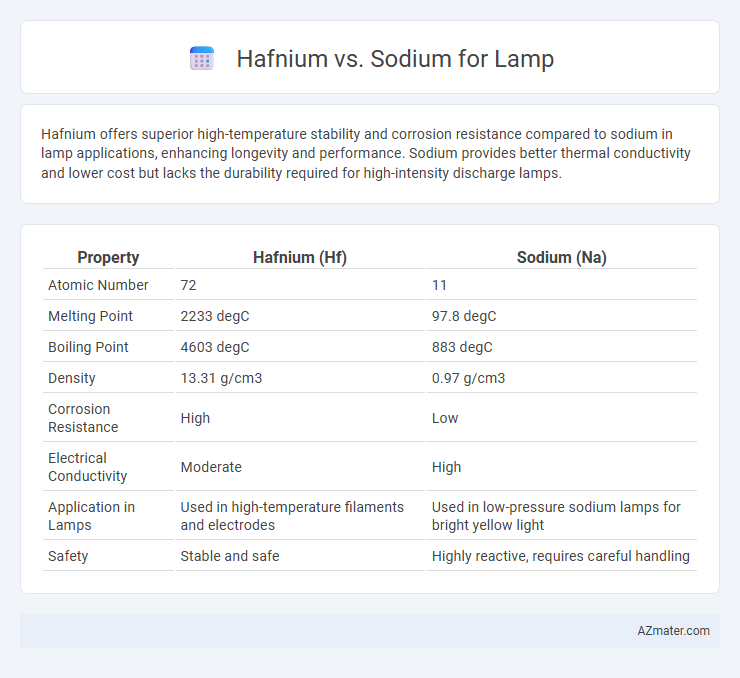
Hafnium offers superior high-temperature stability and corrosion resistance compared to sodium in lamp applications, enhancing longevity and performance. Sodium provides better thermal conductivity and lower cost but lacks the durability required for high-intensity discharge lamps.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hafnium (Hf) | Sodium (Na) |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 72 | 11 |
| Melting Point | 2233 degC | 97.8 degC |
| Boiling Point | 4603 degC | 883 degC |
| Density | 13.31 g/cm3 | 0.97 g/cm3 |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | Low |
| Electrical Conductivity | Moderate | High |
| Application in Lamps | Used in high-temperature filaments and electrodes | Used in low-pressure sodium lamps for bright yellow light |
| Safety | Stable and safe | Highly reactive, requires careful handling |
Introduction to Hafnium and Sodium in Lamp Applications
Hafnium is valued in lamp technology for its high melting point and excellent electron emission properties, making it ideal for use in high-intensity discharge lamps and electron emitters. Sodium, widely used in street lighting, excels due to its efficient light output and distinctive bright yellow emission, which ensures visibility and energy savings in low-light conditions. Comparing the two, hafnium enhances lamp longevity and performance in demanding environments, while sodium offers cost-effective illumination solutions with characteristic color rendering.
Chemical Properties: Hafnium vs Sodium
Hafnium exhibits excellent corrosion resistance and high melting point (2233degC), making it ideal for lamp filaments requiring durability under intense heat. Sodium, with a low melting point (97.8degC) and high reactivity, is unsuitable for lamp components but is often used in discharge lamps for its bright yellow emission spectrum. The chemical stability and refractory nature of hafnium contrast sharply with the highly reactive, soft characteristics of sodium, influencing their distinct applications in lighting technology.
Light Emission Efficiency Comparison
Hafnium lamps exhibit higher light emission efficiency than sodium lamps due to their ability to produce a broader spectrum of visible light with greater intensity, resulting in improved luminous efficacy. Sodium lamps primarily emit light in the yellow spectrum, limiting their color rendering index and overall efficiency compared to hafnium-based lamps that offer enhanced spectral output. The superior energy conversion rates in hafnium lamps lead to reduced power consumption and longer lamp lifespan, making them more efficient for lighting applications.
Lifespan and Durability of Hafnium and Sodium Lamps
Hafnium lamps exhibit exceptional lifespan and durability due to hafnium's high melting point and strong resistance to corrosion, often surpassing 10,000 hours of continuous use. Sodium lamps, commonly low-pressure or high-pressure types, offer moderate lifespan, typically ranging from 12,000 to 24,000 hours, but their durability is limited by sensitivity to vibration and electrode degradation. The robust thermal and chemical stability of hafnium enhances lamp longevity and performance in demanding industrial applications compared to the more widespread but less durable sodium-based lamps.
Color Rendering and Light Quality Differences
Hafnium lamps produce a light with superior color rendering index (CRI) due to their spectrum closely matching natural sunlight, enhancing true color perception in illuminated objects. Sodium lamps emit a narrower spectrum primarily in the yellow-orange range, resulting in lower CRI and less accurate color differentiation, which can distort object hues. For applications demanding high light quality and accurate color recognition, hafnium-based lighting offers significant advantages over sodium lamps.
Energy Consumption and Cost Analysis
Hafnium-based lamps exhibit higher energy efficiency compared to sodium lamps, consuming about 20-30% less power for equivalent luminous output, which translates to significant energy savings over time. Although hafnium lamps have a higher initial cost, approximately 40-50% more than sodium lamps, their longer lifespan and reduced energy consumption result in lower overall operational expenses. Sodium lamps, while cheaper upfront, tend to incur higher maintenance and electricity costs due to less efficient energy use and shorter durability.
Environmental Impact and Safety Considerations
Hafnium lamps produce less hazardous waste compared to sodium lamps, as hafnium is a non-toxic metal with minimal environmental contamination risks during disposal. Sodium lamps emit hazardous sodium vapors and have higher energy consumption, contributing to environmental pollution and potential health issues if the lamp breaks. Safety considerations favor hafnium lamps due to their stability and lower toxicity, reducing risks related to accidental exposure or environmental release.
Industrial and Commercial Usage Scenarios
Hafnium lamps offer superior corrosion resistance and longer lifespan, making them ideal for industrial environments requiring high durability and stable light output. Sodium lamps, widely used in commercial street lighting, provide high luminous efficacy and energy efficiency, suitable for large-scale outdoor illumination. Both materials cater to distinct industrial and commercial applications, with hafnium preferred for demanding conditions and sodium for cost-effective, energy-saving lighting solutions.
Technological Advancements in Hafnium and Sodium Lamps
Hafnium lamps exhibit superior efficiency and longer lifespan due to advanced electrode materials and enhanced thermal stability compared to traditional sodium lamps. Technological innovations in sodium lamps, such as improved arc tube designs and optimized sodium vapor pressures, have increased luminous efficacy but still lag behind the high color rendering and energy efficiency of hafnium-based lighting. Integration of hafnium alloys in lamp electrodes enables higher operating temperatures, resulting in brighter, more reliable illumination in industrial and specialized lighting applications.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Hafnium and Sodium for Lighting
Hafnium and sodium lamps differ significantly in efficiency, lifespan, and color rendering properties, with sodium lamps offering high luminous efficacy and longer operational life, making them ideal for street lighting and industrial applications. Hafnium lamps provide superior color quality and are used in specialized settings where precise lighting is critical despite higher energy consumption. Selecting between hafnium and sodium lighting depends on prioritizing energy efficiency and longevity versus color accuracy and application-specific requirements.
Infographic: Hafnium vs Sodium for Lamp
 azmater.com
azmater.com