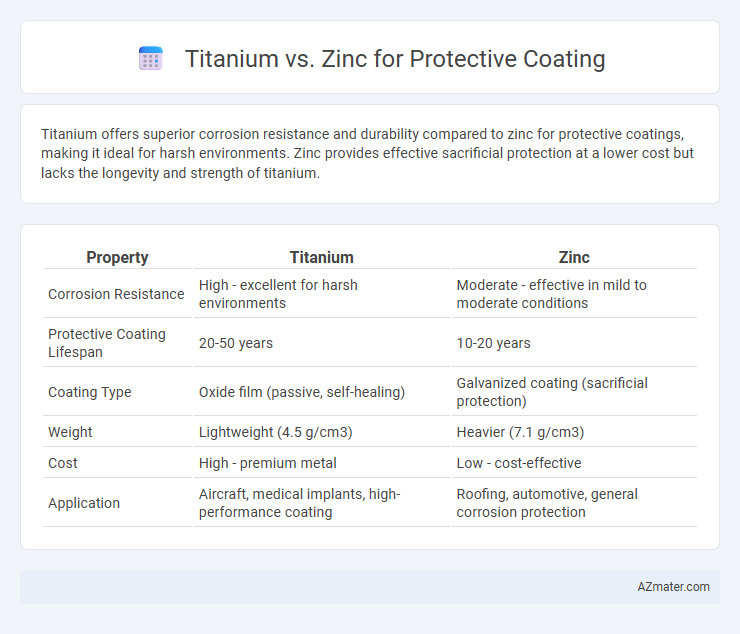
Titanium offers superior corrosion resistance and durability compared to zinc for protective coatings, making it ideal for harsh environments. Zinc provides effective sacrificial protection at a lower cost but lacks the longevity and strength of titanium.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Titanium | Zinc |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | High - excellent for harsh environments | Moderate - effective in mild to moderate conditions |
| Protective Coating Lifespan | 20-50 years | 10-20 years |
| Coating Type | Oxide film (passive, self-healing) | Galvanized coating (sacrificial protection) |
| Weight | Lightweight (4.5 g/cm3) | Heavier (7.1 g/cm3) |
| Cost | High - premium metal | Low - cost-effective |
| Application | Aircraft, medical implants, high-performance coating | Roofing, automotive, general corrosion protection |
Overview: Titanium vs Zinc in Protective Coatings
Titanium coatings outperform zinc in corrosion resistance and durability, offering superior protection in harsh environments such as marine and industrial applications. Zinc's galvanic properties provide sacrificial protection, making it effective for steel substrates prone to rust. Both metals enhance longevity, but titanium's higher cost is balanced by its extended lifespan and minimal maintenance requirements.
Material Properties: Strength and Durability
Titanium exhibits exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for long-lasting protective coatings in harsh environments. Zinc offers sacrificial protection through galvanization, efficiently preventing rust but with lower overall tensile strength compared to titanium. The durability of titanium coatings surpasses zinc in applications requiring high mechanical stress and prolonged exposure to corrosive elements.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Titanium exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to zinc due to its ability to form a stable, dense oxide layer that protects underlying metal from aggressive environmental conditions. Zinc acts as a sacrificial anode in protective coatings, offering effective corrosion protection primarily through galvanic corrosion but is less durable in highly acidic or marine environments. The long-term corrosion resistance of titanium outperforms zinc, making it ideal for critical applications requiring extended durability and minimal maintenance.
Application Methods and Techniques
Titanium coatings are typically applied using physical vapor deposition (PVD) and plasma spraying, offering superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability for aerospace and industrial applications. Zinc coatings employ hot-dip galvanizing, electroplating, and thermal spraying techniques, providing effective sacrificial protection primarily for steel structures in construction and automotive industries. The choice between titanium and zinc coatings depends on specific environmental exposure and mechanical demands, with titanium favored for extreme conditions and zinc widely used for cost-effective corrosion prevention.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Titanium coatings typically present higher initial costs due to expensive raw materials and complex application processes compared to zinc, which is more abundant and cheaper to produce. Zinc coatings offer cost-effective corrosion protection, making them favorable for large-scale, budget-sensitive projects, while titanium's durability can reduce long-term maintenance expenses. Economic decisions often weigh zinc's upfront affordability against titanium's potential savings from extended coating lifespan and reduced repair frequency.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Titanium offers superior corrosion resistance and durability, reducing the frequency of recoating and minimizing material waste, which supports sustainable building practices. Zinc coatings, while renewable and recyclable, can release zinc ions into the environment during corrosion, potentially impacting soil and water quality. Evaluating both metals, titanium provides a longer-lasting, eco-friendly option with lower environmental impact compared to traditional zinc coatings.
Performance in Harsh Environments
Titanium offers superior corrosion resistance and maintains structural integrity in highly acidic and saline environments, outperforming zinc in long-term durability. Zinc coatings provide effective sacrificial protection, but their performance diminishes faster under extreme temperature fluctuations and aggressive chemical exposure. The inherent strength and oxidation resistance of titanium make it the preferred choice for protective coatings in harsh environments requiring prolonged resilience.
Maintenance and Longevity
Titanium coatings exhibit exceptional corrosion resistance and maintain structural integrity for over 50 years, significantly reducing maintenance frequency compared to zinc, which typically requires reapplication every 10-15 years due to faster degradation. Titanium's oxide layer self-heals when scratched, enhancing longevity in harsh environments, whereas zinc relies on sacrificial protection that diminishes with time. Choosing titanium for protective coatings results in lower long-term costs and superior durability in industrial and marine applications.
Common Industries and Use Cases
Titanium coatings are extensively used in aerospace, automotive, and medical industries due to their exceptional corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, and high strength-to-weight ratio. Zinc coatings dominate in construction, automotive, and infrastructure sectors for their excellent corrosion protection through galvanization, especially on steel surfaces prone to rust. Both metals serve crucial protective roles; titanium excels in high-performance environments while zinc offers cost-effective, widespread corrosion prevention.
Choosing the Right Coating: Key Factors
Selecting the right protective coating between titanium and zinc depends on factors such as corrosion resistance, durability, and environmental conditions. Titanium offers superior resistance to harsh chemicals and high temperatures, making it ideal for marine and industrial applications, while zinc provides excellent sacrificial protection against rust in atmospheric environments. Consider cost-effectiveness, substrate compatibility, and long-term maintenance requirements to determine the most suitable coating for specific project needs.
Infographic: Titanium vs Zinc for Protective Coating
 azmater.com
azmater.com