Cast iron pipes offer superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to lead pipes, which pose significant health risks due to lead leaching. Modern plumbing standards favor cast iron for its longevity and safety in potable water systems.
Table of Comparison
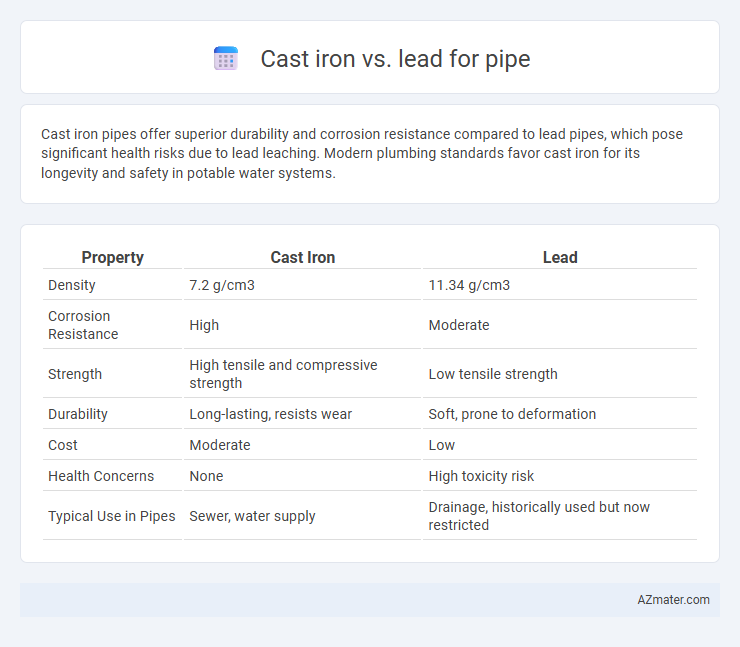
| Property | Cast Iron | Lead |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 7.2 g/cm3 | 11.34 g/cm3 |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Strength | High tensile and compressive strength | Low tensile strength |
| Durability | Long-lasting, resists wear | Soft, prone to deformation |
| Cost | Moderate | Low |
| Health Concerns | None | High toxicity risk |
| Typical Use in Pipes | Sewer, water supply | Drainage, historically used but now restricted |
Introduction to Pipe Materials: Cast Iron vs Lead
Cast iron pipes offer superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to lead pipes, making them a safer and longer-lasting choice for plumbing systems. Lead pipes, once common, pose significant health risks due to potential lead leaching and are now largely obsolete in modern construction. Understanding the material properties and health implications of cast iron versus lead is crucial for selecting appropriate piping in residential and commercial applications.
Historical Use of Cast Iron and Lead Pipes
Cast iron pipes were widely used in urban water systems from the mid-19th century through the early 20th century due to their durability and resistance to pressure, while lead pipes date back to Roman times, valued for their malleability and corrosion resistance. Despite lead's ease of installation, its long-term health dangers led to its gradual replacement by cast iron and other materials in the 20th century. Cast iron pipes dominated historical infrastructure projects such as sewer and water supply networks, contributing significantly to urban sanitation advancements.
Physical Properties: Strength and Durability
Cast iron pipes exhibit superior strength and durability due to their high compressive strength and resistance to external loads, making them ideal for heavy-duty plumbing and sewage systems. Lead pipes, while flexible and resistant to corrosion, lack the mechanical strength of cast iron and are prone to deformation and cracking under pressure. The dense, brittle nature of cast iron ensures longevity and structural integrity, whereas lead's softness compromises its durability in long-term applications.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Cast iron pipes exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to lead, as the iron forms a protective oxide layer that slows deterioration over time. Lead pipes are highly susceptible to corrosion, leading to leaching of toxic metals and compromised water quality. In terms of longevity, cast iron pipes typically last 50 to 100 years, while lead pipes often fail much sooner due to faster corrosion and potential health hazards, making cast iron the preferred choice for durable plumbing systems.
Health and Safety Considerations
Cast iron pipes are widely recognized for their durability and resistance to corrosion, presenting fewer health risks compared to lead pipes, which can leach toxic lead into drinking water and cause severe neurological damage. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) strictly regulates lead levels in plumbing due to lead's known carcinogenic and developmental hazards, making cast iron a safer choice for potable water systems. Health and safety standards increasingly restrict lead usage in pipe manufacturing to protect public health and ensure compliance with modern building codes.
Environmental Impact of Cast Iron and Lead
Cast iron pipes contribute less environmental toxicity compared to lead pipes, as cast iron is more stable and does not leach harmful heavy metals into water supplies. Lead pipes pose significant health risks due to lead contamination, which can cause serious neurological and developmental issues, particularly in children. The durability of cast iron also supports longer service life and reduced frequency of replacements, decreasing waste and resource consumption over time.
Installation and Maintenance Differences
Cast iron pipes require heavy-duty tools and skilled labor for installation due to their weight and rigidity, while lead pipes are more flexible and easier to shape during placement. Maintenance of cast iron involves regular inspections for rust and corrosion, whereas lead pipes demand monitoring to prevent lead leaching, a critical health concern. Cast iron's durability offers longer service life but higher initial installation complexity compared to lead's ease of handling but potential environmental and health risks.
Cost Comparison: Initial and Long-Term Expenses
Cast iron pipes generally have higher initial installation costs due to their weight and labor-intensive fitting processes, while lead pipes are cheaper upfront but pose significant health risks and regulatory restrictions. Over the long term, cast iron offers greater durability and lower maintenance expenses, which can result in cost savings despite the higher initial investment. Lead pipes often incur expensive replacement and health-related costs, making cast iron a more cost-effective and safer choice for plumbing systems.
Modern Alternatives and Pipe Replacement
Modern alternatives to cast iron and lead pipes include PVC, PEX, and copper, offering enhanced durability, corrosion resistance, and safer water quality. Pipe replacement projects prioritize non-toxic materials like cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) for flexibility and cost-effective installation, and copper for its long lifespan and antimicrobial properties. Upgrading from cast iron or lead significantly reduces health risks and maintenance costs while complying with contemporary plumbing codes and environmental standards.
Choosing the Right Pipe Material for Your Needs
Cast iron pipes offer superior durability and resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for underground drainage and heavy-duty plumbing systems. Lead pipes, once common, pose serious health risks due to lead leaching and are no longer recommended for potable water supply. Evaluating factors such as water quality, environmental impact, longevity, and health safety is crucial when choosing between cast iron and lead pipes for your plumbing needs.
Infographic: Cast iron vs Lead for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com