Tungsten offers superior thermal conductivity and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-temperature capacitor applications. Tantalum provides excellent capacitance per volume and corrosion resistance, favoring miniaturized capacitors with stable electrical performance.
Table of Comparison
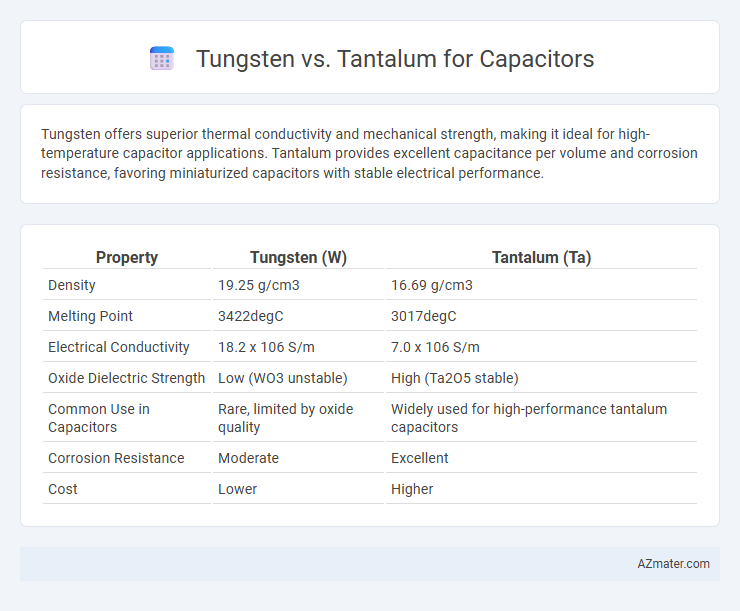
| Property | Tungsten (W) | Tantalum (Ta) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 19.25 g/cm3 | 16.69 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 3422degC | 3017degC |
| Electrical Conductivity | 18.2 x 106 S/m | 7.0 x 106 S/m |
| Oxide Dielectric Strength | Low (WO3 unstable) | High (Ta2O5 stable) |
| Common Use in Capacitors | Rare, limited by oxide quality | Widely used for high-performance tantalum capacitors |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Capacitor Materials
Tungsten and tantalum are critical materials in capacitor manufacturing, each offering distinct electrical properties suitable for different applications. Tungsten capacitors provide high thermal stability and mechanical strength, ideal for high-temperature environments, while tantalum capacitors excel in volumetric efficiency and reliability due to their ability to form a stable oxide layer. The choice between tungsten and tantalum depends on factors such as capacitance requirements, operational voltage, and long-term durability in electronic circuits.
Properties of Tungsten and Tantalum
Tungsten exhibits exceptional hardness, high melting point (3422degC), and excellent electrical conductivity, making it suitable for capacitors requiring durability and thermal stability. Tantalum, valued for its high capacitance per volume and superior corrosion resistance, operates effectively at lower voltages with excellent reliability in electrolytic capacitors. The density of tungsten (19.25 g/cm3) exceeds that of tantalum (16.69 g/cm3), influencing the size-to-performance ratio in capacitor design.
Electrical Performance Comparison
Tungsten capacitors exhibit superior thermal stability and higher melting points, enabling efficient performance under extreme temperature conditions compared to tantalum capacitors. Tantalum capacitors offer lower equivalent series resistance (ESR) and higher capacitance per volume, which results in better frequency response and energy efficiency for high-frequency applications. While tungsten provides enhanced durability and tolerance to electrical surges, tantalum excels in low-voltage, high-capacitance scenarios, making each material optimal for specific electrical performance requirements.
Capacitance and Voltage Ratings
Tungsten capacitors typically offer moderate capacitance values with high stability but have lower voltage ratings compared to tantalum capacitors, which provide higher capacitance in a smaller volume and can handle higher voltage levels. Tantalum capacitors are preferred for applications requiring compact size and high voltage endurance, often supporting voltages up to 50V or more, whereas tungsten capacitors are more common in niche applications with voltage ratings generally below 20V. The dielectric properties of tantalum oxide allow for greater capacitance density, making tantalum an optimal choice for high capacitance and high voltage requirements in electronic circuits.
Reliability and Stability Factors
Tungsten capacitors exhibit superior thermal conductivity and resistance to corrosion, enhancing reliability under high-temperature conditions and ensuring long-term stability. Tantalum capacitors offer excellent volumetric efficiency and stable capacitance but are susceptible to failure from voltage spikes due to their sensitivity to surge currents. The choice between tungsten and tantalum capacitors depends on the specific application requirements, with tungsten preferred for rugged environments requiring durability and tantalum favored for compact designs demanding consistent performance.
Size and Miniaturization Capabilities
Tungsten capacitors generally offer larger size footprints compared to tantalum capacitors due to their material density and construction, limiting their miniaturization capabilities. Tantalum capacitors excel in size reduction, enabling higher capacitance in smaller volumes thanks to their ability to form thin anodic oxide layers and higher volumetric efficiency. This makes tantalum capacitors the preferred choice in compact electronics where space-saving and high capacitance are critical.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Tungsten capacitors generally offer a lower cost due to the metal's greater abundance and less complex extraction process, making them more suitable for budget-conscious applications. Tantalum capacitors, while typically more expensive, provide superior performance with higher capacitance per volume and better stability, which justifies their premium price in high-reliability markets. Market availability favors tungsten as global tantalum supplies face geopolitical risks and stringent mining regulations, restricting tantalum's consistent supply and driving up prices.
Applications in Electronics
Tungsten and tantalum capacitors serve distinct roles in electronics, with tantalum capacitors favored for their high capacitance per volume and reliability in portable devices like smartphones and medical implants. Tungsten capacitors, though less common, offer superior thermal stability and are used in high-temperature or high-frequency applications such as aerospace electronics and power systems. Choosing between tungsten and tantalum capacitors depends on specific performance requirements, environmental conditions, and cost considerations in electronic circuit design.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Tungsten capacitors are favored for their recyclability and lower environmental impact due to the abundance of tungsten and less toxic processing methods compared to tantalum. Tantalum capacitors pose higher safety risks as they are prone to catastrophic failure and thermal runaway when exposed to voltage spikes or overheating, potentially causing fires. Environmental concerns with tantalum include limited supply and unethical mining practices, making tungsten a more sustainable and safer alternative in capacitor manufacturing.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Tungsten and Tantalum Capacitors
Tantalum capacitors offer superior volumetric efficiency, higher capacitance per volume, and better frequency response, making them ideal for miniaturized, high-performance electronic devices. Tungsten capacitors provide enhanced durability, thermal stability, and greater tolerance to surge currents, suitable for harsh environments and power applications. Selecting between tungsten and tantalum capacitors depends on specific application requirements regarding size, performance, temperature range, and cost considerations.
Infographic: Tungsten vs Tantalum for Capacitor
 azmater.com
azmater.com