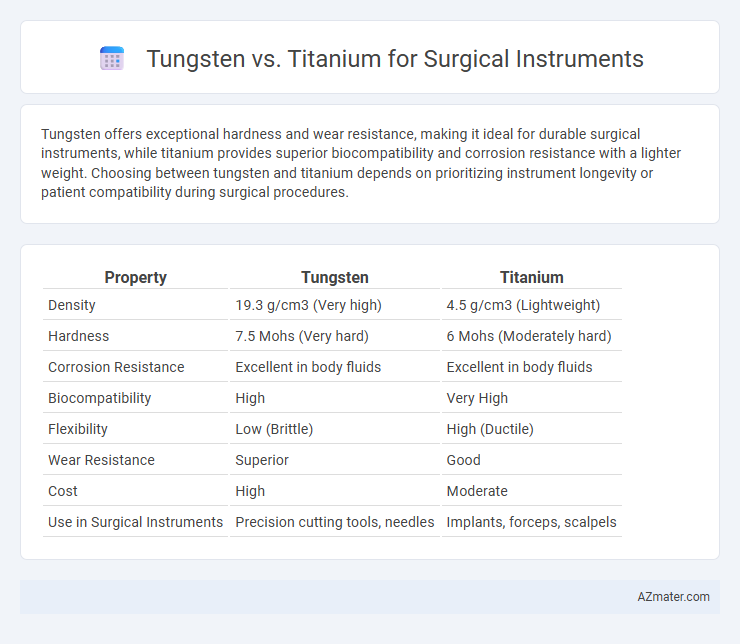
Tungsten offers exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for durable surgical instruments, while titanium provides superior biocompatibility and corrosion resistance with a lighter weight. Choosing between tungsten and titanium depends on prioritizing instrument longevity or patient compatibility during surgical procedures.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tungsten | Titanium |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 19.3 g/cm3 (Very high) | 4.5 g/cm3 (Lightweight) |
| Hardness | 7.5 Mohs (Very hard) | 6 Mohs (Moderately hard) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in body fluids | Excellent in body fluids |
| Biocompatibility | High | Very High |
| Flexibility | Low (Brittle) | High (Ductile) |
| Wear Resistance | Superior | Good |
| Cost | High | Moderate |
| Use in Surgical Instruments | Precision cutting tools, needles | Implants, forceps, scalpels |
Introduction to Tungsten and Titanium in Surgery
Tungsten and titanium are prominent materials in surgical instruments due to their unique mechanical properties and biocompatibility. Tungsten offers exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for precision cutting tools, while titanium is renowned for its strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and compatibility with human tissue. Both metals enhance surgical performance through improved durability and patient safety in various medical applications.
Material Properties: Tungsten vs Titanium
Tungsten offers exceptional hardness and high density, making it highly resistant to wear and deformation in surgical instruments. Titanium, renowned for its superior strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance, provides lightweight durability essential for precision surgical tools. While tungsten excels in rigidity and longevity, titanium's biocompatibility and reduced weight enhance maneuverability and patient safety during medical procedures.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Tungsten offers exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making it highly durable for surgical instruments subjected to repetitive stress and high impact. Titanium combines high strength with excellent corrosion resistance and a lower density, providing instruments that are both strong and lightweight while maintaining durability in sterile environments. The choice between tungsten and titanium depends on the specific surgical application, balancing tungsten's superior hardness against titanium's strength-to-weight ratio and biocompatibility.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Tungsten offers superior corrosion resistance compared to titanium, making it highly durable in harsh surgical environments where exposure to bodily fluids could cause degradation. Titanium, however, provides excellent biocompatibility and maintains longevity through its ability to form a protective oxide layer that prevents corrosion over time. The choice between tungsten and titanium for surgical instruments ultimately depends on the balance between corrosion resistance needs and weight considerations, as tungsten is denser and heavier than titanium.
Weight Differences in Surgical Use
Tungsten offers superior hardness but is significantly denser, weighing approximately 19.3 g/cm3, which makes surgical instruments heavier compared to titanium's density of about 4.5 g/cm3. Titanium's lightweight nature reduces surgeon fatigue during prolonged procedures, enhancing precision and control. Weight differences in surgical tools impact maneuverability, with titanium instruments preferred for their optimal balance of strength and minimal weight.
Precision and Sharpness Retention
Tungsten surgical instruments exhibit exceptional precision due to their high density and hardness, allowing for extremely fine and accurate cuts. Titanium instruments, while lighter and corrosion-resistant, generally offer less sharpness retention compared to tungsten, requiring more frequent sharpening during prolonged use. The superior wear resistance of tungsten ensures prolonged edge retention, making it ideal for procedures demanding sustained precision and sharpness.
Biocompatibility and Patient Safety
Tungsten and titanium are widely used in surgical instruments due to their biocompatibility and patient safety profiles. Titanium exhibits superior corrosion resistance and excellent biocompatibility, reducing the risk of allergic reactions and ensuring minimal tissue irritation. Tungsten offers high strength and wear resistance but may present challenges with brittleness and potential ion release, making titanium the preferred choice for long-term implantable devices.
Cost-Effectiveness for Hospitals
Tungsten surgical instruments offer exceptional durability and wear resistance, reducing the frequency of replacements and lowering long-term hospital expenses. Titanium instruments, while more expensive upfront, provide superior corrosion resistance and lightweight handling, which can improve surgical precision and reduce staff fatigue. Evaluating cost-effectiveness, hospitals benefit from tungsten's longevity in high-use scenarios, whereas titanium's advantages justify its cost in specialized or minimally invasive procedures.
Common Surgical Applications of Each Metal
Tungsten is widely used in surgical instruments requiring extreme hardness and precision, such as scalpels and dental tools, due to its high density and wear resistance. Titanium is favored for implants, orthopedic devices, and instruments needing biocompatibility and corrosion resistance, offering a lightweight yet strong alternative. Both metals play critical roles in surgery, with tungsten excelling in cutting performance and titanium in durability and patient compatibility.
Choosing the Right Material for Surgical Instruments
Tungsten offers exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for precision surgical instruments that require durability and sharpness. Titanium provides superior biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and lightweight properties, enhancing patient safety and ease of handling during surgeries. Selecting the right material depends on the specific surgical application, balancing factors such as instrument strength, weight, and resistance to bodily fluids.
Infographic: Tungsten vs Titanium for Surgical Instrument
 azmater.com
azmater.com