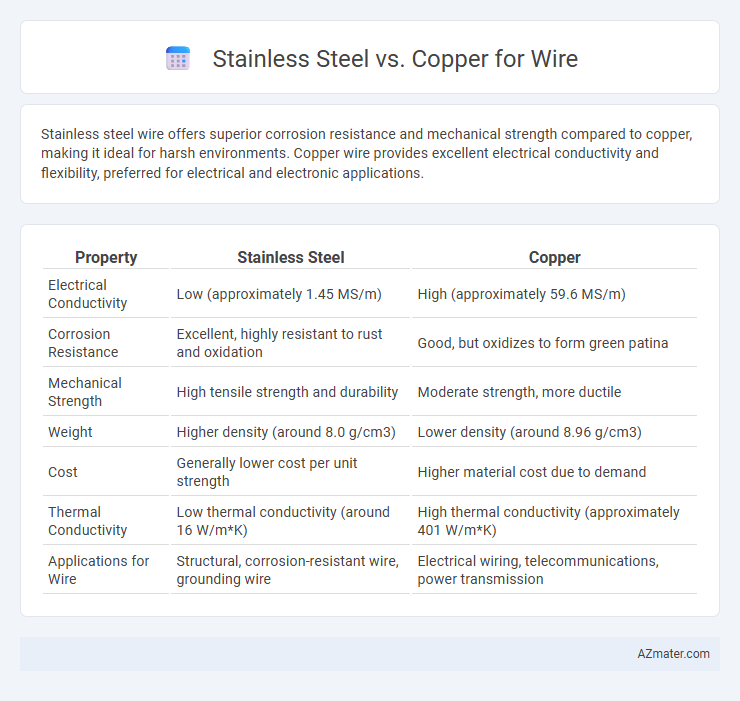
Stainless steel wire offers superior corrosion resistance and mechanical strength compared to copper, making it ideal for harsh environments. Copper wire provides excellent electrical conductivity and flexibility, preferred for electrical and electronic applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Stainless Steel | Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | Low (approximately 1.45 MS/m) | High (approximately 59.6 MS/m) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, highly resistant to rust and oxidation | Good, but oxidizes to form green patina |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and durability | Moderate strength, more ductile |
| Weight | Higher density (around 8.0 g/cm3) | Lower density (around 8.96 g/cm3) |
| Cost | Generally lower cost per unit strength | Higher material cost due to demand |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low thermal conductivity (around 16 W/m*K) | High thermal conductivity (approximately 401 W/m*K) |
| Applications for Wire | Structural, corrosion-resistant wire, grounding wire | Electrical wiring, telecommunications, power transmission |
Introduction to Stainless Steel and Copper Wires
Stainless steel wire offers high tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and durability, making it ideal for structural and industrial applications. Copper wire is renowned for its superior electrical conductivity, malleability, and thermal performance, commonly used in electrical wiring and electronics. Understanding the distinct properties of stainless steel and copper wires helps in selecting the optimal material for specific electrical or mechanical needs.
Material Composition and Properties
Stainless steel wire consists primarily of iron alloyed with chromium, typically around 10.5-30%, which imparts corrosion resistance and high tensile strength, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and resistance to rust. Copper wire is composed of nearly pure copper (typically 99.9%) offering excellent electrical conductivity, superior ductility, and resistance to corrosion in non-oxidizing environments, ideal for electrical wiring and grounding. While stainless steel provides strength and corrosion resistance under harsh mechanical stress, copper excels in electrical performance and thermal conductivity.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Copper exhibits significantly higher electrical conductivity than stainless steel, with a value of approximately 5.96 x 10^7 S/m compared to stainless steel's conductivity around 1.4 x 10^6 S/m. This makes copper a preferred choice for electrical wiring due to its superior ability to transmit electric current efficiently, resulting in less energy loss and heat generation. Despite stainless steel offering better mechanical strength and corrosion resistance, its much lower conductivity limits its use in electrical applications.
Corrosion Resistance: Stainless Steel vs Copper
Stainless steel exhibits superior corrosion resistance in harsh environments due to its chromium oxide passive layer, making it ideal for applications exposed to moisture and chemicals. Copper, while highly conductive, is prone to oxidation and develops a greenish patina, which can compromise electrical performance over time. For wire applications requiring long-term durability and minimal maintenance in corrosive conditions, stainless steel offers a more reliable solution than copper.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Stainless steel wire outperforms copper in mechanical strength, offering higher tensile strength and resistance to deformation under stress, making it ideal for applications requiring load-bearing capacity. Copper wire, while more ductile and less prone to breaking, exhibits lower mechanical strength, which limits its use in structurally demanding environments. Stainless steel also provides superior durability through excellent corrosion resistance and fatigue strength, ensuring long-lasting performance in harsh conditions compared to copper's susceptibility to oxidation and wear.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Stainless steel wire generally costs less than copper wire due to lower raw material prices and simpler manufacturing processes, making it a cost-effective option for many industrial applications. Copper wire offers superior electrical conductivity but is priced higher and subject to market supply fluctuations influenced by mining output and global demand. Market availability favors stainless steel as it is more abundant and less affected by geopolitical factors compared to copper, which faces periodic shortages impacting pricing and procurement timelines.
Applications in Different Industries
Stainless steel wires are widely used in the construction, automotive, and aerospace industries due to their high strength, corrosion resistance, and durability in harsh environments. Copper wires excel in electrical, telecommunications, and electronics applications, offering superior conductivity and flexibility essential for efficient signal transmission and power distribution. Both materials are selected based on specific industry requirements, balancing factors such as mechanical properties, conductivity, and environmental conditions.
Thermal Conductivity and Performance
Copper wire offers superior thermal conductivity, approximately 401 W/m*K, enabling efficient heat dissipation and reducing the risk of overheating in electrical applications. Stainless steel, with a much lower thermal conductivity around 16 W/m*K, exhibits higher resistance to heat flow, making it less efficient for heat transfer but advantageous for mechanical strength and corrosion resistance. The performance of copper wires excels in electrical and thermal applications requiring high conductivity, while stainless steel is preferred where durability and resistance to harsh environments are critical.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Stainless steel wire offers superior corrosion resistance and recyclability, reducing environmental waste and extending product lifespan compared to copper. Copper wire's higher electrical conductivity demands more intensive mining, leading to greater ecological disruption and energy consumption. Opting for stainless steel wire supports sustainable manufacturing by lowering resource depletion and facilitating circular economy practices.
Choosing the Right Wire: Factors to Consider
Stainless steel wire offers superior corrosion resistance and high tensile strength, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and longevity, while copper wire provides excellent electrical conductivity and flexibility, preferred in electrical and communication wiring. Consider factors such as conductivity requirements, environmental exposure, mechanical strength, and cost when selecting between stainless steel and copper wire. The choice depends on the specific application's demands for performance, efficiency, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Stainless steel vs Copper for Wire
 azmater.com
azmater.com