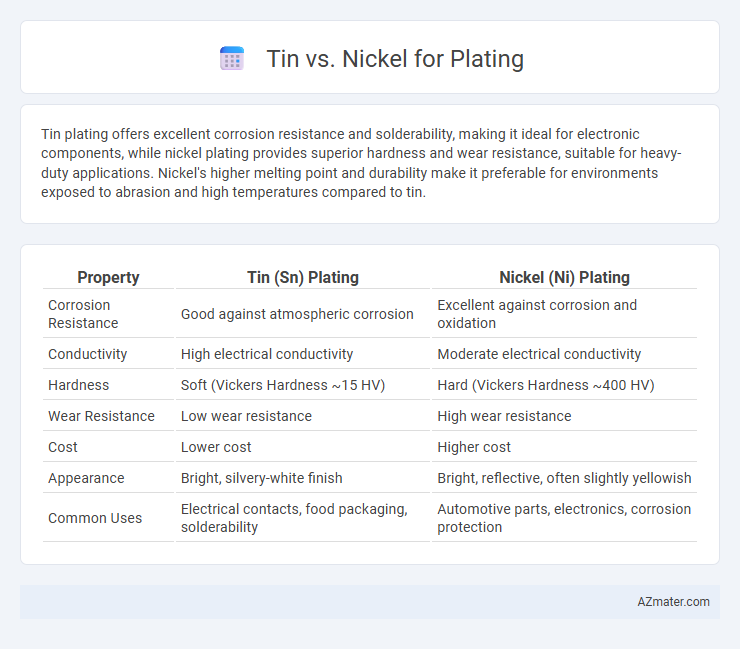
Tin plating offers excellent corrosion resistance and solderability, making it ideal for electronic components, while nickel plating provides superior hardness and wear resistance, suitable for heavy-duty applications. Nickel's higher melting point and durability make it preferable for environments exposed to abrasion and high temperatures compared to tin.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tin (Sn) Plating | Nickel (Ni) Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Good against atmospheric corrosion | Excellent against corrosion and oxidation |
| Conductivity | High electrical conductivity | Moderate electrical conductivity |
| Hardness | Soft (Vickers Hardness ~15 HV) | Hard (Vickers Hardness ~400 HV) |
| Wear Resistance | Low wear resistance | High wear resistance |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Appearance | Bright, silvery-white finish | Bright, reflective, often slightly yellowish |
| Common Uses | Electrical contacts, food packaging, solderability | Automotive parts, electronics, corrosion protection |
Introduction to Metal Plating: Tin vs Nickel
Tin and nickel are prominent metals used in plating to enhance corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, and aesthetic appeal. Tin plating offers excellent solderability and is widely used in electronics and food packaging for its non-toxic properties. Nickel plating provides superior hardness, wear resistance, and bright finish, making it ideal for decorative and industrial applications.
Chemical Properties and Composition
Tin and nickel exhibit distinct chemical properties that influence their plating applications; tin offers excellent corrosion resistance and solderability due to its stable oxide layer, while nickel provides superior hardness and wear resistance attributed to its dense atomic structure and ability to form a protective oxide coating. Tin plating typically consists of pure tin or tin-lead alloys, favoring surfaces requiring low friction and strong electrical conductivity, whereas nickel plating often involves electrolytic deposition of pure nickel or nickel alloys, enhancing durability and resistance to oxidation in harsh environments. The chemical composition of tin (Sn) with atomic number 50 emphasizes its softness and low melting point, contrasting with nickel (Ni), atomic number 28, known for its magnetic properties and higher melting point, which dictates their preferred industrial uses.
Surface Appearance and Aesthetics
Tin plating delivers a bright, silvery finish with excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for decorative and functional coatings where a smooth, reflective surface is desired. Nickel plating provides a harder, more durable layer with a distinct, lustrous metallic sheen that enhances wear resistance and offers a sophisticated aesthetic for high-end applications. While tin yields a softer, matte-like surface, nickel's finish maintains its shine over time, often preferred for jewelry, automotive trim, and electrical connectors.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Nickel plating offers superior corrosion resistance compared to tin plating, especially in harsh environments with exposure to moisture and chemicals. Tin provides good corrosion protection in mild conditions and prevents solderability issues but tends to tarnish and degrade faster in aggressive atmospheres. For applications requiring long-term durability and protection against oxidation, nickel plating is the preferred choice due to its robustness and resistance to wear.
Electrical Conductivity: Tin vs Nickel
Tin plating offers higher electrical conductivity compared to nickel, making it ideal for applications requiring efficient current flow and minimal signal loss. Nickel plating, while more durable and corrosion-resistant, exhibits lower electrical conductivity, which can impact performance in sensitive electronic components. Choosing between tin and nickel depends on balancing conductivity needs with mechanical and environmental protection.
Applications in Electronics and Industry
Tin plating is widely used in electronics for its excellent solderability, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for circuit boards, connectors, and lead frames. Nickel plating offers superior hardness, wear resistance, and oxidation protection, often applied in industrial components like connectors, switches, and mechanical parts requiring durability. Both metals enhance electrical conductivity and protect against environmental damage, with tin preferred for lightweight, low-cost solutions and nickel chosen for high-performance, heavy-duty applications.
Cost Analysis and Economic Impact
Tin plating generally offers a more cost-effective solution compared to nickel plating due to lower raw material and processing expenses, making it a preferred choice for large-scale production. Nickel plating, while more costly, provides superior corrosion resistance and durability, which can reduce long-term maintenance and replacement costs in critical applications. Economic impact analysis shows that industries requiring cost efficiency prioritize tin plating, whereas sectors demanding performance longevity invest in nickel plating despite higher initial costs.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Tin plating offers lower toxicity and is more environmentally friendly compared to nickel plating, which involves hazardous chemicals like nickel sulfate and can release carcinogenic nickel dust. Tin coatings reduce health risks for workers by minimizing allergic reactions and respiratory issues, whereas nickel exposure requires strict safety controls due to its classification as a possible human carcinogen. Disposal of waste from tin plating processes is less problematic, aligning with stricter environmental regulations aimed at reducing heavy metal contamination in industrial effluents.
Longevity and Wear Resistance
Nickel plating offers superior longevity and wear resistance compared to tin, making it ideal for applications requiring durable and corrosion-resistant coatings. Tin plating provides excellent solderability and corrosion protection but tends to wear faster under mechanical stress. Choosing nickel enhances surface hardness and extends component lifespan, especially in harsh environments.
Choosing the Right Plating: Tin or Nickel?
Choosing between tin and nickel plating depends on factors such as corrosion resistance, solderability, and application environment. Tin plating offers excellent solderability and is ideal for electronic components, while nickel plating provides superior hardness, wear resistance, and is suitable for decorative or heavy-duty applications. Evaluating the specific requirements of conductivity, durability, and environmental exposure helps determine the optimal choice for plating needs.
Infographic: Tin vs Nickel for Plating
 azmater.com
azmater.com