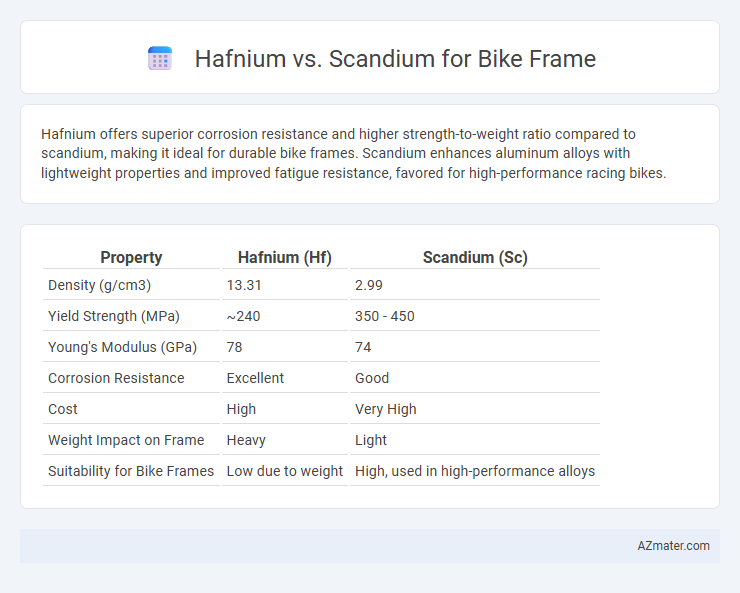
Hafnium offers superior corrosion resistance and higher strength-to-weight ratio compared to scandium, making it ideal for durable bike frames. Scandium enhances aluminum alloys with lightweight properties and improved fatigue resistance, favored for high-performance racing bikes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hafnium (Hf) | Scandium (Sc) |
|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm3) | 13.31 | 2.99 |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | ~240 | 350 - 450 |
| Young's Modulus (GPa) | 78 | 74 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Cost | High | Very High |
| Weight Impact on Frame | Heavy | Light |
| Suitability for Bike Frames | Low due to weight | High, used in high-performance alloys |
Introduction to Hafnium and Scandium in Bike Frames
Hafnium and scandium are emerging materials in bike frame construction, valued for their unique properties. Hafnium offers exceptional strength and corrosion resistance, making frames durable and lightweight for demanding riding conditions. Scandium, an alloying element in aluminum frames, enhances toughness and fatigue resistance, resulting in a smooth yet stiff ride favored by professional cyclists.
Material Properties: Hafnium vs Scandium
Hafnium and scandium both enhance bike frame alloys with distinct material properties: hafnium improves strength and corrosion resistance due to its dense atomic structure, while scandium significantly increases tensile strength and reduces weight through grain refinement in aluminum alloys. Scandium-enhanced frames exhibit superior fatigue resistance and stiffness, making them ideal for high-performance cycling applications. Hafnium's rarity and higher density limit its use, whereas scandium's balanced strength-to-weight ratio offers optimal durability and responsiveness in bike frame manufacturing.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Hafnium alloy bike frames exhibit remarkable strength and corrosion resistance due to their dense atomic structure, making them highly durable under stress and impact. Scandium-enhanced aluminum frames offer excellent strength-to-weight ratios, significantly improving fatigue resistance and extending frame lifespan without adding excessive weight. Choosing between hafnium and scandium alloys depends on whether ultimate durability or lightweight performance is the priority for demanding cycling conditions.
Weight and Density Differences
Hafnium has a significantly higher density of approximately 13.3 g/cm3 compared to scandium's density of about 2.98 g/cm3, making hafnium much heavier for the same volume. Scandium alloys are prized in bike frames for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, resulting in lighter frames that enhance performance and agility. Choosing scandium over hafnium reduces overall bike weight, improving rider efficiency and handling due to its low density and high strength properties.
Corrosion Resistance Abilities
Hafnium alloys exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to scandium, making them highly effective in preventing oxidation and degradation in bike frames exposed to harsh environments. Scandium improves aluminum alloys' strength and corrosion resistance but remains less resistant than hafnium-laden materials in highly corrosive conditions. Selecting hafnium-enhanced alloys for bike frames ensures extended durability and protection against rust in marine or humid climates.
Ride Quality and Performance
Hafnium alloys in bike frames offer enhanced vibration damping and exceptional strength-to-weight ratios, resulting in smoother ride quality and improved shock absorption on rough terrains. Scandium-infused aluminum frames provide increased stiffness and reduced frame weight, which boosts acceleration and power transfer, benefiting high-performance cyclists. Both metals elevate ride dynamics, but hafnium prioritizes comfort and durability while scandium emphasizes responsiveness and agility.
Manufacturing and Fabrication Challenges
Hafnium and scandium alloys present distinct manufacturing and fabrication challenges in bike frame production due to their unique metallurgical properties. Hafnium's high density and melting point complicate welding and require specialized high-temperature equipment, increasing production costs and limiting widespread use. Scandium alloys offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and improved weldability, yet their scarcity and high price pose challenges in sourcing and consistent material quality for mass fabrication.
Cost and Market Availability
Hafnium bike frames are rarely used due to the metal's high cost and limited commercial availability, driven by its scarcity and primary use in aerospace and nuclear industries. Scandium, though also expensive, is more accessible and widely adopted in premium bike frames, offering a favorable strength-to-weight ratio that justifies its price in cycling markets. Market availability of scandium alloys ensures better supply chains and pricing options for manufacturers and consumers compared to the niche and costly hafnium alternatives.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hafnium and scandium both offer unique advantages for bike frames, with scandium being more environmentally sustainable due to its lighter weight, which reduces overall production emissions and improves fuel efficiency during transport. Scandium alloys are often derived from recycled aluminum sources, minimizing mining impact compared to the rarer and less abundant hafnium, whose extraction is more energy-intensive and environmentally disruptive. The recyclability of scandium-enriched aluminum frames further enhances sustainability by reducing waste and resource consumption throughout the product lifecycle.
Conclusion: Which Metal is Better for Bike Frames?
Hafnium offers excellent strength and corrosion resistance, making it a durable choice for bike frames, but its high density increases overall weight. Scandium, known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and aluminum alloy compatibility, provides lightweight frames with superior stiffness and ride quality. For performance-oriented bicycles, scandium alloys are generally preferred due to their balance of lightness and strength, while hafnium remains less common and more specialized in application.
Infographic: Hafnium vs Scandium for Bike Frame
 azmater.com
azmater.com