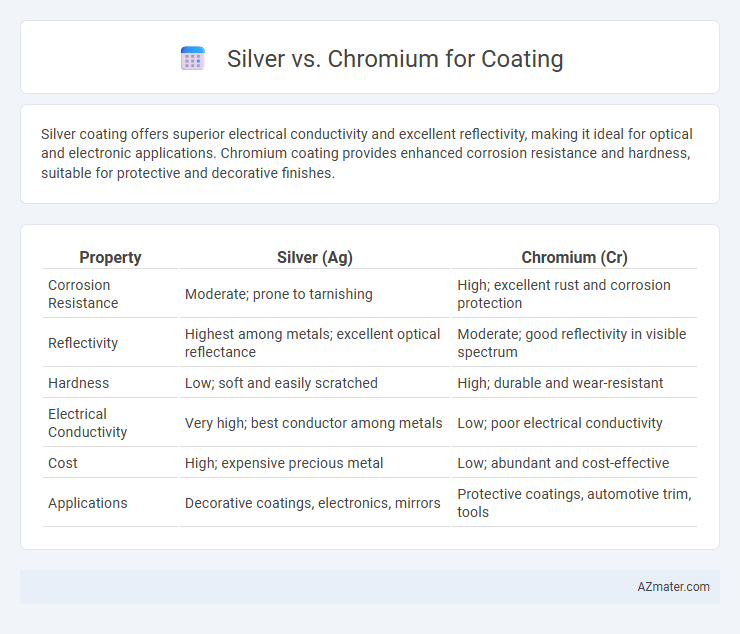
Silver coating offers superior electrical conductivity and excellent reflectivity, making it ideal for optical and electronic applications. Chromium coating provides enhanced corrosion resistance and hardness, suitable for protective and decorative finishes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Silver (Ag) | Chromium (Cr) |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate; prone to tarnishing | High; excellent rust and corrosion protection |
| Reflectivity | Highest among metals; excellent optical reflectance | Moderate; good reflectivity in visible spectrum |
| Hardness | Low; soft and easily scratched | High; durable and wear-resistant |
| Electrical Conductivity | Very high; best conductor among metals | Low; poor electrical conductivity |
| Cost | High; expensive precious metal | Low; abundant and cost-effective |
| Applications | Decorative coatings, electronics, mirrors | Protective coatings, automotive trim, tools |
Introduction: Comparing Silver and Chromium Coatings
Silver coatings offer exceptional electrical conductivity and high thermal reflectivity, making them ideal for electronic and optical applications. Chromium coatings provide superior hardness, corrosion resistance, and wear durability, commonly used in automotive and industrial machinery parts. Comparing these materials highlights silver's excellent conductivity and chromium's mechanical strength for diverse coating needs.
Material Properties: Silver vs Chromium
Silver exhibits superior electrical conductivity and excellent reflectivity, making it ideal for applications requiring efficient electrical contact and high optical performance. Chromium offers exceptional hardness, corrosion resistance, and wear durability, which ensures long-lasting protective coatings in harsh environments. The choice between silver and chromium coatings depends on balancing conductivity and reflectivity against hardness and environmental resilience.
Coating Techniques and Methods
Silver coatings are typically applied using physical vapor deposition (PVD) and electroplating methods, providing excellent conductivity and reflectivity with moderate adhesion. Chromium coatings predominantly utilize electroplating and chemical vapor deposition (CVD), offering exceptional hardness, corrosion resistance, and wear properties essential for industrial applications. Both metals require surface preparation techniques such as cleaning and etching to enhance coating uniformity and durability in their respective applications.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Chromium coatings offer superior corrosion resistance compared to silver, effectively protecting surfaces from rust and oxidation in harsh environments. Silver, while providing excellent electrical conductivity and aesthetic appeal, tends to tarnish and degrade more quickly when exposed to moisture and chemicals. Chromium's hardness and durability make it the preferred choice for industrial applications requiring long-lasting, corrosion-resistant finishes.
Reflectivity and Aesthetic Appeal
Silver outperforms chromium in reflectivity, boasting a reflectance of up to 95%, making it ideal for applications requiring maximum light reflection such as mirrors and optical devices. While chromium offers a highly durable and corrosion-resistant coating with a striking metallic gray finish, its reflectivity typically ranges around 60-70%, which is lower than silver's. The aesthetic appeal of silver is characterized by its bright, shiny, and smooth surface that enhances brightness, whereas chromium provides a modern, industrial look favored in automotive and architectural designs.
Electrical and Thermal Conductivity
Silver exhibits the highest electrical conductivity among metals, approximately 63 x 10^6 S/m, making it exceptionally efficient for electrical coatings in high-performance electronic applications. Its thermal conductivity is also superior, around 429 W/m*K, which enhances heat dissipation in devices requiring efficient thermal management. Chromium, while offering excellent corrosion resistance and hardness, has significantly lower electrical conductivity (~7.9 x 10^6 S/m) and thermal conductivity (~94 W/m*K), limiting its effectiveness where conductive and heat dissipation properties are critical.
Applications in Various Industries
Silver coatings exhibit superior electrical conductivity and antimicrobial properties, making them ideal for electronics, medical devices, and solar panels. Chromium coatings offer exceptional hardness, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal, widely used in automotive parts, decorative finishes, and industrial machinery. The choice between silver and chromium depends on specific industry requirements such as conductivity, durability, and environmental resistance.
Cost Analysis: Silver vs Chromium
Silver coating typically costs more than chromium due to the higher price of raw silver and its more complex application process. Chromium coatings offer a cost-effective solution with excellent corrosion resistance and durability, making them favorable for large-scale industrial applications. The choice between silver and chromium depends on balancing budget constraints against desired properties such as conductivity and aesthetic appeal.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Silver coatings offer excellent antimicrobial properties with relatively low toxicity, making them safer for environmental and human health compared to chromium coatings. Chromium, especially hexavalent chromium, poses significant environmental hazards and health risks due to its carcinogenicity and persistence in ecosystems. Choosing silver over chromium for coatings reduces hazardous waste generation and lowers potential exposure to harmful substances.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Coating Material
Silver offers superior electrical and thermal conductivity, making it ideal for applications requiring enhanced performance and corrosion resistance. Chromium provides excellent hardness and wear resistance, suited for decorative and protective coatings with high durability. Selecting between silver and chromium depends on prioritizing conductivity and corrosion protection versus hardness and wear resistance for the specific application.
Infographic: Silver vs Chromium for Coating
 azmater.com
azmater.com