Silver offers higher durability and resistance to corrosion compared to bronze, making it ideal for fine, detailed sculptures. Bronze, favored for its strength and classic patina, provides greater affordability and longevity in outdoor installations.
Table of Comparison
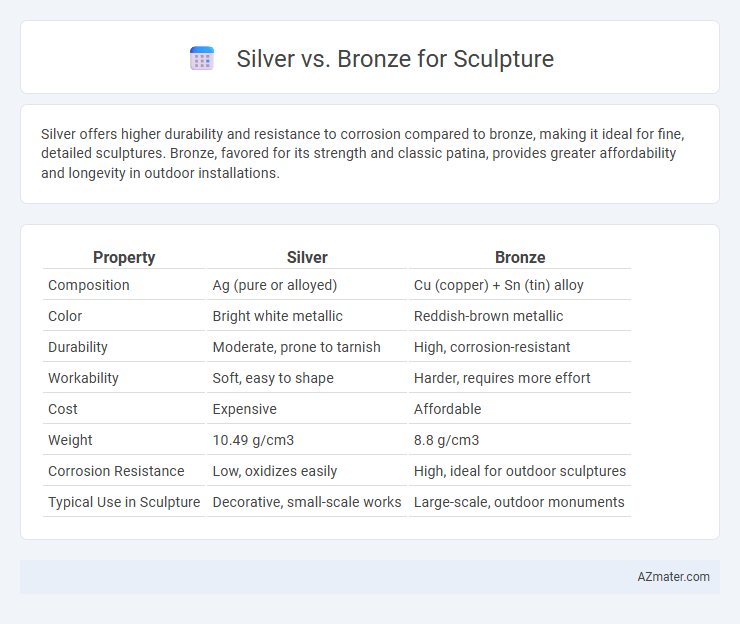
| Property | Silver | Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Ag (pure or alloyed) | Cu (copper) + Sn (tin) alloy |
| Color | Bright white metallic | Reddish-brown metallic |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to tarnish | High, corrosion-resistant |
| Workability | Soft, easy to shape | Harder, requires more effort |
| Cost | Expensive | Affordable |
| Weight | 10.49 g/cm3 | 8.8 g/cm3 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Low, oxidizes easily | High, ideal for outdoor sculptures |
| Typical Use in Sculpture | Decorative, small-scale works | Large-scale, outdoor monuments |
Introduction to Sculpture Materials: Silver and Bronze
Silver and bronze are prominent materials in sculpture, each offering unique aesthetic and physical properties. Bronze, an alloy primarily of copper and tin, is renowned for its durability, corrosion resistance, and warm metallic patina, making it ideal for outdoor sculptures and detailed casting. Silver, a precious metal known for its bright luster and malleability, is often favored for fine, intricate works and smaller-scale sculptures, though it is softer and less weather-resistant compared to bronze.
Historical Significance of Silver and Bronze in Sculpture
Bronze has been the primary metal for sculptures since ancient times due to its durability and ability to capture fine details in casting, exemplified in classical Greek and Roman artworks. Silver, while less commonly used for large sculptures, holds significant historical value in smaller figurines and decorative art because of its luster and association with wealth and status in various cultures. The contrast between bronze's structural strength and silver's ornamental prestige highlights their distinct roles and influences throughout art history.
Physical Properties: Strength, Malleability, and Durability
Silver offers high malleability, allowing artists to create intricate details with ease, but it is softer and less durable compared to bronze, making it prone to scratches and deformation over time. Bronze, an alloy of copper and tin, provides superior strength and durability, resisting corrosion and wear, ideal for outdoor sculptures exposed to environmental elements. The combination of bronze's toughness and moderate malleability makes it preferred for sculptures requiring structural integrity and longevity.
Aesthetic Qualities: Color, Luster, and Patina
Silver sculptures exhibit a bright, reflective white-metallic color with a high luster that enhances fine details and creates a striking visual impact. Bronze offers a warm, rich brown tone that develops a distinctive green or brown patina over time, adding depth and historical character to the artwork. The evolving patina on bronze sculptures provides dynamic surface textures, while silver maintains its polished sheen, making each metal ideal for different aesthetic preferences in sculptural art.
Techniques for Sculpting with Silver vs Bronze
Sculpting with silver requires precise techniques such as lost-wax casting and fine chasing to highlight its reflective surface and delicate details, benefiting from silver's softer malleability. Bronze sculpting employs sand casting and patination processes, leveraging its durability and strength for larger, more complex forms with varied textures. The choice of metal influences tool selection, heating methods, and finishing processes critical to achieving the desired artistic effect in silver versus bronze sculptures.
Cost and Accessibility of Silver and Bronze
Bronze remains more cost-effective than silver for sculpture due to its lower price per pound and greater availability, making it a preferred material for large-scale or multiple works. Silver, while offering a unique luster and prestigious appearance, is significantly more expensive and less accessible, limiting its use primarily to small, high-value pieces or detailed decorative sculpture. Artists often choose bronze for durability and affordability, whereas silver's high cost restricts its application in large or mass-produced sculptures.
Longevity and Preservation of Sculptures
Silver sculptures exhibit superior longevity due to their resistance to corrosion and tarnish when properly maintained, making them ideal for long-term preservation. Bronze, while highly durable and favored for outdoor sculptures, can develop a patina over time, which may protect the metal but also requires careful conservation to prevent degradation. Preservation efforts for both materials depend on environmental conditions, but silver typically demands more controlled environments to maintain its original luster and structural integrity.
Environmental Impact of Using Silver and Bronze
Silver extraction involves extensive mining that releases toxic chemicals like cyanide and mercury, causing significant soil and water contamination. Bronze, primarily composed of copper and tin, also results from mining activities, but copper's environmental impact is more severe due to energy-intensive extraction and harmful acid mine drainage. Recycling bronze offers notable environmental benefits, reducing the need for fresh mining and lowering greenhouse gas emissions compared to the more chemically intensive processing required for silver.
Suitability for Different Styles and Sizes
Silver offers a smooth, lustrous surface ideal for intricate, delicate sculptures and smaller, detailed works due to its malleability and fine grain. Bronze, with its robust strength and excellent tensile properties, suits larger, outdoor sculptures and dynamic, expressive styles that demand durability and weather resistance. The choice between silver and bronze hinges on the desired scale, style complexity, and environmental exposure of the sculpture.
Choosing Between Silver and Bronze: Artist and Collector Perspectives
Silver offers a lustrous, reflective finish favored by artists seeking intricate detail and a modern aesthetic in sculpture, while bronze provides durability and a warm, traditional patina that appeals to collectors valuing timelessness and historical significance. Artists prioritize silver for its malleability and ability to capture fine textures, whereas bronze's robustness ensures longevity and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for outdoor displays. Collectors often choose bronze for its established market value and classic appeal, while silver sculptures attract those interested in contemporary works and investment potential due to silver's intrinsic metal value.
Infographic: Silver vs Bronze for Sculpture
 azmater.com
azmater.com