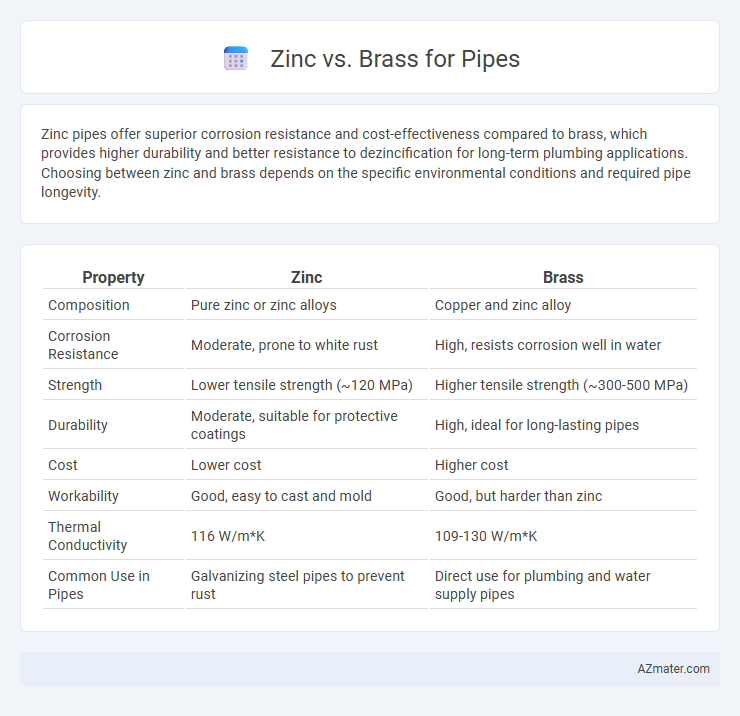
Zinc pipes offer superior corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness compared to brass, which provides higher durability and better resistance to dezincification for long-term plumbing applications. Choosing between zinc and brass depends on the specific environmental conditions and required pipe longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Zinc | Brass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure zinc or zinc alloys | Copper and zinc alloy |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate, prone to white rust | High, resists corrosion well in water |
| Strength | Lower tensile strength (~120 MPa) | Higher tensile strength (~300-500 MPa) |
| Durability | Moderate, suitable for protective coatings | High, ideal for long-lasting pipes |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Workability | Good, easy to cast and mold | Good, but harder than zinc |
| Thermal Conductivity | 116 W/m*K | 109-130 W/m*K |
| Common Use in Pipes | Galvanizing steel pipes to prevent rust | Direct use for plumbing and water supply pipes |
Introduction to Zinc and Brass Pipes
Zinc pipes are valued for their corrosion resistance and affordability, commonly used in plumbing and outdoor applications where durability against rust is essential. Brass pipes, an alloy of copper and zinc, offer superior strength, malleability, and resistance to high temperatures, making them ideal for complex plumbing systems and industrial uses. Both metals provide effective solutions for piping but differ significantly in mechanical properties and suitability for specific environments.
Chemical Composition and Properties
Zinc pipes primarily contain high percentages of zinc, offering excellent corrosion resistance and antimicrobial properties, making them suitable for plumbing applications requiring durability against rust and bacteria. Brass pipes comprise a copper-zinc alloy with variable copper content (typically 55-95%), providing enhanced strength, machinability, and resistance to dezincification, crucial for high-pressure and temperature environments. The chemical composition directly influences their mechanical properties and corrosion resistance, with brass favoring structural stability and zinc excelling in corrosion preventative uses.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Zinc coatings provide superior corrosion resistance for pipes in environments prone to moisture, effectively preventing rust and extending pipe lifespan. Brass pipes, composed of copper and zinc alloys, offer excellent corrosion resistance against freshwater and mildly corrosive conditions but may tarnish or weaken in highly acidic or saline environments. Choosing between zinc-coated steel and brass pipes depends on specific environmental factors, with zinc excelling in outdoor and wet settings while brass performs well in domestic plumbing with moderate exposure to corrosive agents.
Strength and Durability
Zinc pipes offer moderate strength with good corrosion resistance but tend to be softer and less durable under high-pressure conditions compared to brass. Brass pipes, composed primarily of copper and zinc alloys, provide superior mechanical strength and excellent resistance to wear, making them ideal for heavy-duty plumbing applications. The enhanced durability of brass ensures longer service life with minimal maintenance in both residential and industrial piping systems.
Cost and Availability
Zinc pipes typically cost less than brass pipes due to lower raw material expenses and simpler manufacturing processes, making them more budget-friendly for large projects. Brass pipes, while more expensive, offer superior durability and corrosion resistance, which can reduce long-term maintenance costs. Availability varies regionally, but zinc pipes are generally more accessible in mass-market hardware stores, whereas brass pipes may require specialized suppliers due to their premium nature.
Ease of Installation
Zinc pipes offer moderate ease of installation due to their corrosion-resistant properties but may require specialized fittings for secure joints. Brass pipes are highly favored for ease of installation, as their malleability allows for simple bending and threading without cracking or fracturing. Both materials benefit from compatibility with standard plumbing tools, but brass generally reduces labor time and ensures tighter seals.
Applications in Plumbing Systems
Zinc pipes offer excellent corrosion resistance and are commonly used in water supply lines and fittings due to their durability and cost-effectiveness. Brass pipes, composed of copper and zinc alloy, provide superior strength, high resistance to corrosion, and antimicrobial properties, making them ideal for hot and cold water distribution, especially in potable water systems. Plumbing systems leverage brass for valves, faucets, and connectors, while zinc is often selected for outdoor plumbing where environmental stress is minimal.
Environmental Impact
Zinc pipes offer a lower environmental footprint due to their natural corrosion resistance, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing metal waste. Brass pipes, while durable and corrosion-resistant, require a more energy-intensive production process that results in higher carbon emissions. Recyclability is high for both metals, but zinc's eco-friendlier extraction and lower toxicity make it a preferable choice for sustainable plumbing solutions.
Maintenance and Lifespan
Zinc pipes generally require more frequent maintenance due to their tendency to corrode and develop white rust over time, which compromises their structural integrity. Brass pipes exhibit superior corrosion resistance, resulting in a longer lifespan and reduced need for repairs, making them ideal for plumbing systems with hard water or chemically aggressive environments. The durability of brass also ensures less buildup of mineral deposits, contributing to sustained water flow efficiency and lower maintenance costs.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Piping System
Zinc pipes offer superior corrosion resistance and are ideal for water supply lines, while brass pipes provide enhanced strength and durability, making them suitable for high-pressure applications. Zinc's antifungal and antimicrobial properties ensure cleaner water flow, whereas brass's alloy composition allows for better mechanical performance and longevity. Selecting between zinc and brass depends on factors like fluid type, pressure requirements, and environmental conditions to ensure optimal functionality and lifespan in your piping system.
Infographic: Zinc vs Brass for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com