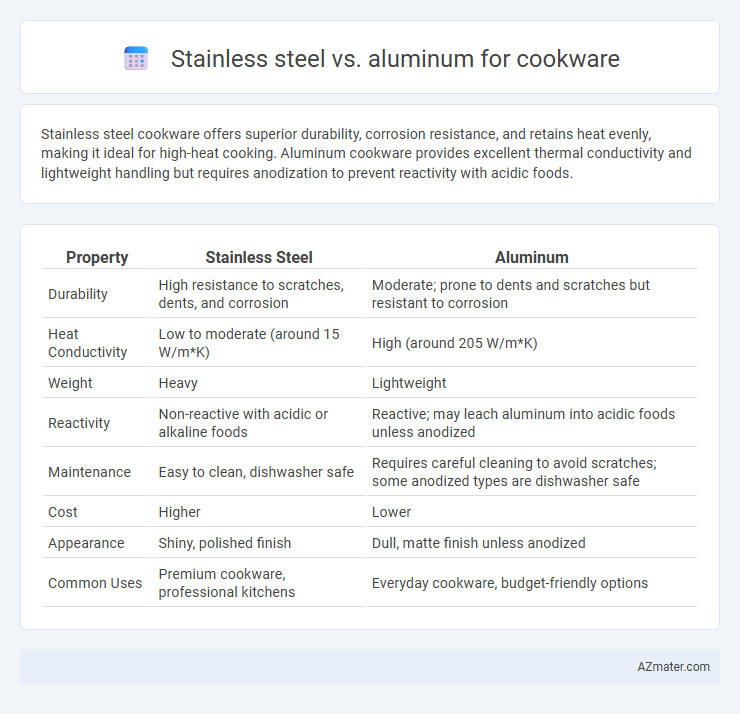
Stainless steel cookware offers superior durability, corrosion resistance, and retains heat evenly, making it ideal for high-heat cooking. Aluminum cookware provides excellent thermal conductivity and lightweight handling but requires anodization to prevent reactivity with acidic foods.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Stainless Steel | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to scratches, dents, and corrosion | Moderate; prone to dents and scratches but resistant to corrosion |
| Heat Conductivity | Low to moderate (around 15 W/m*K) | High (around 205 W/m*K) |
| Weight | Heavy | Lightweight |
| Reactivity | Non-reactive with acidic or alkaline foods | Reactive; may leach aluminum into acidic foods unless anodized |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, dishwasher safe | Requires careful cleaning to avoid scratches; some anodized types are dishwasher safe |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Appearance | Shiny, polished finish | Dull, matte finish unless anodized |
| Common Uses | Premium cookware, professional kitchens | Everyday cookware, budget-friendly options |
Introduction to Stainless Steel and Aluminum Cookware
Stainless steel cookware offers exceptional durability, resistance to corrosion, and a non-reactive surface ideal for cooking acidic foods. Aluminum cookware provides superior heat conductivity, ensuring even cooking and quick temperature response, but often requires anodizing or coating to prevent reactive interactions with food. Both materials present distinct advantages in kitchen performance, with stainless steel favored for longevity and aluminum prized for thermal efficiency.
Material Composition and Properties
Stainless steel cookware consists primarily of iron alloyed with chromium and nickel, providing excellent corrosion resistance, durability, and a non-reactive cooking surface that won't alter food flavors. Aluminum cookware, made from lightweight aluminum metal, offers superior heat conduction and even heat distribution but is more prone to scratching, denting, and reacting with acidic foods unless coated or anodized. The choice between stainless steel and aluminum hinges on balancing durability and resistance against thermal performance and weight.
Heat Conductivity and Distribution
Aluminum cookware offers superior heat conductivity, approximately 205 W/m*K, enabling rapid and even heat distribution ideal for precise cooking. Stainless steel, with a lower thermal conductivity around 16 W/m*K, often requires an aluminum or copper core to enhance heat distribution and prevent hotspots. Choosing cookware depends on heat responsiveness preferences and cooking techniques requiring consistent temperature control.
Durability and Longevity
Stainless steel cookware offers superior durability and resists corrosion, dents, and scratches, making it ideal for long-term use in busy kitchens. Aluminum cookware is lightweight and conducts heat well but tends to warp and wear faster due to its softness and susceptibility to oxidation. Stainless steel's robust composition ensures longevity, maintaining performance and appearance despite frequent use and cleaning.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Stainless steel cookware demands regular cleaning to prevent discoloration and maintain its polished finish, often benefiting from immediate washing with warm soapy water and occasional polishing to restore shine. Aluminum cookware requires careful handling to avoid scratching and discoloration, with anodized aluminum being more resistant to wear and easier to maintain, usually needing gentle cleaning without abrasive materials. Both materials benefit from avoiding dishwasher use to preserve longevity, but stainless steel generally exhibits higher durability and resistance to corrosion in everyday kitchen environments.
Cooking Performance and Results
Stainless steel cookware excels in heat retention and even cooking, providing consistent browning and searing for meats due to its dense material and heavy construction. Aluminum cookware offers superior heat conductivity, allowing for rapid and uniform temperature changes, which is ideal for delicate sauces and quick cooking tasks. Choosing between the two depends on the desired cooking technique: stainless steel suits high-heat searing and durability, while aluminum enhances precision and responsiveness in temperature control.
Reactivity with Foods
Stainless steel cookware exhibits low reactivity with acidic and alkaline foods due to its chromium content, preventing metallic taste and discoloration. Aluminum, on the other hand, is highly reactive with acidic or alkaline ingredients, which can leach metal ions into food and alter flavor. Many aluminum pans are anodized or coated to reduce this reactivity and enhance durability.
Weight and Handling
Stainless steel cookware is heavier than aluminum, offering greater durability and stability during cooking but requiring more effort to lift and maneuver. Aluminum is significantly lighter, enhancing ease of handling and reducing fatigue, especially for larger pots and pans. However, aluminum's lighter weight can sometimes compromise the feeling of sturdiness compared to the solid feel of stainless steel.
Price Comparison
Stainless steel cookware typically ranges from $50 to $300 per set, offering durability and resistance to corrosion at a moderate price point. Aluminum cookware is generally more affordable, with prices starting as low as $20 and rarely exceeding $150, making it a budget-friendly option for everyday cooking. While stainless steel commands a higher initial investment, aluminum provides cost-effective performance, especially for heat conductivity and lightweight handling.
Choosing the Best Cookware for Your Needs
Stainless steel cookware offers excellent durability, corrosion resistance, and superior heat retention, making it ideal for searing and browning. Aluminum cookware provides lightweight handling and rapid heat conduction, perfect for quick cooking and even heat distribution. Selecting the best cookware depends on cooking style, desired heat control, and maintenance preferences.
Infographic: Stainless steel vs Aluminum for Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com