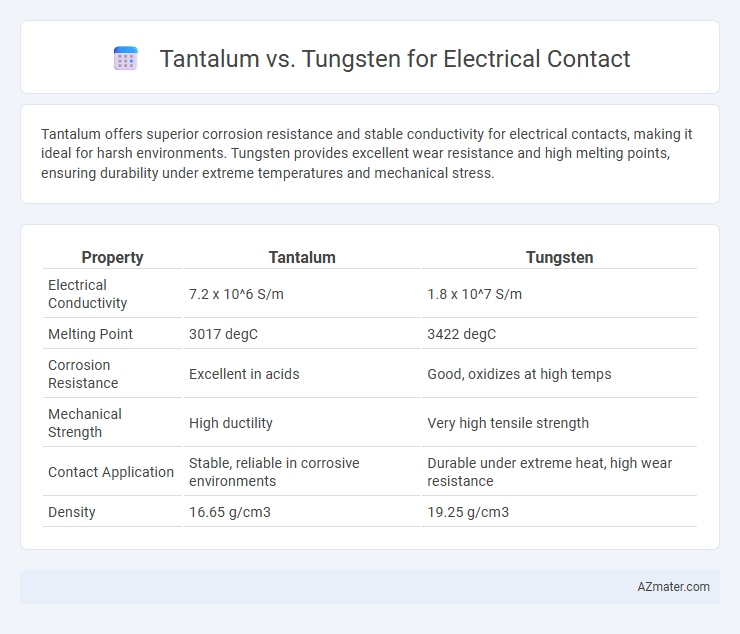
Tantalum offers superior corrosion resistance and stable conductivity for electrical contacts, making it ideal for harsh environments. Tungsten provides excellent wear resistance and high melting points, ensuring durability under extreme temperatures and mechanical stress.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tantalum | Tungsten |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 7.2 x 10^6 S/m | 1.8 x 10^7 S/m |
| Melting Point | 3017 degC | 3422 degC |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in acids | Good, oxidizes at high temps |
| Mechanical Strength | High ductility | Very high tensile strength |
| Contact Application | Stable, reliable in corrosive environments | Durable under extreme heat, high wear resistance |
| Density | 16.65 g/cm3 | 19.25 g/cm3 |
Introduction to Tantalum and Tungsten in Electrical Contacts
Tantalum and tungsten are widely used materials in electrical contacts due to their exceptional properties. Tantalum offers excellent corrosion resistance and stable electrical conductivity, making it ideal for high-reliability connectors in harsh environments. Tungsten provides superior hardness and high melting point, ensuring durability and performance under extreme temperature and mechanical stress in electrical switching applications.
Material Properties Overview: Tantalum vs Tungsten
Tantalum exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, high melting point around 3017degC, and superior ductility, making it ideal for electrical contacts requiring durability and stability in harsh environments. Tungsten offers an even higher melting point of about 3422degC and exceptional hardness but is more brittle, which can limit its use in applications needing mechanical flexibility. Both metals provide excellent electrical conductivity, but tantalum's combination of toughness and corrosion resistance often makes it preferable for long-lasting electrical contacts.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Tungsten exhibits an electrical conductivity of approximately 18.6% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard), whereas tantalum offers slightly higher conductivity around 25% IACS, making tantalum more efficient for electrical contacts requiring better current flow. Tungsten's superior melting point and mechanical strength contribute to durability in high-temperature environments despite its lower conductivity. For applications prioritizing electrical performance in conductive pathways, tantalum typically outperforms tungsten due to its balanced conductivity and corrosion resistance.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Tantalum offers excellent corrosion resistance and good electrical conductivity, but Tungsten surpasses it in mechanical strength and durability, making Tungsten more suitable for high-wear electrical contacts. The high melting point of Tungsten (3422degC) enhances its resistance to deformation under thermal stress, whereas Tantalum melts at 3017degC and tends to soften at elevated temperatures. Tungsten's superior hardness and wear resistance extend the lifespan of electrical contacts in demanding environments, ensuring reliable performance over time.
Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
Tantalum exhibits superior corrosion resistance in electrical contacts, maintaining stability in harsh chemical environments and acidic conditions, making it ideal for high-reliability applications. Tungsten offers excellent oxidation resistance at elevated temperatures but is more prone to oxidative degradation in moist or acidic atmospheres compared to tantalum. The inherent passivation layer of tantalum significantly enhances its durability against corrosion, whereas tungsten requires protective coatings to achieve comparable longevity in aggressive environments.
Thermal Stability and Performance
Tungsten exhibits superior thermal stability compared to tantalum, maintaining structural integrity and electrical conductivity at temperatures above 3,400degC, making it ideal for high-temperature electrical contacts. Tantalum, with a melting point of around 3,020degC, offers excellent corrosion resistance and reliable performance in moderate thermal environments but may suffer from reduced durability under extreme heat. Tungsten's higher melting point and lower thermal expansion contribute to enhanced performance in demanding electrical applications requiring prolonged thermal cycling.
Cost and Availability Factors
Tantalum offers excellent corrosion resistance and stability for electrical contacts but comes at a higher cost due to limited global supply and concentrated mining regions, primarily in Africa. Tungsten is more abundant and cost-effective, with superior hardness and high-temperature performance, making it a preferred choice for applications requiring durability and electrical conductivity. The availability of tungsten ensures lower material costs and more consistent supply chains compared to the relatively scarce and expensive tantalum.
Common Applications in Electrical Engineering
Tantalum is widely used in electrical contacts within aerospace and medical devices due to its excellent corrosion resistance and stable electrical conductivity under high temperatures. Tungsten, known for its exceptional hardness and high melting point, is preferred for electrical contacts in heavy-duty switches and high-power electrical circuits where wear resistance and durability are critical. Both metals are integral in manufacturing reliable, long-lasting electrical contacts in various industrial and high-performance electronic applications.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Tantalum offers superior corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, making it a safer choice for electrical contacts in medical and environmentally sensitive applications. Tungsten presents higher mechanical strength and thermal stability but poses greater risks due to its toxicity and environmental impact during mining and processing. Selecting tantalum over tungsten reduces hazardous waste generation and exposure to harmful substances, enhancing overall sustainability and workplace safety.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Tantalum and Tungsten
Tantalum offers excellent corrosion resistance and good conductivity, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and stable electrical performance. Tungsten provides superior hardness and high melting points, suitable for high-temperature or high-wear electrical contacts. Selecting between tantalum and tungsten depends on the specific operating environment, with tantalum favored for chemical resistance and tungsten preferred for thermal and mechanical stress conditions.
Infographic: Tantalum vs Tungsten for Electrical contact
 azmater.com
azmater.com