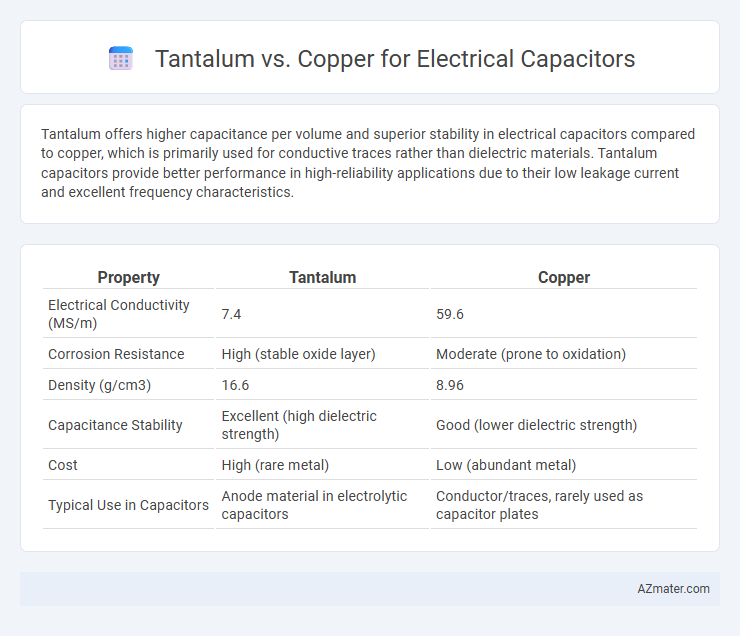
Tantalum offers higher capacitance per volume and superior stability in electrical capacitors compared to copper, which is primarily used for conductive traces rather than dielectric materials. Tantalum capacitors provide better performance in high-reliability applications due to their low leakage current and excellent frequency characteristics.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tantalum | Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity (MS/m) | 7.4 | 59.6 |
| Corrosion Resistance | High (stable oxide layer) | Moderate (prone to oxidation) |
| Density (g/cm3) | 16.6 | 8.96 |
| Capacitance Stability | Excellent (high dielectric strength) | Good (lower dielectric strength) |
| Cost | High (rare metal) | Low (abundant metal) |
| Typical Use in Capacitors | Anode material in electrolytic capacitors | Conductor/traces, rarely used as capacitor plates |
Introduction to Electrical Capacitor Materials
Tantalum and copper serve distinct roles in electrical capacitor manufacturing, with tantalum primarily used for its stable oxide layer that functions as a high-performance dielectric material. Tantalum capacitors offer high capacitance per volume and excellent reliability under temperature and voltage stress, which contrasts with copper's primary use as a conductive element in capacitor leads and electrodes. Material selection impacts capacitor efficiency, energy density, and lifespan, making tantalum crucial in applications demanding compact size and long-term stability.
Key Properties of Tantalum and Copper
Tantalum exhibits high capacitance per volume, excellent stability, and superior corrosion resistance, making it ideal for compact, reliable capacitors in high-performance electronics. Copper offers exceptional electrical conductivity and thermal management, enhancing current-carrying capacity and heat dissipation in capacitor leads and circuitry. Combining tantalum's dielectric properties with copper's conductive strengths optimizes capacitor efficiency and longevity in demanding electrical applications.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Tantalum capacitors exhibit lower electrical conductivity compared to copper, as tantalum's conductivity is approximately 7.4 million S/m, while copper boasts a significantly higher conductivity of 59.6 million S/m. This difference impacts the internal resistance and efficiency of capacitors, where copper's superior conductivity reduces energy loss and improves performance at high frequencies. However, tantalum capacitors provide advantages in stability and size despite the lower electrical conductivity relative to copper.
Capacitance Performance Differences
Tantalum capacitors exhibit higher capacitance per volume and better stability under varying temperatures compared to copper-based capacitors, which typically rely on copper foil for electrodes but use different dielectric materials. The intrinsic properties of tantalum oxide dielectric allow for superior volumetric efficiency and lower equivalent series resistance (ESR), enhancing performance in high-frequency applications. Copper capacitors, while offering good conductivity, generally have lower capacitance density and higher loss factors, limiting their use in miniaturized, high-precision circuits.
Thermal Stability and Reliability
Tantalum capacitors exhibit superior thermal stability compared to copper-based capacitors due to their oxide layer, which maintains performance at higher temperatures up to 125degC and beyond. Copper is primarily used as a conductor in capacitor terminals rather than the dielectric material; its thermal conductivity aids heat dissipation but does not directly enhance capacitor reliability under thermal stress. Tantalum capacitors provide higher long-term reliability in high-temperature environments, making them ideal for applications requiring stable capacitance and low equivalent series resistance (ESR) over extended periods.
Size and Weight Considerations
Tantalum capacitors offer higher capacitance per volume compared to copper-based electrolytic capacitors, resulting in smaller and lighter components ideal for compact electronic devices. The high volumetric efficiency of tantalum enables miniaturization without sacrificing performance, which is crucial in portable and aerospace applications. Copper capacitors, while effective for power delivery, tend to be bulkier and heavier, limiting their use in size-sensitive designs.
Cost and Availability of Tantalum vs Copper
Tantalum capacitors are generally more expensive than copper capacitors due to the scarcity and complex extraction process of tantalum ore, primarily sourced from regions with limited mining infrastructure. Copper, abundant and widely distributed globally, offers significantly lower material costs and better availability, making it a preferred choice for large-scale capacitor production. The higher price and limited supply of tantalum impact its use mostly in specialized applications requiring high capacitance and stability, while copper caters to cost-sensitive, high-volume uses.
Applications in Modern Electronics
Tantalum capacitors are preferred in modern electronics for their high capacitance per volume, exceptional stability, and reliability in low-voltage applications such as smartphones, medical devices, and aerospace systems. Copper capacitors, while less common as primary capacitor materials, are essential in high-frequency circuitry and power distribution due to their excellent electrical conductivity and thermal management capabilities. The choice between tantalum and copper-based components depends on specific application requirements including voltage rating, size constraints, and operational environment.
Environmental and Safety Concerns
Tantalum capacitors offer high capacitance in a compact size but pose significant environmental risks due to the mining of tantalum, which is linked to habitat destruction and conflict minerals. Copper, while less energy-dense for capacitors, is more abundant and recyclable, reducing long-term environmental impact and resource depletion concerns. From a safety standpoint, tantalum capacitors can fail catastrophically if exposed to voltage surges, whereas copper-based capacitors typically exhibit safer failure modes with lower risk of fire or explosion.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material
Tantalum capacitors offer higher capacitance per volume and better stability at high temperatures compared to copper-based capacitors, making them ideal for compact and high-performance applications. Copper capacitors generally provide lower cost and excellent conductivity but may lack the durability and capacitance density required for advanced electronic devices. Selecting the right material depends on balancing cost, capacitance needs, temperature tolerance, and application-specific reliability requirements.
Infographic: Tantalum vs Copper for Electrical Capacitor
 azmater.com
azmater.com