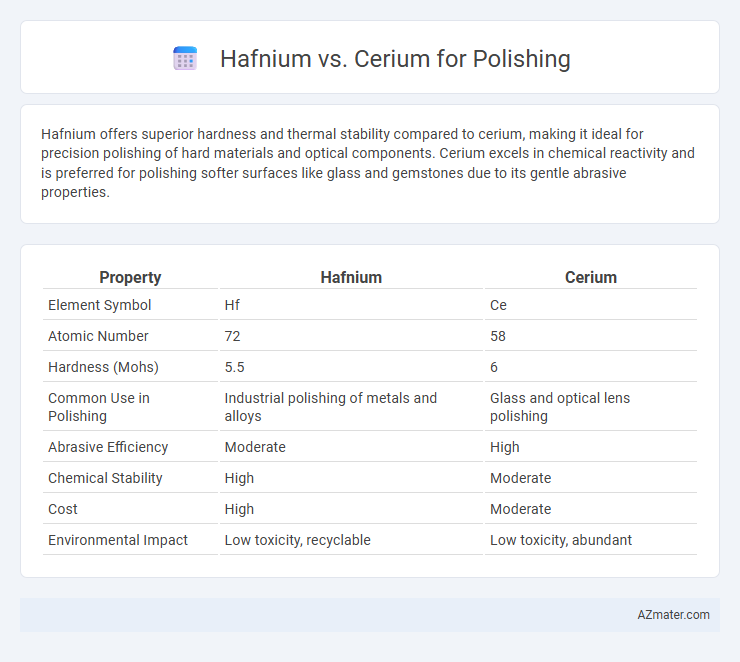
Hafnium offers superior hardness and thermal stability compared to cerium, making it ideal for precision polishing of hard materials and optical components. Cerium excels in chemical reactivity and is preferred for polishing softer surfaces like glass and gemstones due to its gentle abrasive properties.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hafnium | Cerium |
|---|---|---|
| Element Symbol | Hf | Ce |
| Atomic Number | 72 | 58 |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 5.5 | 6 |
| Common Use in Polishing | Industrial polishing of metals and alloys | Glass and optical lens polishing |
| Abrasive Efficiency | Moderate | High |
| Chemical Stability | High | Moderate |
| Cost | High | Moderate |
| Environmental Impact | Low toxicity, recyclable | Low toxicity, abundant |
Introduction to Polishing Applications
Hafnium and Cerium are both used in polishing applications, with Cerium oxide being the industry standard for optical-grade glass and semiconductor wafers due to its exceptional hardness and chemical reactivity. Hafnium oxide offers unique advantages in polishing hard materials, providing enhanced surface smoothness and precision in electronics and aerospace components. The choice between Hafnium and Cerium depends on the material's hardness and desired finish quality in precision polishing processes.
Overview of Hafnium and Cerium
Hafnium and cerium are both critical materials in polishing applications, with Hafnium prized for its high melting point and excellent mechanical stability, making it ideal for precise surface finishing. Cerium oxide is widely known for its chemical-mechanical polishing (CMP) capabilities, particularly in semiconductor and optical industries due to its ability to remove microscopic layers without damaging substrates. The choice between Hafnium and Cerium depends on the required polishing precision, material compatibility, and specific industry standards.
Chemical Properties Comparison
Hafnium exhibits exceptional chemical stability and resistance to oxidation, making it highly effective for polishing applications requiring durability and precision. Cerium, known for its high reactivity and ability to form cerium oxide (CeO2), excels in abrasive polishing due to its catalytic surface properties that enhance material removal rates. The differing chemical properties--hafnium's inertness versus cerium's reactive oxide formation--define their specific roles in polishing processes, with hafnium suitable for fine finishing and cerium favored for aggressive surface conditioning.
Abrasive Performance Differences
Hafnium exhibits higher hardness and thermal stability compared to cerium, resulting in superior abrasive performance for polishing applications, especially on hard materials like silicon wafers and optical lenses. Cerium, known for its unique chemical-mechanical polishing properties, excels in removing surface defects and achieving ultra-smooth finishes on softer substrates but may cause surface scratches on harder materials. The choice between hafnium and cerium abrasives depends on balancing hardness, chemical reactivity, and specific surface finish requirements in semiconductor or optical manufacturing.
Surface Finish Quality
Hafnium offers superior surface finish quality in polishing applications due to its ability to produce ultra-smooth and defect-free surfaces, making it ideal for precision optics and semiconductor wafers. Its fine abrasive particles enable consistent material removal rates while minimizing subsurface damage compared to cerium, which tends to leave micro-scratches and slight surface irregularities. The chemical stability and hardness of hafnium contribute to enhanced polishing uniformity and longer-lasting slurry performance versus cerium-based compounds.
Cost and Availability
Hafnium is significantly more expensive and less abundant than Cerium, making Cerium the preferred choice for polishing applications due to its cost-effectiveness and widespread availability. Cerium oxide, commonly used in glass and semiconductor polishing, is readily sourced from rare-earth minerals, while Hafnium, being a rare transition metal, has limited supply mainly tied to zirconium ores. The cost difference directly impacts industrial usage, with Cerium dominating the market for polishing powders due to budget constraints and ease of procurement.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Hafnium and cerium both serve as polishing agents, but cerium oxide is widely favored for its lower environmental impact and safer handling properties. Cerium oxide is less toxic and more environmentally benign compared to hafnium compounds, which can pose greater health risks due to their heavy-metal characteristics. The use of cerium reduces concerns related to hazardous waste disposal and occupational exposure in polishing applications.
Common Industrial Uses
Hafnium is commonly used in high-precision polishing for aerospace components and nuclear reactors due to its excellent resistance to corrosion and high melting point. Cerium oxide, widely used in glass, semiconductor, and automotive industries, offers superior abrasive qualities for polishing optical lenses and flat glass surfaces. Both materials serve critical roles in industrial polishing, with hafnium favored for metal finishing and cerium oxide preferred for glass and ceramic applications.
User Experiences and Case Studies
Users report that hafnium oxide yields superior surface finishes with minimal scratches compared to cerium oxide, especially on hard materials like sapphire and silicon wafers. Case studies highlight hafnium's enhanced polishing rate and reduced residue, resulting in higher optical clarity and smoother surfaces in semiconductor and optics industries. Feedback notes cerium's affordability but lower efficiency and potential for micro-scratching when used on ultra-hard substrates, making hafnium a preferred choice for precision polishing applications.
Final Recommendation and Conclusion
Hafnium offers superior hardness and chemical stability compared to cerium, making it more effective for precision polishing applications requiring fine surface finishes. Cerium's abrasive properties and lower cost make it a popular choice for general polishing tasks but may leave micro-scratches on ultra-smooth surfaces. For high-precision polishing where surface integrity is critical, hafnium-based abrasives provide a more reliable and durable solution.
Infographic: Hafnium vs Cerium for Polishing
 azmater.com
azmater.com