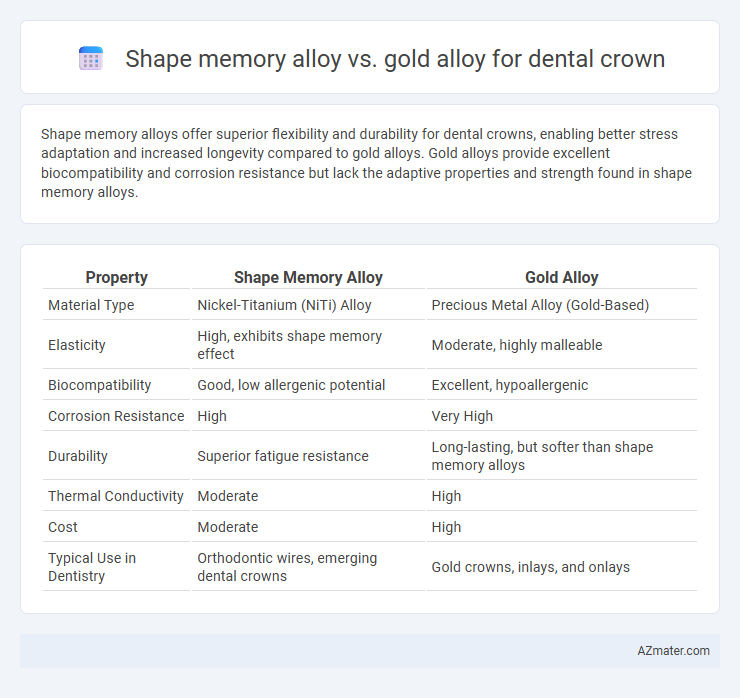
Shape memory alloys offer superior flexibility and durability for dental crowns, enabling better stress adaptation and increased longevity compared to gold alloys. Gold alloys provide excellent biocompatibility and corrosion resistance but lack the adaptive properties and strength found in shape memory alloys.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Shape Memory Alloy | Gold Alloy |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Nickel-Titanium (NiTi) Alloy | Precious Metal Alloy (Gold-Based) |
| Elasticity | High, exhibits shape memory effect | Moderate, highly malleable |
| Biocompatibility | Good, low allergenic potential | Excellent, hypoallergenic |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | Very High |
| Durability | Superior fatigue resistance | Long-lasting, but softer than shape memory alloys |
| Thermal Conductivity | Moderate | High |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
| Typical Use in Dentistry | Orthodontic wires, emerging dental crowns | Gold crowns, inlays, and onlays |
Introduction to Dental Crown Materials
Dental crown materials primarily include Shape Memory Alloys (SMAs) and Gold Alloys, each offering distinct benefits in restorative dentistry. Shape Memory Alloys, known for their unique ability to return to a pre-defined shape upon heating, provide excellent flexibility and durability under masticatory forces. Gold Alloys are favored for their superior biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and long-term wear properties, making them a traditional choice for dental crowns.
Overview of Shape Memory Alloys in Dentistry
Shape memory alloys (SMAs), particularly nickel-titanium (NiTi) alloys, are increasingly utilized in dentistry due to their unique properties of superelasticity and shape memory effect, allowing for improved adaptation and durability of dental crowns. These alloys provide enhanced flexibility and stress distribution compared to traditional gold alloys, which primarily offer excellent biocompatibility and corrosion resistance but lack the mechanical adaptability of SMAs. The integration of SMAs in dental crowns ultimately supports better clinical outcomes by reducing crown failure rates and improving patient comfort.
Gold Alloys: Traditional Choice for Dental Crowns
Gold alloys have long been the traditional choice for dental crowns due to their exceptional biocompatibility, durability, and resistance to wear and corrosion. These alloys provide a precise fit with minimal margin gaps, reducing the risk of decay and gum irritation compared to other materials like shape memory alloys. Their aesthetic limitations are often outweighed by their proven longevity and compatibility with natural tooth structures.
Biocompatibility: Shape Memory Alloy vs Gold Alloy
Shape memory alloys (SMAs) used in dental crowns demonstrate superior biocompatibility due to their corrosion resistance and ability to adapt to dynamic oral environments without releasing harmful ions. Gold alloys have long been favored for their excellent biocompatibility, minimal allergenicity, and noble metal properties that resist oxidation and corrosion in the oral cavity. Both materials offer reliable biocompatibility, but SMAs provide added benefits in mechanical adaptability while gold alloys ensure stable, inert performance with minimal tissue irritation.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Shape memory alloys, such as nickel-titanium, exhibit superior elasticity and fatigue resistance compared to traditional gold alloys, enhancing their performance under repeated masticatory loads. Gold alloys offer excellent corrosion resistance and biocompatibility but have lower tensile strength and wear resistance, which may reduce crown longevity in high-stress areas. The enhanced mechanical properties of shape memory alloys contribute to improved durability and resistance to deformation, making them advantageous for dental crowns subjected to dynamic oral environments.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Shape memory alloys exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to gold alloys in dental crowns, due to their titanium-based composition which forms a stable oxide layer preventing degradation. Gold alloys, while biocompatible and corrosion-resistant in oral environments, can suffer from wear and surface deterioration over extended periods. The enhanced corrosion resistance of shape memory alloys contributes to increased longevity and durability of dental crowns in harsh oral conditions.
Esthetics and Color Compatibility
Shape memory alloys in dental crowns offer superior durability but often lack the natural luster and color matching of gold alloys, which closely mimic natural tooth hues with excellent biocompatibility. Gold alloys provide a warm, metallic tone that blends seamlessly with natural teeth, enhancing esthetic appeal and color compatibility for anterior restorations. The inherent color flexibility of gold alloys ensures superior shade matching compared to the typically grayish or metallic tint of shape memory alloys, making gold the preferred choice for visible crowns.
Cost Comparison: Shape Memory Alloy vs Gold Alloy
Shape memory alloys for dental crowns typically cost significantly less than gold alloys due to the lower price of base metals like nickel-titanium compared to precious metals. Gold alloy crowns can range from $800 to $2,500 per tooth, reflecting the high material and fabrication costs, whereas shape memory alloy crowns generally fall between $300 and $700. The substantial cost difference makes shape memory alloys a more budget-friendly option without compromising essential durability and biocompatibility.
Clinical Performance and Patient Outcomes
Shape memory alloys (SMAs) in dental crowns offer superior flexibility and biocompatibility, reducing the risk of crown fracture and improving patient comfort compared to gold alloys. Gold alloys remain the gold standard for longevity and corrosion resistance, with excellent marginal adaptation minimizing secondary caries risk. Clinical studies reveal SMAs enhance periodontal health due to their precise fit and reduced plaque accumulation, while gold alloys excel in durability and occlusal stability over extended use.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Alloy for Dental Crowns
Shape memory alloys offer exceptional flexibility and durability, making them ideal for patients requiring crowns that adapt to dynamic oral conditions, while gold alloys provide superior biocompatibility and corrosion resistance, ensuring long-term stability and minimal wear. Clinical outcomes favor gold alloys for their proven longevity and minimal allergic reactions, whereas shape memory alloys enhance comfort in cases demanding mechanical adaptability. Selecting the appropriate alloy depends on patient-specific factors such as oral environment, aesthetic preferences, and functional demands, with gold alloys remaining the gold standard for traditional dental restorations.
Infographic: Shape memory alloy vs Gold alloy for Dental crown
 azmater.com
azmater.com