Chromium offers superior hardness, corrosion resistance, and durability compared to silver, which provides excellent electrical conductivity and aesthetic appeal for electroplating. Silver is preferred for electronic components and decorative finishes, while chromium is ideal for industrial applications requiring wear resistance and oxidation protection.
Table of Comparison
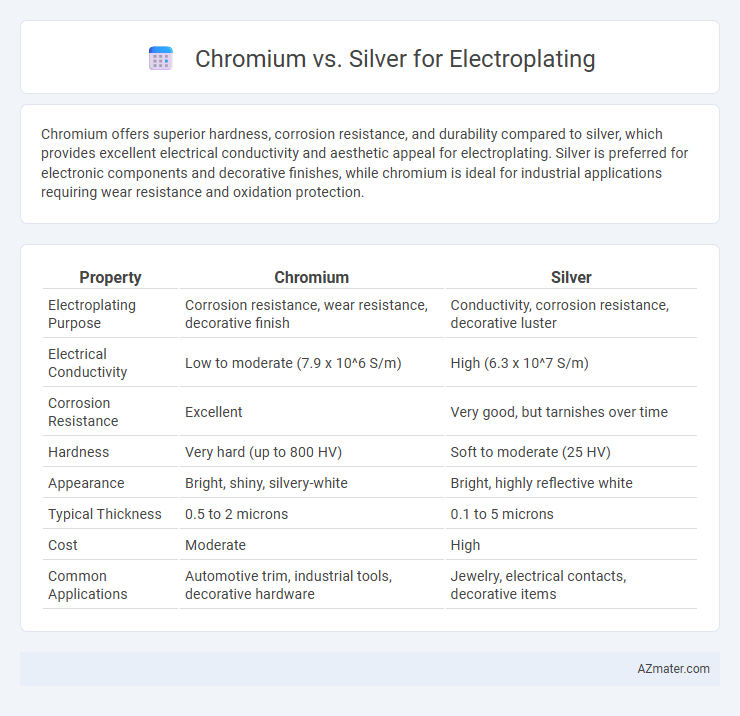
| Property | Chromium | Silver |
|---|---|---|
| Electroplating Purpose | Corrosion resistance, wear resistance, decorative finish | Conductivity, corrosion resistance, decorative luster |
| Electrical Conductivity | Low to moderate (7.9 x 10^6 S/m) | High (6.3 x 10^7 S/m) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Very good, but tarnishes over time |
| Hardness | Very hard (up to 800 HV) | Soft to moderate (25 HV) |
| Appearance | Bright, shiny, silvery-white | Bright, highly reflective white |
| Typical Thickness | 0.5 to 2 microns | 0.1 to 5 microns |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
| Common Applications | Automotive trim, industrial tools, decorative hardware | Jewelry, electrical contacts, decorative items |
Overview of Electroplating Processes
Electroplating involves depositing a metal layer onto a substrate through an electrochemical process, enhancing surface properties like corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Chromium electroplating uses hexavalent or trivalent chromium baths to create a hard, wear-resistant, and bright finish often applied in automotive and hardware industries. Silver electroplating employs silver cyanide or silver nitrate solutions to produce conductive, highly reflective coatings ideal for electronics and decorative purposes.
Introduction to Chromium and Silver Electroplating
Chromium electroplating provides a hard, corrosion-resistant surface often used in automotive and industrial applications due to its durability and bright finish. Silver electroplating offers excellent electrical conductivity and antimicrobial properties, making it ideal for electronic components and medical instruments. The choice between chromium and silver depends on the required physical and chemical characteristics for specific applications.
Chemical Properties: Chromium vs Silver
Chromium exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance and hardness due to its stable oxide layer, making it ideal for electroplating applications requiring durability and wear resistance. Silver offers superior electrical and thermal conductivity with excellent reflectivity but is more prone to tarnishing and softer compared to chromium. The chemical inertness of chromium contrasts with silver's tendency to react with sulfur compounds, impacting their respective performance and maintenance in plating uses.
Key Applications in Industry
Chromium electroplating is widely used in automotive and aerospace industries for its exceptional hardness, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal, enhancing components like engine parts and aircraft landing gear. Silver electroplating finds key applications in electronics and electrical industries due to its superior electrical conductivity, making it ideal for connectors, circuit boards, and switches. Both metals offer distinct benefits tailored to specific industrial requirements, with chromium favored for durability and silver for electrical performance.
Surface Finish and Appearance Comparison
Chromium electroplating provides a highly reflective, mirror-like surface finish with excellent hardness and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for decorative and protective applications. Silver electroplating produces a bright, lustrous appearance with superior electrical conductivity but is softer and more prone to tarnishing over time. The choice between chromium and silver for electroplating depends on the desired combination of durability, aesthetic appeal, and functional properties.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Chromium electroplating offers superior durability and corrosion resistance due to its hardness and dense oxide layer, which effectively protects underlying metals from rust and wear. Silver plating, while providing excellent electrical conductivity and aesthetic appeal, is softer and more prone to tarnishing and corrosion over time. For applications requiring long-lasting protection in harsh environments, chromium plating is typically preferred over silver.
Cost Analysis: Chromium vs Silver Plating
Chromium electroplating typically costs less than silver plating due to the lower price of chromium raw materials and more efficient industrial processes. Silver plating involves higher material costs driven by fluctuating silver market prices and requires more frequent maintenance to prevent tarnishing. The choice between chromium and silver plating depends heavily on budget constraints and the desired aesthetic or functional properties of the finished product.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Chromium electroplating often involves hexavalent chromium compounds, which are highly toxic and carcinogenic, posing significant environmental and health risks due to hazardous waste and air emissions. Silver electroplating uses less toxic chemicals like silver nitrate but still requires careful waste management to prevent water contamination and skin exposure risks. Implementing advanced filtration and proper disposal methods is crucial in minimizing the ecological footprint and occupational hazards of both chromium and silver electroplating processes.
Maintenance and Longevity of Plated Surfaces
Chromium electroplating offers superior hardness and corrosion resistance, making it highly durable with minimal maintenance for industrial applications. Silver plating, while providing excellent electrical conductivity and aesthetic appeal, is prone to tarnishing and requires regular cleaning and polishing to maintain its appearance. In terms of longevity, chromium coatings typically outlast silver in harsh environments due to their resistance to oxidation and wear.
Choosing the Right Metal for Electroplating
Chromium offers superior hardness, corrosion resistance, and a bright, reflective finish, making it ideal for automotive parts and tools requiring durability. Silver excels in electrical conductivity and antimicrobial properties, preferred for electronic components and medical devices. Selecting the right metal depends on the application's functional requirements, balancing aesthetics, conductivity, and wear resistance.
Infographic: Chromium vs Silver for Electroplating
 azmater.com
azmater.com