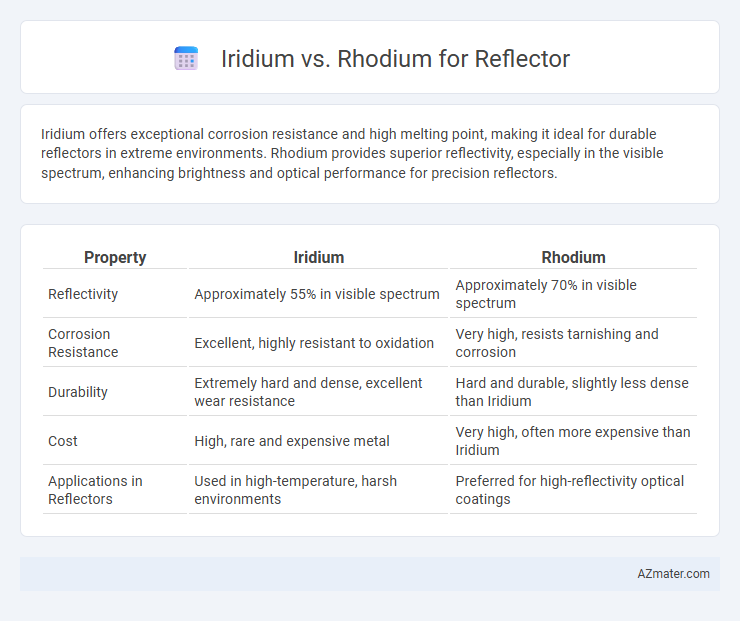
Iridium offers exceptional corrosion resistance and high melting point, making it ideal for durable reflectors in extreme environments. Rhodium provides superior reflectivity, especially in the visible spectrum, enhancing brightness and optical performance for precision reflectors.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Iridium | Rhodium |
|---|---|---|
| Reflectivity | Approximately 55% in visible spectrum | Approximately 70% in visible spectrum |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, highly resistant to oxidation | Very high, resists tarnishing and corrosion |
| Durability | Extremely hard and dense, excellent wear resistance | Hard and durable, slightly less dense than Iridium |
| Cost | High, rare and expensive metal | Very high, often more expensive than Iridium |
| Applications in Reflectors | Used in high-temperature, harsh environments | Preferred for high-reflectivity optical coatings |
Introduction to Iridium and Rhodium Reflectors
Iridium and rhodium reflectors possess unique optical and chemical properties, making them essential in high-performance lighting and optical devices. Iridium reflectors exhibit exceptional corrosion resistance and high reflectivity in the infrared spectrum, while rhodium reflectors are prized for their superior reflectance in the visible light range and excellent durability. Both metals provide efficient light reflection and thermal stability, influencing their selection in precision optics and specialized illumination applications.
Chemical and Physical Properties Comparison
Iridium exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance and high melting point (2446degC), making it ideal for reflector coatings that require durability in extreme environments. Rhodium, with a melting point of 1964degC and superior reflectivity, excels in applications demanding high optical performance but offers less chemical stability than iridium. Both metals possess excellent hardness and electrical conductivity, but iridium's superior chemical inertness ensures longer lifespan under harsh chemical exposures.
Reflective Efficiency: Iridium vs Rhodium
Rhodium exhibits superior reflective efficiency compared to iridium, with reflectance rates often exceeding 85% in the visible spectrum, making it highly effective for reflector applications. Iridium, while valued for its durability and high melting point, typically reflects around 50-60%, which is significantly lower than rhodium's performance. The enhanced reflective efficiency of rhodium ensures optimal light output and energy conservation in optical devices and lighting fixtures.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Iridium offers exceptional durability and outstanding corrosion resistance, making it ideal for reflector applications exposed to harsh environments and high temperatures. Rhodium is also highly corrosion-resistant and provides excellent reflectivity but is generally less durable than iridium under extreme conditions. For long-lasting performance and superior resistance to oxidation, iridium is often the preferred choice in reflective coatings.
Thermal Stability and Heat Tolerance
Iridium exhibits exceptional thermal stability with a melting point of 2446degC, making it highly resistant to heat-induced deformation in reflector applications. Rhodium, melting at 1964degC, offers good heat tolerance but is more prone to oxidation and structural changes at elevated temperatures compared to iridium. For reflectors exposed to extreme thermal conditions, iridium's superior heat resistance ensures longer lifespan and consistent performance.
Cost Analysis: Iridium vs Rhodium
Iridium reflectors generally cost less than rhodium due to the relative abundance and lower extraction costs of iridium, impacting overall project budgets significantly. Rhodium's higher price stems from its rarity and more complex refining process, making it a premium choice for applications demanding exceptional reflectivity and corrosion resistance. When budgeting for reflectors, the cost premium of rhodium must be balanced against its performance benefits to determine the most cost-effective option.
Common Applications in Reflector Technology
Iridium and rhodium are both used in reflector technology due to their high reflectivity and resistance to corrosion, with iridium commonly employed in high-temperature environments such as aerospace and specialized optical devices. Rhodium is favored for automotive headlight reflectors and architectural lighting because of its superior brightness and durability under moderate heat conditions. Reflector coatings leveraging iridium excel in infrared and ultraviolet applications, while rhodium's excellent visible light reflectance makes it ideal for decorative and functional lighting solutions.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Iridium and rhodium both offer high corrosion resistance and durability for reflector coatings, but rhodium is preferred environmentally due to lower toxicity and easier recycling processes. Iridium's mining and refining generate more hazardous waste, raising environmental concerns and requiring stricter safety protocols for workers. Rhodium's inertness and reduced reactivity also minimize health risks during manufacturing and application, making it a safer choice for reflective surfaces.
Availability and Manufacturing Challenges
Iridium reflectors offer higher corrosion resistance but face limited availability due to scarce natural deposits and complex extraction processes. Rhodium, although rarer and more expensive, provides superior reflectance and is often sourced through recycling from automotive catalytic converters, presenting manufacturing challenges related to purity and consistency. Both metals require specialized manufacturing techniques to address brittleness and high melting points, impacting production scalability and cost efficiency.
Choosing the Right Metal for Your Reflector Needs
Iridium and rhodium both offer exceptional reflectivity and durability, making them prime choices for reflectors in high-precision applications. Iridium excels in high-temperature resistance and corrosion durability, ideal for harsh environments, while rhodium provides superior brightness and oxidation resistance, perfect for enhanced optical clarity. Selecting the right metal depends on the specific requirements of durability, reflectance, and environmental exposure to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Iridium vs Rhodium for Reflector
 azmater.com
azmater.com