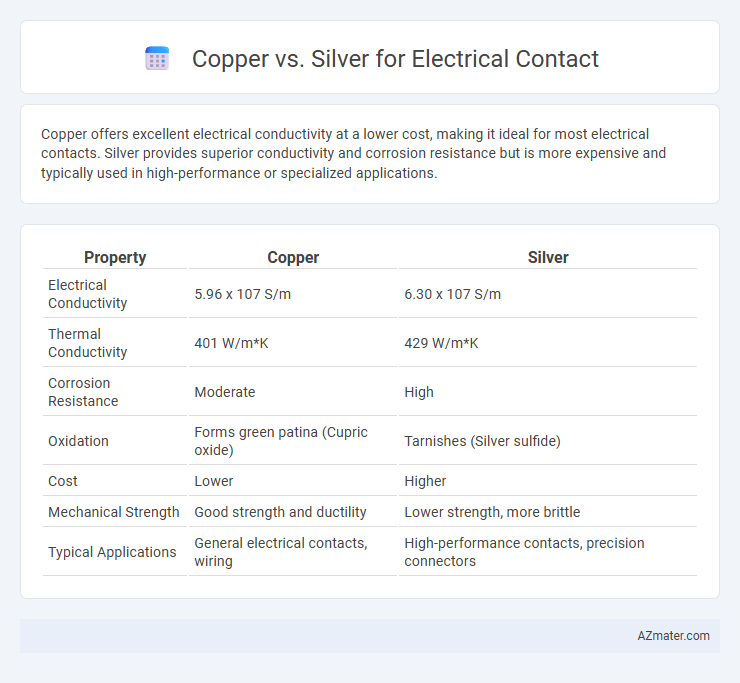
Copper offers excellent electrical conductivity at a lower cost, making it ideal for most electrical contacts. Silver provides superior conductivity and corrosion resistance but is more expensive and typically used in high-performance or specialized applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Copper | Silver |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 5.96 x 107 S/m | 6.30 x 107 S/m |
| Thermal Conductivity | 401 W/m*K | 429 W/m*K |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Oxidation | Forms green patina (Cupric oxide) | Tarnishes (Silver sulfide) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Mechanical Strength | Good strength and ductility | Lower strength, more brittle |
| Typical Applications | General electrical contacts, wiring | High-performance contacts, precision connectors |
Introduction to Electrical Contacts
Electrical contacts are critical components in electronic devices, responsible for establishing and maintaining an efficient conductive path. Copper is widely favored for electrical contacts due to its excellent electrical conductivity, cost-effectiveness, and resistance to corrosion under normal conditions. Silver, however, offers the highest electrical conductivity among metals and superior resistance to oxidation, making it ideal for high-performance or high-reliability applications despite its higher cost.
Overview of Copper and Silver as Conductive Materials
Copper and silver are two of the most efficient conductive materials used in electrical contacts, with silver exhibiting the highest electrical conductivity among all metals, approximately 6.30x10^7 S/m. Copper closely follows, with a conductivity of about 5.96x10^7 S/m, making it an excellent alternative in terms of performance and cost-effectiveness. While silver offers superior conductivity and corrosion resistance, copper's widespread availability and lower price make it the preferred choice for most electrical contact applications.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Copper offers excellent electrical conductivity with a value of approximately 5.96 x 10^7 S/m at room temperature, making it a popular choice for electrical contacts due to its balance of conductivity, cost, and mechanical strength. Silver surpasses copper in electrical conductivity, measured at about 6.30 x 10^7 S/m, providing the highest conductivity of all metals, which enhances performance in critical electrical contacts that require minimal resistance. Despite silver's superior conductivity, copper remains widely used because of its lower cost and better resistance to oxidation, factors important in many electrical applications.
Corrosion Resistance and Oxidation Behavior
Copper exhibits excellent electrical conductivity but is more prone to oxidation and corrosion, forming a greenish patina that can increase contact resistance over time. Silver resists corrosion and oxidation better, maintaining low contact resistance even in harsh environments due to the formation of a stable silver oxide layer. For electrical contacts requiring long-term reliability in oxidative conditions, silver is generally preferred despite its higher cost.
Thermal Conductivity Considerations
Copper's thermal conductivity of approximately 400 W/m*K allows for efficient heat dissipation in electrical contacts, reducing the risk of overheating and contact degradation during high current flow. Silver surpasses copper with one of the highest thermal conductivities at about 430 W/m*K, enhancing thermal management in critical electrical components where minimal resistance and heat buildup are essential. Selecting silver over copper in electrical contacts improves longevity and reliability, especially in applications with rapid thermal cycling and high power density.
Cost and Availability Factors
Copper offers a cost-effective solution for electrical contacts due to its widespread availability and lower market price compared to silver. Silver, despite its superior electrical conductivity, commands a significantly higher price and limited supply, making it less economical for large-scale applications. The choice between copper and silver hinges on balancing budget constraints against performance needs, with copper favored for cost-sensitive projects.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Copper exhibits superior mechanical strength and excellent ductility, making it highly durable under repeated mechanical stress in electrical contacts. Silver, while offering the highest electrical conductivity, is softer and more prone to wear and deformation over time, reducing its mechanical durability. Copper-silver alloys combine copper's mechanical robustness with silver's conductivity, enhancing overall performance and lifespan in demanding electrical contact applications.
Applications in Electrical and Electronic Devices
Copper offers excellent electrical conductivity, thermal stability, and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for electrical contacts in power distribution, motors, and transformers. Silver exhibits superior conductivity and low contact resistance, often used in high-performance electronic devices, switches, and connectors where minimizing signal loss is crucial. Both metals balance conductivity and durability, with copper favored for cost efficiency and silver preferred in applications demanding maximum electrical performance.
Maintenance and Longevity
Copper offers excellent conductivity and durability, making it a reliable choice for electrical contacts with lower maintenance requirements due to its resistance to corrosion. Silver, while boasting superior conductivity, demands more frequent maintenance because it tarnishes easily, which can impair performance over time. Choosing copper ensures longer-lasting contacts with less upkeep, whereas silver contacts require ongoing cleaning to maintain optimal electrical connectivity.
Choosing the Right Material for Electrical Contacts
Copper offers excellent electrical conductivity, making it a preferred choice for most electrical contacts due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of fabrication. Silver boasts the highest electrical conductivity of all metals, providing superior performance in low-resistance connections and high-frequency applications despite its higher cost and susceptibility to tarnish. Selecting between copper and silver for electrical contacts depends on balancing conductivity requirements, budget constraints, and environmental factors such as corrosion resistance and contact durability.
Infographic: Copper vs Silver for Electrical Contact
 azmater.com
azmater.com