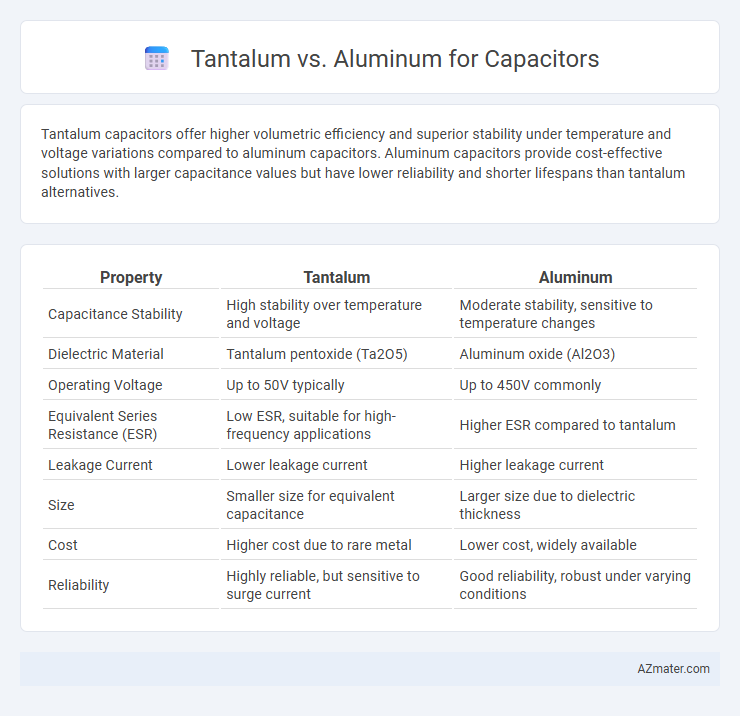
Tantalum capacitors offer higher volumetric efficiency and superior stability under temperature and voltage variations compared to aluminum capacitors. Aluminum capacitors provide cost-effective solutions with larger capacitance values but have lower reliability and shorter lifespans than tantalum alternatives.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tantalum | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Capacitance Stability | High stability over temperature and voltage | Moderate stability, sensitive to temperature changes |
| Dielectric Material | Tantalum pentoxide (Ta2O5) | Aluminum oxide (Al2O3) |
| Operating Voltage | Up to 50V typically | Up to 450V commonly |
| Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) | Low ESR, suitable for high-frequency applications | Higher ESR compared to tantalum |
| Leakage Current | Lower leakage current | Higher leakage current |
| Size | Smaller size for equivalent capacitance | Larger size due to dielectric thickness |
| Cost | Higher cost due to rare metal | Lower cost, widely available |
| Reliability | Highly reliable, but sensitive to surge current | Good reliability, robust under varying conditions |
Introduction to Capacitor Materials
Tantalum and aluminum are two primary materials used in capacitor manufacturing, each offering distinct electrical and physical properties. Tantalum capacitors provide higher capacitance per volume and better stability at high frequencies, making them ideal for compact, high-performance electronics. Aluminum capacitors, typically electrolytic types, are favored for their cost-effectiveness and large capacitance values in bulk power applications.
Overview of Tantalum Capacitors
Tantalum capacitors provide high capacitance per volume with excellent stability and reliability, making them ideal for space-constrained electronic circuits. Their inherent low equivalent series resistance (ESR) enhances performance in high-frequency applications compared to aluminum electrolytic capacitors. Tantalum capacitors maintain consistent capacitance and exhibit superior temperature and voltage characteristics, positioning them as a preferred choice for power supply filtering and decoupling tasks.
Overview of Aluminum Capacitors
Aluminum capacitors utilize an aluminum oxide layer as the dielectric and are known for their high capacitance and cost-effectiveness in bulk storage applications. These capacitors offer excellent performance in filtering and smoothing circuits due to their stable capacitance and high ripple current tolerance. Compared to tantalum capacitors, aluminum capacitors generally provide larger capacitance values but have lower volumetric efficiency and lifespan under high-temperature conditions.
Electrical Performance Comparison
Tantalum capacitors offer higher volumetric efficiency and superior capacitance stability over a wide temperature range compared to aluminum electrolytic capacitors. They exhibit lower equivalent series resistance (ESR) and better frequency response, making them ideal for high-performance applications requiring stable electrical characteristics. While aluminum capacitors provide cost-effective solutions with higher ripple current tolerance, their electrical performance typically falls short in precision and reliability under stringent conditions.
Capacitance and Voltage Ratings
Tantalum capacitors typically offer higher capacitance values per volume compared to aluminum capacitors, making them ideal for miniaturized electronic circuits. They also feature superior voltage ratings, often ranging from 4V to 50V, suitable for applications requiring stable performance under higher voltage stress. Aluminum capacitors generally support a wider voltage range, from 6.3V up to 500V, but with larger physical sizes for equivalent capacitance levels.
Size and Weight Differences
Tantalum capacitors offer higher volumetric efficiency, allowing for smaller sizes compared to aluminum electrolytic capacitors with equivalent capacitance and voltage ratings. In terms of weight, tantalum capacitors are generally lighter due to their compact ceramic or manganese dioxide construction, while aluminum capacitors are bulkier because of the thicker aluminum foil and liquid electrolyte inside. These size and weight advantages make tantalum capacitors ideal for compact, portable electronic devices requiring stable performance in limited spaces.
Reliability and Lifespan
Tantalum capacitors are renowned for their superior reliability and longer lifespan compared to aluminum capacitors, especially in high-temperature and high-frequency applications. The solid electrolyte in tantalum capacitors reduces the risk of leakage and failure modes, enhancing their stability over time. Aluminum capacitors, while cost-effective and versatile, typically exhibit shorter lifespans and higher failure rates due to their liquid electrolyte and susceptibility to drying out or swelling under thermal stress.
Cost and Availability
Tantalum capacitors typically carry higher costs due to the scarcity and mining complexities of tantalum ore, making them less economically viable for large-scale applications compared to aluminum capacitors. Aluminum capacitors, sourced from abundant bauxite and refined into aluminum, benefit from lower material costs and widespread availability, allowing more cost-effective production and procurement. The price and supply chain stability of aluminum capacitors make them a preferred option in cost-sensitive and high-volume electronic manufacturing.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Tantalum capacitors excel in applications requiring high capacitance stability and reliability under extreme conditions, such as aerospace, military, and medical devices. Aluminum capacitors are widely used in consumer electronics, power supplies, and automotive industries due to their cost-effectiveness and higher voltage ratings. Both materials serve distinct roles, with tantalum favored for compact, high-performance circuits and aluminum preferred for general-purpose, high-voltage filtering and energy storage.
Choosing the Right Capacitor: Tantalum vs Aluminum
Tantalum capacitors offer higher capacitance per volume and superior stability under varying temperatures, making them ideal for space-constrained, high-reliability applications. Aluminum capacitors excel in handling high surge currents and provide cost-effective solutions for general-purpose filtering and smoothing tasks. Selecting between tantalum and aluminum capacitors depends on factors such as required capacitance density, voltage rating, frequency response, and budget constraints in the specific electronic design.
Infographic: Tantalum vs Aluminum for Capacitor
 azmater.com
azmater.com