Iridium alloys provide exceptional corrosion resistance and high strength, making them ideal for premium alloy wheels. Magnesium alloys offer lightweight properties that enhance vehicle performance but require protective coatings to prevent oxidation.
Table of Comparison
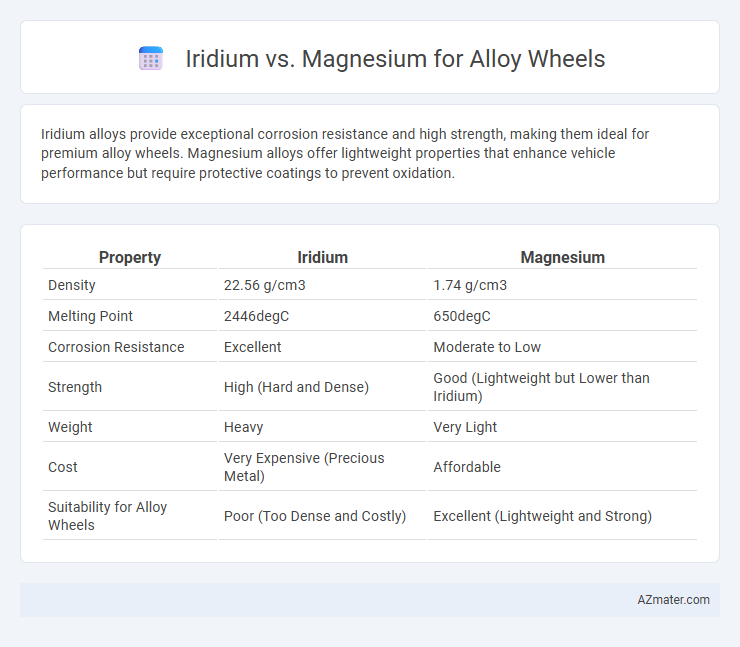
| Property | Iridium | Magnesium |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 22.56 g/cm3 | 1.74 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 2446degC | 650degC |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Moderate to Low |
| Strength | High (Hard and Dense) | Good (Lightweight but Lower than Iridium) |
| Weight | Heavy | Very Light |
| Cost | Very Expensive (Precious Metal) | Affordable |
| Suitability for Alloy Wheels | Poor (Too Dense and Costly) | Excellent (Lightweight and Strong) |
Introduction to Alloy Wheel Materials
Iridium and magnesium represent two distinct materials used in alloy wheel manufacturing, each offering unique properties that influence performance and durability. Magnesium alloy wheels are renowned for their lightweight nature and excellent strength-to-weight ratio, enhancing vehicle handling and fuel efficiency. Iridium, though less common in wheels due to its rarity and cost, provides superior corrosion resistance and hardness, contributing to long-lasting and resilient wheel surfaces.
Overview of Iridium in Alloy Wheels
Iridium is an exceptional metal used in alloy wheels due to its high corrosion resistance and excellent strength-to-weight ratio, enhancing durability and performance. Its incorporation in alloy wheels improves resistance to wear and thermal stability compared to magnesium, which is lighter but more susceptible to oxidation and structural degradation. The superior hardness and stability of iridium alloys contribute to longer-lasting wheels capable of withstanding extreme driving conditions.
Magnesium: Properties and Applications
Magnesium is prized for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance, making it a preferred material in alloy wheel manufacturing. Its lightweight nature significantly enhances vehicle performance by reducing unsprung mass, leading to better handling and improved fuel efficiency. Magnesium alloy wheels also exhibit superior thermal conductivity, aiding in heat dissipation from brakes and extending component lifespan.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Iridium alloy wheels exhibit superior strength and exceptional durability compared to magnesium wheels, owing to iridium's higher tensile strength and resistance to corrosion. Magnesium wheels, while lightweight and offering good performance, are more prone to fatigue and corrosion, reducing their lifespan under harsh conditions. The enhanced structural integrity of iridium alloys ensures better impact resistance and longevity, making them ideal for demanding automotive applications.
Weight Efficiency: Iridium vs Magnesium
Iridium alloys exhibit higher density than magnesium, resulting in heavier alloy wheels despite superior strength and durability. Magnesium alloy wheels offer exceptional weight efficiency due to their low density, significantly reducing the unsprung mass of vehicles and enhancing performance and fuel economy. Choosing magnesium over iridium maximizes weight savings, crucial for applications demanding lightweight components without compromising structural integrity.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Iridium alloys exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to magnesium alloys, making them more durable for alloy wheel applications exposed to harsh environments. Magnesium alloys, while lightweight and cost-effective, are prone to oxidation and require protective coatings to prevent corrosion, which can compromise their longevity. The enhanced corrosion resistance of iridium alloys results in longer-lasting alloy wheels with reduced maintenance needs.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Iridium alloy wheels are significantly more expensive due to the rarity and high extraction costs of iridium, often limiting their use to luxury or specialized vehicles. Magnesium alloys offer a cost-effective alternative, with wider market availability and lower raw material prices, making them popular in both performance and mass-market applications. The cost difference between iridium and magnesium alloys directly influences production scale and consumer accessibility, with magnesium alloy wheels dominating due to affordability and supply chain stability.
Performance Impact on Vehicles
Iridium alloys offer superior strength and corrosion resistance compared to magnesium alloys, significantly enhancing the durability and longevity of alloy wheels under high-performance driving conditions. Magnesium wheels provide a lightweight advantage that improves vehicle acceleration and handling by reducing unsprung mass, but they tend to be less durable and more prone to corrosion. Optimizing alloy wheel performance involves balancing iridium's robustness for extreme conditions with magnesium's lightweight properties for agility and fuel efficiency.
Environmental and Maintenance Considerations
Iridium alloy wheels offer superior corrosion resistance and durability, reducing the frequency of maintenance and extending wheel lifespan, which minimizes environmental waste. Magnesium alloy wheels, while lighter and improving fuel efficiency to lower carbon emissions, are more prone to oxidation and require regular protective coatings to prevent corrosion. Choosing iridium alloys contributes to sustainable vehicle operation with lower upkeep, whereas magnesium demands more frequent care that could increase environmental impact through chemical treatments and replacements.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Alloy Wheels
Iridium offers superior hardness and corrosion resistance compared to magnesium, making it ideal for alloy wheels that require long-lasting durability and performance in harsh environments. Magnesium wheels provide lightweight advantages, enhancing vehicle acceleration and fuel efficiency but may sacrifice some strength and corrosion resistance. Selecting between iridium and magnesium alloy wheels depends on prioritizing durability and resistance versus weight reduction and performance benefits.
Infographic: Iridium vs Magnesium for Alloy Wheel
 azmater.com
azmater.com