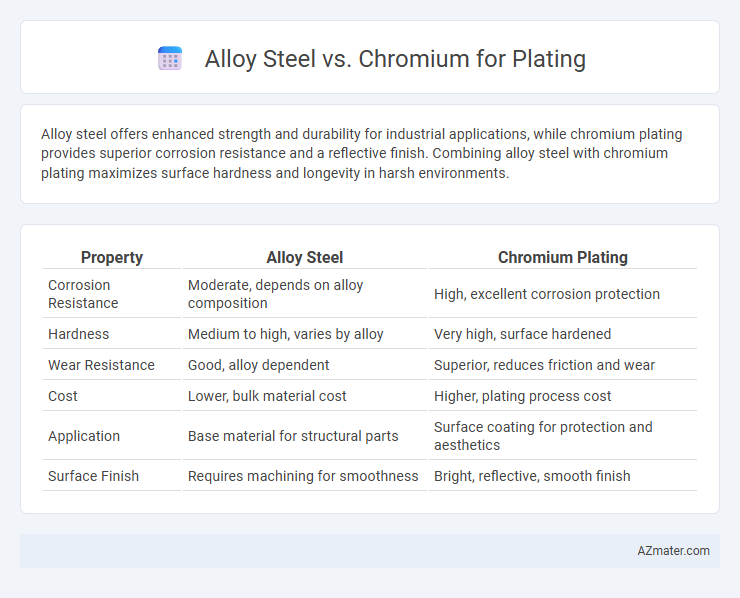
Alloy steel offers enhanced strength and durability for industrial applications, while chromium plating provides superior corrosion resistance and a reflective finish. Combining alloy steel with chromium plating maximizes surface hardness and longevity in harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Alloy Steel | Chromium Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate, depends on alloy composition | High, excellent corrosion protection |
| Hardness | Medium to high, varies by alloy | Very high, surface hardened |
| Wear Resistance | Good, alloy dependent | Superior, reduces friction and wear |
| Cost | Lower, bulk material cost | Higher, plating process cost |
| Application | Base material for structural parts | Surface coating for protection and aesthetics |
| Surface Finish | Requires machining for smoothness | Bright, reflective, smooth finish |
Introduction to Alloy Steel and Chromium Plating
Alloy steel is a versatile metal composed primarily of iron with varying amounts of elements such as chromium, nickel, and molybdenum, enhancing its strength, toughness, and corrosion resistance. Chromium plating involves electroplating a thin layer of chromium onto a substrate, significantly improving surface hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion protection. The combination of alloy steel substrate and chromium plating creates durable components widely used in automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications requiring superior mechanical properties and surface durability.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Alloy steel typically contains a blend of iron, carbon, manganese, and varying amounts of elements like nickel, chromium, and molybdenum to enhance hardness and corrosion resistance. Chromium plating involves depositing a thin layer of chromium metal, known for its high hardness, wear resistance, and excellent corrosion protection properties. Comparing chemical compositions, alloy steel's bulk material incorporates chromium as an alloying element usually in the range of 0.5% to 12%, whereas chromium plating provides a concentrated, nearly pure chromium surface layer with minimal impurities.
Mechanical Properties and Performance
Alloy steel offers enhanced mechanical properties such as higher tensile strength and better fatigue resistance compared to chromium-plated surfaces, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Chromium plating primarily improves surface hardness, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance without significantly altering the substrate's bulk mechanical properties. In applications requiring a balance of structural strength and surface durability, alloy steel substrates with chromium plating provide optimal performance by combining core toughness with enhanced surface protection.
Corrosion Resistance Factors
Alloy steel exhibits enhanced corrosion resistance compared to standard steel due to added elements like chromium, nickel, and molybdenum that form a protective oxide layer. Chromium plating, specifically, offers superior corrosion resistance by creating a hard, inert surface that protects underlying metals from oxidation and chemical attack. The choice between alloy steel and chromium plating depends on the application requirements for durability, environmental exposure, and maintenance, with chromium plating often preferred for high-wear, corrosive conditions.
Wear and Abrasion Resistance
Alloy steel provides excellent wear resistance due to its high hardness and toughness, making it ideal for applications subjected to heavy mechanical stress. Chromium plating enhances surface abrasion resistance by creating a hard, corrosion-resistant layer that significantly reduces friction and wear. Combining alloy steel substrates with chromium plating optimizes durability, extending service life in demanding industrial environments.
Application Suitability and Industry Uses
Alloy steel offers superior strength and durability for heavy-duty applications, making it ideal for automotive components, structural parts, and industrial machinery. Chromium plating enhances corrosion resistance and provides a hard, wear-resistant surface commonly used in aerospace, tooling, and decorative finishes. Industries requiring a balance of mechanical performance and surface protection often combine alloy steel substrates with chromium plating to maximize component lifespan and functionality.
Cost Analysis: Alloy Steel vs Chromium Plating
Alloy steel generally offers lower initial material costs but may require more frequent maintenance and replacement due to lower corrosion resistance compared to chromium plating. Chromium plating, despite its higher upfront cost, extends the lifespan of components by providing superior hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion protection, reducing long-term expenses. Cost analysis favors chromium plating in applications demanding durability and reduced maintenance, while alloy steel suits budget-sensitive projects with shorter service life expectations.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Alloy steel plating often involves toxic chemicals and heavy metals that pose significant environmental hazards during manufacturing and disposal, increasing risks of soil and water contamination. Chromium plating, especially hexavalent chromium, is notorious for its carcinogenic properties and strict regulatory controls due to its severe health impacts on workers and surrounding communities. Safer alternatives and proper waste management are critical to mitigate these risks, with trivalent chromium offering a less toxic option but still requiring careful handling.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Alloy steel plated with chromium offers superior durability due to the hard, corrosion-resistant chromium layer that protects against wear, oxidation, and chemical damage. Chromium plating reduces maintenance requirements by minimizing surface degradation and preventing rust, extending the component's service life. Compared to non-plated alloy steel, chromium-plated surfaces demand less frequent maintenance, improving operational efficiency in industrial applications.
Final Verdict: Choosing Between Alloy Steel and Chromium Plating
Alloy steel offers superior strength and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications, while chromium plating provides excellent corrosion resistance and a bright, decorative finish. When selecting between alloy steel and chromium plating, consider the operational environment and required aesthetic quality; alloy steel suits structural uses, whereas chromium plating enhances wear resistance and appearance. The final choice hinges on balancing mechanical performance with corrosion protection and visual appeal.
Infographic: Alloy steel vs Chromium for Plating
 azmater.com
azmater.com