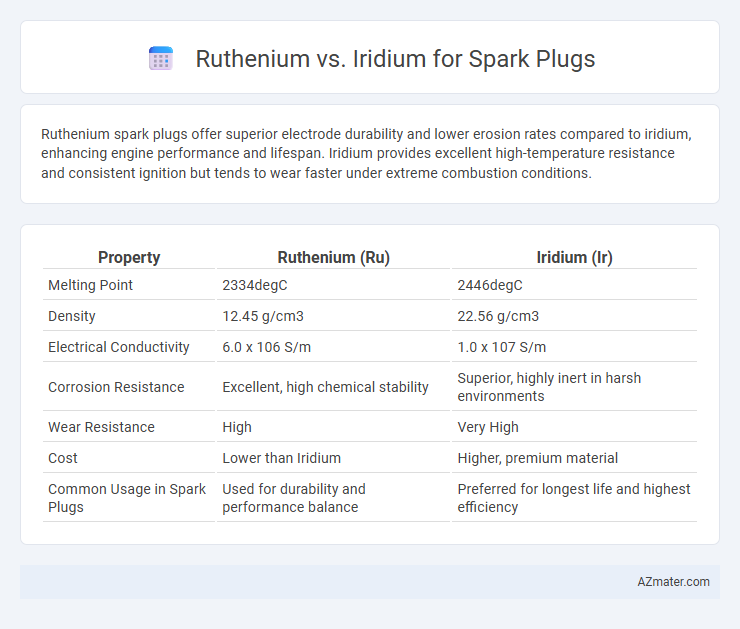
Ruthenium spark plugs offer superior electrode durability and lower erosion rates compared to iridium, enhancing engine performance and lifespan. Iridium provides excellent high-temperature resistance and consistent ignition but tends to wear faster under extreme combustion conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ruthenium (Ru) | Iridium (Ir) |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | 2334degC | 2446degC |
| Density | 12.45 g/cm3 | 22.56 g/cm3 |
| Electrical Conductivity | 6.0 x 106 S/m | 1.0 x 107 S/m |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, high chemical stability | Superior, highly inert in harsh environments |
| Wear Resistance | High | Very High |
| Cost | Lower than Iridium | Higher, premium material |
| Common Usage in Spark Plugs | Used for durability and performance balance | Preferred for longest life and highest efficiency |
Introduction to Spark Plug Materials
Ruthenium and iridium are critical materials used in high-performance spark plugs due to their exceptional hardness and corrosion resistance, enhancing ignition reliability and durability. Ruthenium offers superior wear resistance and lower electrical resistance compared to iridium, making it effective for prolonged spark plug life and efficient spark delivery. Iridium remains popular for its high melting point and oxidation resistance, ensuring stable performance under extreme combustion conditions in modern engines.
Overview of Ruthenium and Iridium
Ruthenium and iridium are both platinum-group metals widely used in spark plug electrodes due to their exceptional hardness, high melting points, and excellent corrosion resistance. Ruthenium offers improved electrical conductivity and wear resistance, enhancing spark plug durability and ignition efficiency in high-performance engines. Iridium, known for its superior oxidation resistance and stability at extreme temperatures, provides longer service life and consistent spark delivery under demanding conditions.
Chemical and Physical Properties Comparison
Ruthenium and iridium both belong to the platinum group metals with high melting points, but ruthenium melts at approximately 2,334degC while iridium has a higher melting point around 2,446degC, contributing to better heat resistance in spark plugs. Chemically, ruthenium exhibits greater hardness and corrosion resistance, but iridium displays superior oxidation resistance at elevated temperatures, enhancing electrode durability under combustion conditions. The density of iridium is higher (22.56 g/cm3) compared to ruthenium (12.45 g/cm3), influencing electrode wear and thermal conductivity critical for consistent spark generation.
Durability and Lifespan Analysis
Ruthenium spark plugs exhibit exceptional durability due to their high melting point (2334degC) and superior electrical conductivity, resulting in enhanced wear resistance and extended lifespan compared to conventional materials. Iridium spark plugs, while also highly durable with a melting point of 2446degC, tend to offer slightly longer service life because of their exceptional hardness and corrosion resistance under extreme combustion conditions. Both materials outperform platinum and nickel alternatives, but iridium's balance of toughness and thermal stability typically translates to a lifespan of up to 100,000 miles, whereas ruthenium plugs often reach around 80,000 to 90,000 miles depending on engine conditions.
Performance Efficiency in Engines
Ruthenium spark plugs offer superior ignition sensitivity and improved fuel efficiency due to their lower electrode wear and higher melting point compared to iridium. Iridium spark plugs provide excellent durability but may exhibit slightly less stable spark consistency under high-performance engine conditions. The enhanced catalytic properties of ruthenium result in better combustion stability, optimizing engine power output and reducing emissions.
Heat Resistance and Conductivity
Ruthenium spark plugs offer superior heat resistance due to their high melting point of 2,334degC, ensuring durability under extreme combustion temperatures. Iridium spark plugs provide excellent electrical conductivity with a resistivity of 5.3 uO*cm, enhancing ignition efficiency and consistent spark performance. Both metals improve spark plug longevity, but ruthenium excels in thermal stability while iridium leads in conductivity.
Cost and Value Considerations
Ruthenium spark plugs generally offer a lower cost compared to iridium plugs while maintaining high durability and efficient performance, making them cost-effective for everyday use. Iridium plugs, though more expensive, provide superior longevity and enhanced ignition reliability in high-performance engines, delivering greater value for demanding conditions. Evaluating total ownership costs, including lifespan and fuel efficiency, often positions ruthenium as the best budget choice, whereas iridium suits drivers prioritizing premium performance and longer intervals between replacements.
Suitability for Different Vehicle Types
Ruthenium spark plugs offer superior durability and improved ignition performance, making them well-suited for high-performance gasoline engines and modern vehicles requiring consistent spark efficiency. Iridium spark plugs provide excellent wear resistance and stable performance, ideal for heavy-duty trucks and older vehicles with higher combustion temperatures. Selecting between ruthenium and iridium depends on specific engine demands, fuel types, and driving conditions to maximize spark plug lifespan and engine efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ruthenium spark plugs typically offer longer lifespans and lower emissions due to their enhanced durability and efficient ignition, contributing to reduced environmental impact. Iridium spark plugs, while also highly durable, often require more frequent replacement, leading to increased resource consumption and waste generation over time. The sustainability of ruthenium-based spark plugs is generally favored because their extended service life decreases the need for raw material extraction and manufacturing, supporting more eco-friendly automotive maintenance practices.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Spark Plug Material
Ruthenium spark plugs offer superior durability and enhanced ignition performance due to their excellent catalytic properties, making them ideal for high-performance engines. Iridium spark plugs provide exceptional wear resistance and reliable spark efficiency, suitable for everyday driving conditions and longevity. Selecting the right spark plug material depends on engine requirements, with ruthenium preferred for precision and iridium for consistent durability.
Infographic: Ruthenium vs Iridium for Spark Plug
 azmater.com
azmater.com