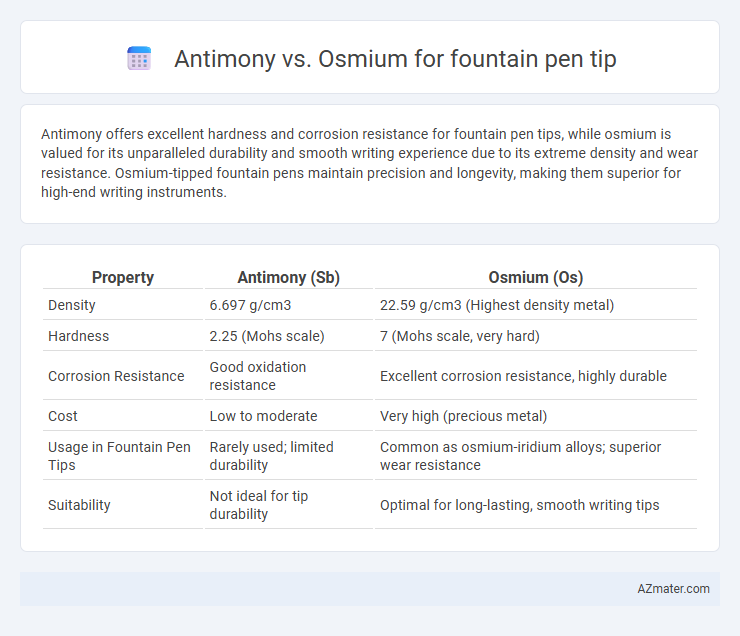
Antimony offers excellent hardness and corrosion resistance for fountain pen tips, while osmium is valued for its unparalleled durability and smooth writing experience due to its extreme density and wear resistance. Osmium-tipped fountain pens maintain precision and longevity, making them superior for high-end writing instruments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Antimony (Sb) | Osmium (Os) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 6.697 g/cm3 | 22.59 g/cm3 (Highest density metal) |
| Hardness | 2.25 (Mohs scale) | 7 (Mohs scale, very hard) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good oxidation resistance | Excellent corrosion resistance, highly durable |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Very high (precious metal) |
| Usage in Fountain Pen Tips | Rarely used; limited durability | Common as osmium-iridium alloys; superior wear resistance |
| Suitability | Not ideal for tip durability | Optimal for long-lasting, smooth writing tips |
Introduction to Fountain Pen Tip Materials
Antimony and osmium are both metals used in fountain pen tip manufacturing, with osmium being the most durable and corrosion-resistant element, providing exceptional smoothness and longevity. Antimony, though less common, is often alloyed with osmium or iridium to enhance the hardness and wear resistance of the pen nib. The choice between these materials impacts the writing experience, with osmium-tipped pens favored for premium quality due to their superior durability and resistance to bending or deformation.
Overview of Antimony and Osmium
Antimony and osmium are both metals used in fountain pen tips to enhance durability and smoothness. Antimony, a brittle metalloid, is often alloyed with lead to increase hardness and wear resistance in nibs, while osmium, one of the densest and hardest elements, is valued for its exceptional corrosion resistance and longevity when used as a tip material. Osmium's superior hardness makes it ideal for high-end fountain pen tips, whereas antimony offers a more cost-effective alternative with adequate performance for everyday writing.
Physical and Chemical Properties Comparison
Antimony and osmium differ significantly in their physical and chemical properties relevant to fountain pen tips. Osmium, a dense, hard, and corrosion-resistant transition metal with a high melting point of 3045degC, offers superior durability and wear resistance for pen nibs, while antimony, a brittle metalloid with a melting point of 630.63degC and moderate corrosion resistance, is less suitable for long-term use but can be alloyed to modify hardness. Osmium's chemical inertness and resistance to oxidation under normal conditions make it ideal for maintaining smooth ink flow and nib integrity compared to the more reactive and softer antimony.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Osmium stands out as the most durable and wear-resistant material for fountain pen tips due to its exceptional hardness and corrosion resistance, ensuring long-lasting smooth writing. Antimony, while harder than many metals, lacks the extreme wear resistance of osmium and tends to erode faster under constant use and ink exposure. Pen manufacturers prefer osmium-coated nibs or pen tips for superior longevity and minimal degradation over time compared to antimony alternatives.
Writing Experience and Smoothness
Osmium is renowned for its exceptional hardness and corrosion resistance, making it a premium choice for fountain pen tips that deliver a smooth, consistent writing experience with minimal wear over time. Antimony, being softer, provides a slightly lighter touch but may wear down faster, affecting long-term smoothness and line precision. The densely packed atomic structure of osmium ensures superior glide on paper, resulting in a refined and effortless flow of ink compared to the relatively less durable antimony tips.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Osmium fountain pen tips exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to antimony, due to osmium's high density and chemical inertness, making it highly durable in acidic or humid environments. Antimony, while offering moderate hardness, is more prone to corrosion and wear over time, reducing the longevity of pen tips made from this element. Osmium's robustness ensures longer-lasting performance and smoother ink flow, making it the preferred choice for premium, corrosion-resistant fountain pen nibs.
Cost and Availability
Antimony is generally more cost-effective and readily available than osmium for fountain pen tips, making it a popular choice among manufacturers seeking affordable materials. Osmium, one of the rarest and densest metals, commands a significantly higher price point and limited supply, resulting in restricted use for luxury or specialized pen tips. The economic advantage of antimony combined with its sufficient hardness meets most functional requirements, whereas osmium is favored primarily for its superior durability and prestige in high-end pens.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Antimony, commonly used in fountain pen tips, poses environmental and health risks due to its toxic nature and potential for bioaccumulation, requiring careful manufacturing and disposal processes. Osmium, while rarer and more expensive, offers greater stability and lower toxicity, reducing environmental impact and health hazards in pen production and use. Choosing osmium-coated tips supports sustainable pen manufacturing by minimizing exposure to harmful heavy metals and mitigating ecological contamination.
User Reviews and Industry Preferences
Antimony is prized in fountain pen tips for its moderate hardness and smooth ink flow, with user reviews highlighting consistent performance and reduced nib wear. Osmium, the hardest metal used in tipping, is favored by the industry for its exceptional durability and resistance to corrosion, although some users report a stiffer writing feel. Manufacturing trends show a preference for osmium alloys in premium pens, while antimony alloys are common in mid-range models due to their balance of cost and performance.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Fountain Pen Tip Material
Antimony and osmium are both valuable materials for fountain pen tips, with osmium offering superior hardness and corrosion resistance, enhancing durability and smooth writing performance. Antimony provides a cost-effective alternative with reasonable wear resistance but falls short of osmium's longevity and resilience under frequent use. Choosing osmium tip material ensures optimal longevity and writing quality, making it the preferred choice for high-end fountain pens.
Infographic: Antimony vs Osmium for Fountain pen tip
 azmater.com
azmater.com