Palladium spark plugs offer superior oxidation resistance and a longer lifespan compared to traditional copper plugs, while iridium spark plugs provide even greater durability and improved ignitability due to their higher melting point and finer electrode size. Iridium's enhanced performance makes it ideal for high-performance engines, although palladium remains a cost-effective alternative with reliable efficiency.
Table of Comparison
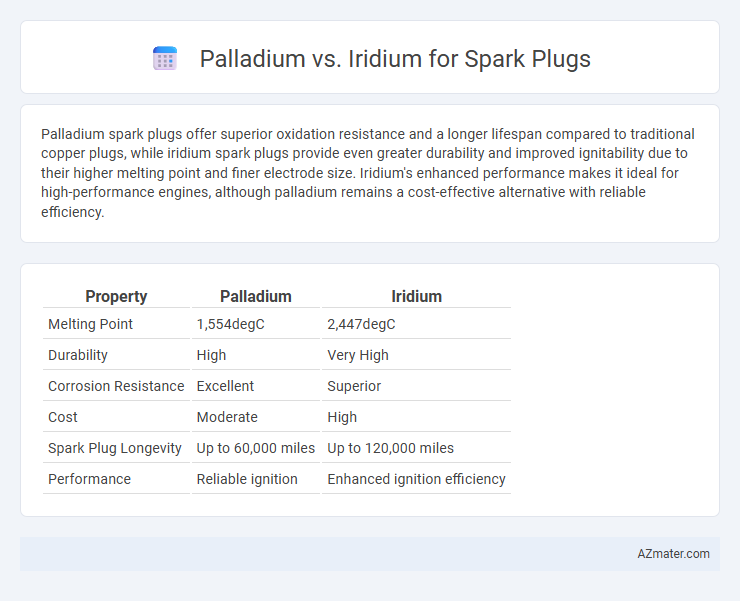
| Property | Palladium | Iridium |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | 1,554degC | 2,447degC |
| Durability | High | Very High |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Superior |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
| Spark Plug Longevity | Up to 60,000 miles | Up to 120,000 miles |
| Performance | Reliable ignition | Enhanced ignition efficiency |
Introduction to Palladium and Iridium Spark Plugs
Palladium and iridium spark plugs are high-performance automotive components designed to enhance ignition efficiency and durability. Palladium spark plugs offer improved wear resistance and a lower cost alternative, while iridium spark plugs provide superior electrode strength and longer lifespan due to their higher melting point. Both materials deliver better combustion and fuel economy compared to traditional copper spark plugs, making them popular choices for modern engines.
Chemical Properties and Composition
Palladium and iridium are both platinum group metals commonly used in spark plugs due to their excellent catalytic properties and high melting points. Palladium has a melting point of 1,554degC and is chemically more reactive, often alloyed to improve wear resistance, whereas iridium has a higher melting point of 2,447degC and greater corrosion resistance, enhancing spark plug durability in extreme conditions. The chemical stability and oxidation resistance of iridium make it a superior choice for long-lasting spark plugs, while palladium offers a balance of performance and cost-effectiveness.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Palladium spark plug electrodes exhibit higher electrical conductivity than iridium, enhancing spark efficiency and ignition performance. The superior conductivity of palladium reduces voltage loss, enabling a stronger and more consistent spark. Iridium, while highly durable, has slightly lower electrical conductivity, which may affect ignition reliability under extreme conditions.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Stability
Palladium spark plugs offer excellent heat resistance, maintaining optimal performance in high-temperature engine conditions, but typically have lower thermal stability compared to iridium. Iridium spark plugs exhibit superior thermal stability, withstanding extreme heat and preventing electrode wear, which enhances longevity and consistent ignition. The choice between palladium and iridium depends on engine design requirements, with iridium favored for high-performance engines requiring maximum heat endurance and durability.
Lifespan and Durability Analysis
Palladium spark plugs typically offer a lifespan of around 60,000 to 100,000 miles, benefiting from good corrosion resistance and moderate wear rates. Iridium spark plugs outperform palladium with lifespans exceeding 100,000 miles due to their higher melting point and superior hardness, which enhances electrode durability under extreme combustion conditions. The durability of iridium electrodes contributes to more consistent performance and extended intervals between replacements compared to palladium variants.
Engine Performance Impact
Palladium spark plugs offer enhanced ignition efficiency and longer lifespan due to their higher melting point and excellent conductivity, improving engine performance by ensuring stable combustion and smoother acceleration. Iridium spark plugs provide superior durability and consistently strong sparks, which contribute to better fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and more reliable starts, especially in high-performance engines. Choosing between palladium and iridium depends on the engine's design and driving conditions, with iridium often favored for demanding applications requiring optimal spark strength and longevity.
Fuel Efficiency Considerations
Palladium spark plugs offer excellent fuel efficiency due to their lower firing voltage and consistent ignition performance, which enhances combustion and reduces fuel consumption. Iridium spark plugs provide superior durability and higher melting points, maintaining optimal spark quality over longer periods, resulting in sustained fuel efficiency in high-performance engines. Selecting between palladium and iridium depends on engine requirements, driving conditions, and the balance between initial cost and long-term fuel savings.
Maintenance and Replacement Frequency
Palladium spark plugs typically offer longer maintenance intervals, often lasting up to 60,000 to 100,000 miles, due to their resistance to wear and high-temperature durability. Iridium spark plugs provide even greater longevity, with replacement intervals extending beyond 100,000 miles, thanks to the metal's exceptional hardness and corrosion resistance. Both types reduce the frequency of maintenance compared to conventional copper plugs, but iridium plugs demand the least frequent replacement, contributing to lower overall engine service costs.
Cost Differences and Value for Money
Palladium spark plugs generally cost less than iridium plugs, making them an attractive option for budget-conscious drivers seeking reliable engine performance. Iridium plugs, though pricier, offer superior durability and improved ignition efficiency, translating to longer intervals between replacements and potentially lower long-term maintenance costs. Considering cost differences alongside longevity and performance benefits helps determine the best value for money based on specific driving needs and vehicle requirements.
Choosing the Right Spark Plug for Your Vehicle
Palladium and iridium spark plugs both offer excellent durability and performance, but iridium spark plugs generally provide better thermal conductivity and longer service life due to their higher melting point. Palladium spark plugs are often more cost-effective and offer improved ignition performance compared to traditional copper plugs, making them a good option for many vehicles. When choosing the right spark plug for your vehicle, consider factors such as engine type, manufacturer recommendations, and driving conditions to ensure optimal ignition efficiency and fuel economy.
Infographic: Palladium vs Iridium for Spark Plug
 azmater.com
azmater.com