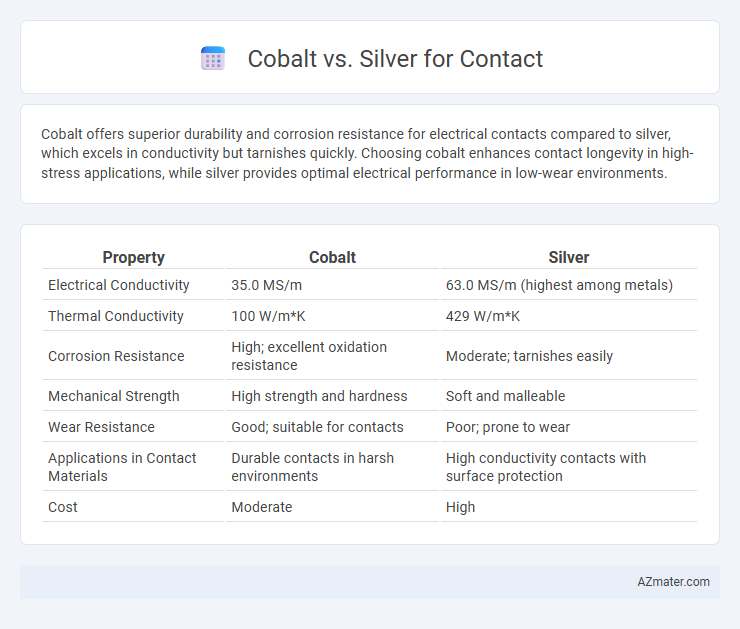
Cobalt offers superior durability and corrosion resistance for electrical contacts compared to silver, which excels in conductivity but tarnishes quickly. Choosing cobalt enhances contact longevity in high-stress applications, while silver provides optimal electrical performance in low-wear environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cobalt | Silver |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 35.0 MS/m | 63.0 MS/m (highest among metals) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 100 W/m*K | 429 W/m*K |
| Corrosion Resistance | High; excellent oxidation resistance | Moderate; tarnishes easily |
| Mechanical Strength | High strength and hardness | Soft and malleable |
| Wear Resistance | Good; suitable for contacts | Poor; prone to wear |
| Applications in Contact Materials | Durable contacts in harsh environments | High conductivity contacts with surface protection |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
Overview: Cobalt vs Silver in Electrical Contacts
Cobalt offers superior mechanical strength and corrosion resistance compared to silver, making it ideal for high-wear electrical contacts in harsh environments. Silver provides exceptional electrical conductivity and lower contact resistance, which is crucial for minimizing energy loss and ensuring efficient current flow. The choice between cobalt and silver contacts depends on balancing conductivity needs with durability requirements in specific applications.
Conductivity: Comparing Cobalt and Silver
Silver exhibits the highest electrical conductivity among all metals, around 63 x 10^6 S/m, making it exceptionally efficient for electrical contacts. Cobalt, with a significantly lower conductivity of approximately 17 x 10^6 S/m, is less effective in minimizing resistance and energy loss. Despite lower conductivity, cobalt offers superior mechanical strength and corrosion resistance, but silver remains the preferred choice for contacts where maximum electrical performance is critical.
Cost Differences: Cobalt vs Silver
Cobalt contacts typically cost less than silver contacts due to the lower raw material price and greater availability of cobalt. Silver offers superior electrical conductivity but comes at a higher price, influenced by market fluctuations and purity requirements. Choosing between cobalt and silver contacts depends on balancing budget constraints with performance needs, where cobalt presents a more economical option without sacrificing basic functional reliability.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Cobalt exhibits superior durability and wear resistance compared to silver, making it ideal for high-contact applications such as industrial machinery and medical implants. Its hardness and corrosion resistance significantly reduce material degradation over time, ensuring longer-lasting performance under stress. Silver, while highly conductive, is softer and more prone to wear, limiting its effectiveness in environments requiring sustained mechanical contact.
Corrosion Resistance: Which Performs Better?
Cobalt exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to silver, especially in harsh environments where oxidation and sulfide formation are prevalent. While silver offers excellent electrical conductivity, it tarnishes quickly when exposed to air and sulfur-containing compounds, leading to reduced performance over time. Cobalt's stability in corrosive conditions makes it the preferred choice for contacts demanding long-term reliability and durability.
Applications in the Electronics Industry
Cobalt offers superior wear resistance and thermal stability in electronic contacts, making it ideal for high-reliability connectors and switches in aerospace and automotive electronics. Silver, known for its exceptional electrical conductivity and low contact resistance, is preferred in printed circuit boards and RF connectors where signal integrity is critical. The electronics industry often combines cobalt's durability with silver's conductivity in alloyed contacts to optimize performance under high electrical loads and harsh operating conditions.
Thermal Properties and Heat Management
Cobalt exhibits superior thermal conductivity and higher melting point compared to silver, making it ideal for contact applications requiring efficient heat dissipation and durability under high temperatures. Silver offers excellent electrical conductivity but lower thermal stability and lower oxidation resistance, which can limit its performance in high-heat environments. In heat management, cobalt's ability to maintain structural integrity and thermal performance at elevated temperatures gives it a critical advantage for reliable contact materials.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cobalt mining poses significant environmental challenges, including habitat destruction, high energy consumption, and toxic waste generation, while silver extraction, though also environmentally taxing, generally involves less harmful chemical processes. Cobalt's supply chain faces ethical and sustainability concerns due to concentrated mining activities in conflict regions, which contrasts with silver's more diverse and regulated global mining operations. Recycling rates for silver are higher, enhancing its sustainability profile compared to cobalt, which currently has limited recycling infrastructure and higher reliance on virgin material extraction.
Availability and Supply Chain Considerations
Cobalt is predominantly sourced from the Democratic Republic of Congo, where geopolitical instability and ethical concerns impact its availability and complicate supply chains. Silver enjoys broader global distribution, with substantial production in countries like Mexico, Peru, and China, ensuring more stable supply and less risk of disruption. Supply chain resilience for silver is generally higher due to diversified mining locations and more established recycling processes compared to cobalt.
Choosing the Right Material for Electrical Contacts
Cobalt offers superior wear resistance and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for high-load electrical contacts in harsh environments. Silver provides excellent electrical conductivity and low contact resistance, which is essential for sensitive or low-power applications. Selecting the right material depends on balancing durability needs with conductivity requirements to ensure optimal performance and longevity of electrical contacts.
Infographic: Cobalt vs Silver for Contact
 azmater.com
azmater.com