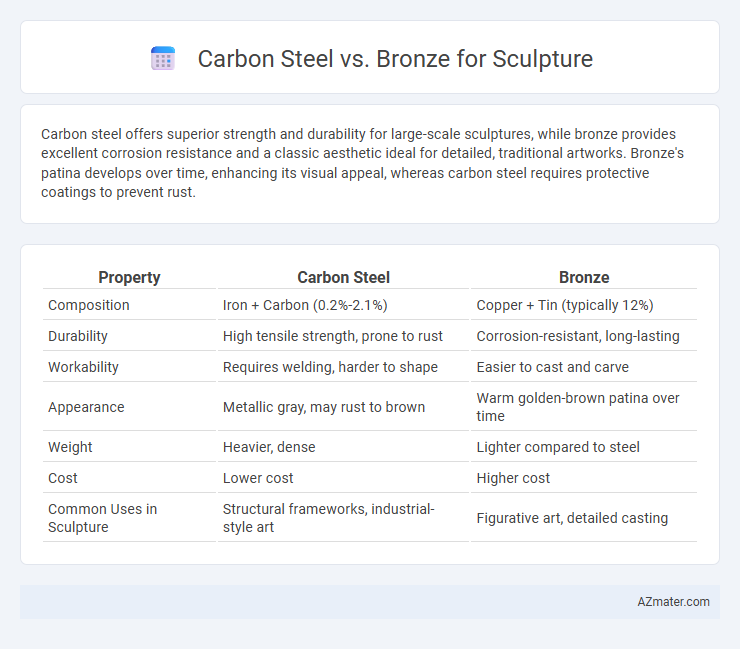
Carbon steel offers superior strength and durability for large-scale sculptures, while bronze provides excellent corrosion resistance and a classic aesthetic ideal for detailed, traditional artworks. Bronze's patina develops over time, enhancing its visual appeal, whereas carbon steel requires protective coatings to prevent rust.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Steel | Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Iron + Carbon (0.2%-2.1%) | Copper + Tin (typically 12%) |
| Durability | High tensile strength, prone to rust | Corrosion-resistant, long-lasting |
| Workability | Requires welding, harder to shape | Easier to cast and carve |
| Appearance | Metallic gray, may rust to brown | Warm golden-brown patina over time |
| Weight | Heavier, dense | Lighter compared to steel |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Common Uses in Sculpture | Structural frameworks, industrial-style art | Figurative art, detailed casting |
Introduction to Sculpture Materials
Carbon steel offers high strength and durability, making it ideal for large-scale sculptures requiring structural integrity and resistance to deformation. Bronze is valued for its corrosion resistance and ability to capture fine details through casting, resulting in timeless, intricate sculptures with a warm patina finish. Selecting between carbon steel and bronze depends on factors like desired texture, longevity, intended environment, and budget constraints in sculpture creation.
Overview of Carbon Steel
Carbon steel offers high tensile strength and durability, making it ideal for large-scale sculptures exposed to outdoor elements. Its composition, primarily iron with a small percentage of carbon, enables excellent weldability and versatility in shaping intricate designs. Compared to bronze, carbon steel is typically more cost-effective and easier to source, though it requires protective coatings to prevent rust and corrosion over time.
Overview of Bronze
Bronze, an alloy primarily composed of copper and tin, is prized in sculpture for its durability, corrosion resistance, and warm, rich color that enhances fine detail. Its lower melting point compared to carbon steel allows for intricate casting processes, making it ideal for lifelike representations and outdoor installations. The metal's natural patina develops over time, providing both protection and a unique aesthetic that carbon steel lacks.
Historical Use in Sculpture
Bronze has been the preferred material for sculpture since ancient civilizations like Mesopotamia and Greece, celebrated for its durability, corrosion resistance, and ability to capture fine details through lost-wax casting. Carbon steel, while not traditionally used in historic sculpture due to its susceptibility to rust and difficulty in casting, gained popularity in modern and contemporary art for its strength and affordability. The historical preference for bronze reflects its superior long-term preservation and aesthetic qualities in outdoor statuary and monumental works.
Durability and Longevity
Carbon steel sculptures offer superior strength and resistance to impact, making them highly durable for outdoor installations, though they require protective coatings to prevent rust and corrosion. Bronze, an alloy primarily of copper and tin, exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance and develops a stable patina over time, enhancing both its durability and aesthetic appeal. The longevity of bronze sculptures often surpasses carbon steel due to their inherent resistance to environmental elements and minimal maintenance needs.
Workability and Artistic Flexibility
Carbon steel offers superior workability for sculpture due to its high strength and ability to be welded, cut, and shaped with precision, making it ideal for creating intricate and durable designs. Bronze provides greater artistic flexibility because of its excellent casting properties and smooth surface finish, allowing for fine detail and patination that enhance aesthetic appeal. Sculptors often choose carbon steel for structural elements and large forms, while bronze is preferred for detailed, traditional, and polished artworks.
Aesthetic Qualities and Finishes
Carbon steel offers a sleek, industrial appearance with a smooth, dark finish that can develop a natural patina over time, enhancing its visual appeal. Bronze provides a warm, rich color and is highly valued for its ability to capture fine details and develop a green or brown patina that adds depth and character. Both materials allow diverse finishing techniques, but bronze's traditional use in sculptures highlights its timeless aesthetic and durability.
Cost and Availability
Carbon steel offers a cost-effective option for sculptures due to its widespread availability and lower price compared to bronze. Bronze, an alloy primarily of copper and tin, commands higher costs influenced by fluctuating metal markets and its limited availability. Sculptors often choose carbon steel for budget-conscious projects while bronze remains preferred for its timeless aesthetic despite higher expenses.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbon steel production generates higher carbon emissions due to intensive mining and energy use, whereas bronze, an alloy of copper and tin, relies on metals with significant mining impacts but can be recycled extensively. Bronze sculptures often have a longer lifespan and better resistance to corrosion, reducing the need for replacement and conserving resources over time. Choosing bronze or carbon steel depends on sourcing practices and facility emissions, with recycled materials enhancing sustainability in both cases.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Sculpture
Selecting the right material for your sculpture depends heavily on the desired durability and aesthetic qualities; carbon steel offers exceptional strength and weather resistance, making it ideal for outdoor installations, while bronze provides a timeless, classic look with excellent corrosion resistance and patina development. Consider the environmental exposure and maintenance requirements, as carbon steel may require protective coatings to prevent rust, whereas bronze naturally forms a protective layer that enhances its longevity. Budget and artist preference also play crucial roles, with carbon steel often being more cost-effective and bronze favored for its traditional sculptural appeal.
Infographic: Carbon steel vs Bronze for Sculpture
 azmater.com
azmater.com