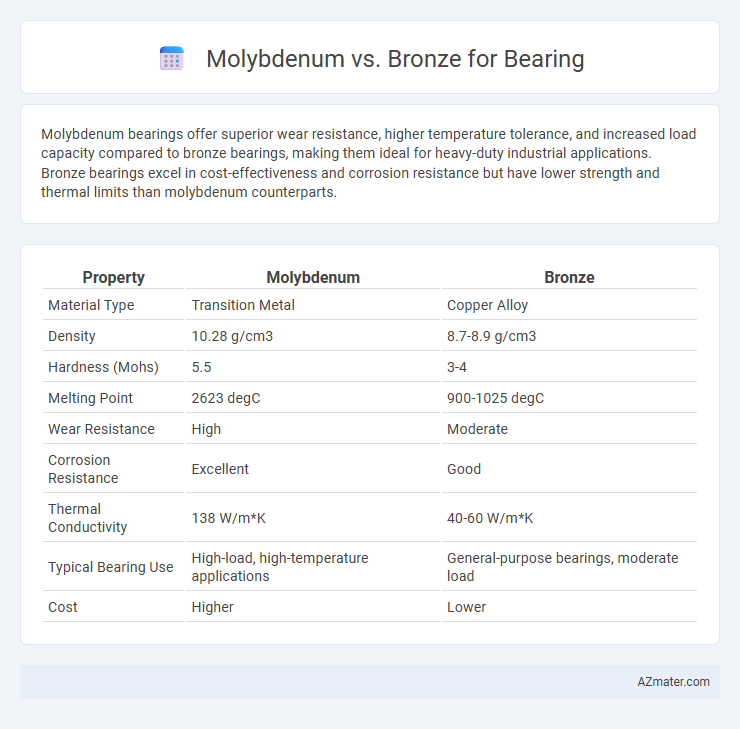
Molybdenum bearings offer superior wear resistance, higher temperature tolerance, and increased load capacity compared to bronze bearings, making them ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications. Bronze bearings excel in cost-effectiveness and corrosion resistance but have lower strength and thermal limits than molybdenum counterparts.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Molybdenum | Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Transition Metal | Copper Alloy |
| Density | 10.28 g/cm3 | 8.7-8.9 g/cm3 |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 5.5 | 3-4 |
| Melting Point | 2623 degC | 900-1025 degC |
| Wear Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Thermal Conductivity | 138 W/m*K | 40-60 W/m*K |
| Typical Bearing Use | High-load, high-temperature applications | General-purpose bearings, moderate load |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Bearing Materials
Molybdenum and bronze are two prominent materials commonly used in bearing applications due to their unique mechanical properties and wear resistance. Molybdenum bearings excel in high-temperature environments and offer superior hardness and load-carrying capacity, while bronze bearings provide excellent corrosion resistance and adaptability to different lubrication conditions. Selecting the appropriate bearing material depends on specific operational requirements such as load, temperature, and environmental factors.
Overview of Molybdenum Bearings
Molybdenum bearings exhibit exceptional strength, high temperature resistance up to 1,100degC, and excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for demanding industrial applications. Their low coefficient of friction and superior wear resistance outperform traditional bronze bearings, enhancing durability in heavy-load and high-speed environments. Molybdenum's unique crystalline structure enables self-lubrication properties, reducing maintenance requirements compared to bronze alternatives.
Overview of Bronze Bearings
Bronze bearings, composed primarily of copper and tin, are widely recognized for their excellent wear resistance and load-carrying capacity in various industrial applications. Their inherent self-lubricating properties and ability to operate effectively under heavy loads and low speeds make them a preferred choice for machinery requiring durability and reduced friction. Compared to molybdenum bearings, bronze offers superior corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for environments exposed to moisture or corrosive elements.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Molybdenum bearings exhibit superior wear resistance and higher load-carrying capacity due to their excellent hardness and tensile strength compared to bronze bearings. Bronze bearings offer good corrosion resistance and lower friction coefficients but typically have lower fatigue strength and can deform under heavy loads. The choice between molybdenum and bronze bearings hinges on application-specific mechanical demands such as load intensity, thermal stability, and lifespan requirements.
Wear Resistance and Durability
Molybdenum bearings offer superior wear resistance due to their excellent hardness and ability to maintain structural integrity under high load and temperature conditions, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Bronze bearings, while durable, exhibit lower wear resistance compared to molybdenum, often requiring additional lubrication to prevent premature surface fatigue. The enhanced durability of molybdenum bearings results in longer service life and reduced maintenance costs in demanding environments.
Friction and Lubrication Performance
Molybdenum coatings exhibit superior friction reduction and enhanced lubrication retention compared to bronze bearings, resulting in lower wear rates and extended service life. The lamellar structure of molybdenum disulfide provides excellent boundary lubrication, minimizing metal-to-metal contact under high load and low-speed conditions. Bronze bearings offer good fatigue resistance but typically require consistent lubrication, leading to higher friction coefficients and increased maintenance frequency relative to molybdenum-based alternatives.
Corrosion Resistance Analysis
Molybdenum bearings demonstrate superior corrosion resistance due to their inherent chemical stability and oxide layer formation in harsh environments, significantly outperforming bronze counterparts. Bronze bearings, while traditionally favored for their cost-effectiveness and ease of machining, are more susceptible to corrosion, especially in marine or acidic conditions, often requiring additional coatings or treatments to enhance durability. The enhanced corrosion resistance of molybdenum bearings makes them an optimal choice for applications exposed to aggressive chemicals or high moisture levels, ensuring longer lifespan and reduced maintenance.
Cost and Availability
Molybdenum bearings typically cost more than bronze due to the metal's high-purity extraction process and superior heat resistance properties, making it suitable for demanding industrial applications. Bronze bearings are widely available and more affordable, benefiting from long-established manufacturing processes and extensive supplier networks. In terms of availability, bronze is easier to source globally, while molybdenum may face supply constraints due to limited mining locations and fluctuating market demand.
Typical Applications and Industries
Molybdenum bearings excel in high-temperature, high-load environments such as aerospace, automotive, and heavy machinery due to their superior wear resistance and thermal stability. Bronze bearings are widely used in general industrial applications, including agriculture, construction, and marine industries, offering good corrosion resistance and machinability. Both materials provide durability, but molybdenum is preferred for extreme conditions while bronze is chosen for cost-effectiveness and versatility.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Bearing Needs
Choosing between molybdenum and bronze for bearings depends on factors like load capacity, temperature resistance, and wear properties. Molybdenum bearings excel in high-temperature and high-load environments due to their superior hardness and low friction, making them ideal for heavy machinery. Bronze bearings, known for their excellent corrosion resistance and good machinability, are more suitable for moderate loads and applications requiring easier maintenance.
Infographic: Molybdenum vs Bronze for Bearing
 azmater.com
azmater.com