between molybdenum and gold in connectors involves balancing molybdenum's mechanical durability with gold's proven performance in electrical contact integrity.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Molybdenum exhibits an electrical conductivity of approximately 18.7 million siemens per meter (MS/m), which is significantly lower than gold's conductivity of 45.2 MS/m, making gold a superior choice for connectors requiring optimal electrical performance. Despite molybdenum's lower conductivity, its high melting point and mechanical strength offer advantages in harsh environments where gold connectors might degrade. Gold connectors provide exceptional corrosion resistance and stable conductivity over time, critical for high-reliability electrical connections.
Corrosion Resistance Analysis
Molybdenum exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to gold in highly oxidative and acidic environments, making it ideal for connectors exposed to harsh industrial settings. Gold offers excellent resistance to tarnishing and oxidation under normal atmospheric conditions, ensuring reliable conductivity and long-term stability in electronic connectors. Corrosion resistance analysis confirms that molybdenum's oxide layer provides robust protection against corrosion, while gold maintains inertness against most environmental factors, highlighting the choice depends on the specific application environment.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Molybdenum exhibits exceptional mechanical strength and high tensile properties, making it ideal for connectors requiring robust structural integrity under stress. Its superior hardness and resistance to deformation outperform gold, which is softer and more prone to wear despite its excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance. Molybdenum's durability under mechanical load ensures longer connector lifespan in demanding environments compared to gold-plated alternatives.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Molybdenum offers a cost-efficient alternative to gold for connectors due to its significantly lower price and stable availability, making it suitable for high-volume manufacturing. Gold connectors provide superior corrosion resistance and conductivity but come with higher material costs and potential supply constraints influenced by market demand. Selecting molybdenum enhances cost efficiency and supply chain reliability without severely compromising performance in many electronic applications.
Thermal Properties in Connectors
Molybdenum exhibits superior thermal conductivity and a low coefficient of thermal expansion, making it ideal for connectors that require stability under high temperatures and thermal cycling. Gold, while offering excellent corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity, has lower thermal conductivity and a higher thermal expansion rate compared to molybdenum, which can lead to mechanical stress in thermal-critical applications. Selecting molybdenum over gold enhances connector durability and performance in environments with significant thermal fluctuations.
Industry Applications and Preferences
Molybdenum is favored in industrial connectors for its high melting point, excellent thermal conductivity, and strong resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for aerospace, automotive, and semiconductor applications. Gold, known for its superior electrical conductivity and resistance to oxidation, is preferred in high-reliability electronics such as telecommunications, medical devices, and precision instrumentation connectors. Industry preferences often balance molybdenum's durability and thermal stability against gold's superior conductivity and corrosion resistance based on specific operational environments and performance requirements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Molybdenum connectors exhibit lower environmental impact compared to gold due to their higher abundance and reduced mining footprint, enabling more sustainable sourcing practices. Unlike gold, which involves energy-intensive extraction and associated toxic byproducts, molybdenum mining generates fewer greenhouse gas emissions and less chemical waste. The recyclability of molybdenum further enhances its sustainability profile, making it an eco-friendly alternative for connector applications.
Summary: Choosing the Right Material
Molybdenum offers excellent mechanical strength, high melting point, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for high-temperature and robust connector applications. Gold provides superior corrosion resistance, exceptional electrical conductivity, and reliable performance in low-signal environments but comes at a higher cost. Selecting between molybdenum and gold depends on balancing required durability, environmental conditions, and budget constraints for optimal connector performance.
Infographic: Molybdenum vs Gold for Connector
 azmater.com
azmater.com