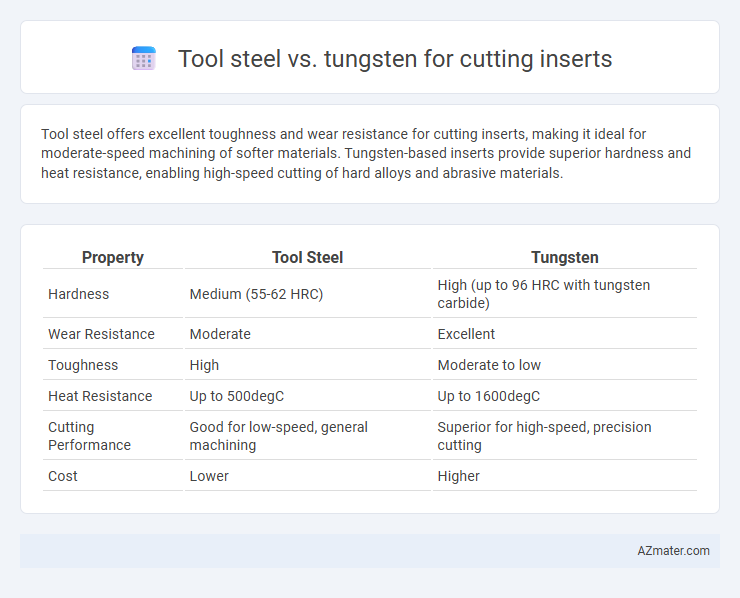
Tool steel offers excellent toughness and wear resistance for cutting inserts, making it ideal for moderate-speed machining of softer materials. Tungsten-based inserts provide superior hardness and heat resistance, enabling high-speed cutting of hard alloys and abrasive materials.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tool Steel | Tungsten |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | Medium (55-62 HRC) | High (up to 96 HRC with tungsten carbide) |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Toughness | High | Moderate to low |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 500degC | Up to 1600degC |
| Cutting Performance | Good for low-speed, general machining | Superior for high-speed, precision cutting |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Cutting Insert Materials
Cutting inserts are often made from tool steel or tungsten carbide, two materials chosen for their durability and wear resistance in machining applications. Tool steel offers toughness and resistance to deformation ideal for general-purpose cutting, while tungsten carbide provides superior hardness and heat resistance suitable for high-speed cutting and heavy-duty operations. Selecting the appropriate material depends on the machining conditions, including workpiece material and cutting speed, to optimize tool life and performance.
Overview of Tool Steel Properties
Tool steel exhibits excellent hardness, wear resistance, and toughness, making it ideal for cutting inserts that require durability under high stress. It maintains sharp edges at elevated temperatures due to its capable heat treatment properties. Compared to tungsten, tool steel offers easier machinability and cost-effectiveness for various cutting applications.
Tungsten: Composition and Characteristics
Tungsten, primarily composed of tungsten carbide (WC), is a dense metal known for its exceptional hardness and high melting point, making it ideal for cutting inserts. Its superior wear resistance, toughness, and ability to maintain a sharp edge at elevated temperatures outperform conventional tool steels, which typically consist of iron alloys with varying carbon and alloying elements. Tungsten carbide cutting inserts offer enhanced durability and precision in machining applications, especially in high-speed and heavy-duty operations.
Hardness and Wear Resistance Comparison
Tool steel cutting inserts exhibit hardness typically ranging from 55 to 65 HRC, offering moderate wear resistance suitable for general machining applications. Tungsten-based inserts, particularly tungsten carbide, demonstrate significantly higher hardness levels around 1500 HV and exceptional wear resistance, making them ideal for high-speed and abrasive cutting operations. The superior hardness and toughness of tungsten carbide result in prolonged tool life and better performance under extreme cutting conditions compared to conventional tool steels.
Toughness and Durability in Cutting Operations
Tool steel cutting inserts offer excellent toughness due to their ability to absorb impacts and resist chipping under heavy-duty machining, making them suitable for interrupted cuts and roughing tasks. Tungsten inserts, particularly tungsten carbide, provide superior hardness and wear resistance, significantly enhancing durability in high-speed and precision cutting operations. While tungsten excels in maintaining sharpness over prolonged use, tool steel inserts generally deliver better resistance to thermal shock, balancing toughness and durability in various cutting environments.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Stability
Tool steel cutting inserts exhibit moderate heat resistance with thermal stability typically up to 600degC, making them suitable for conventional machining operations. Tungsten-based inserts, particularly tungsten carbide, offer superior heat resistance and maintain structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 900degC, enabling higher cutting speeds and enhanced tool life. The enhanced thermal conductivity and hardness of tungsten inserts reduce thermal deformation and wear, optimizing performance in high-temperature cutting environments.
Cost Analysis: Tool Steel vs Tungsten
Tool steel cutting inserts typically offer a lower initial cost compared to tungsten inserts, making them more economical for applications with less demanding wear resistance requirements. Tungsten inserts, known for their superior hardness and heat resistance, incur higher material and manufacturing expenses, which increase overall tooling costs. When factoring in tool life and performance, tungsten inserts may provide better value in high-speed or abrasive cutting operations despite their premium price.
Application Suitability and Industry Use Cases
Tool steel cutting inserts excel in applications requiring high toughness and moderate wear resistance, making them suitable for general machining tasks in automotive and manufacturing industries. Tungsten inserts offer superior hardness and heat resistance, ideal for high-speed cutting and abrasive materials in aerospace and heavy metalworking sectors. The choice between tool steel and tungsten depends on the specific cutting conditions, including material hardness, cutting speed, and tool life requirements.
Machinability and Maintenance Considerations
Tool steel offers good machinability with ease of grinding and sharpening, making it suitable for versatile cutting applications that require frequent tool reconditioning. Tungsten carbide inserts excel in wear resistance and maintain sharp cutting edges longer, reducing downtime and maintenance frequency despite requiring specialized equipment for machining and resharpening. Maintenance of tool steel is simpler and less costly, but tungsten's durability lowers overall tool replacement rates, impacting cost-efficiency in high-volume or abrasive cutting tasks.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Cutting Inserts
Tool steel offers excellent toughness and versatility for cutting inserts, making it suitable for general machining tasks with moderate wear resistance. Tungsten, known for its superior hardness and high-temperature stability, excels in high-speed cutting and abrasive environments where prolonged tool life is critical. Selecting the right material depends on specific application requirements such as cutting speed, material hardness, and thermal conditions, with tungsten carbide inserts preferred for heavy-duty operations and tool steel favored for cost-effective, flexible machining.
Infographic: Tool steel vs Tungsten for Cutting insert
 azmater.com
azmater.com