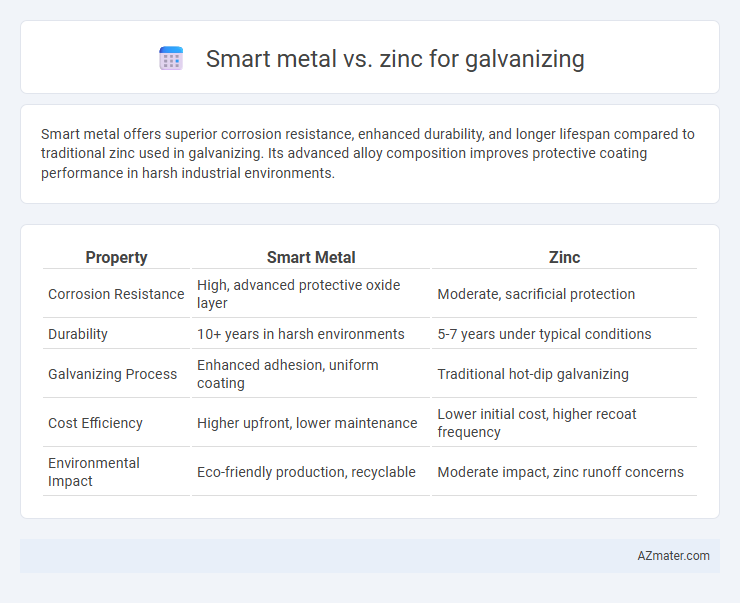
Smart metal offers superior corrosion resistance, enhanced durability, and longer lifespan compared to traditional zinc used in galvanizing. Its advanced alloy composition improves protective coating performance in harsh industrial environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Smart Metal | Zinc |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | High, advanced protective oxide layer | Moderate, sacrificial protection |
| Durability | 10+ years in harsh environments | 5-7 years under typical conditions |
| Galvanizing Process | Enhanced adhesion, uniform coating | Traditional hot-dip galvanizing |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher upfront, lower maintenance | Lower initial cost, higher recoat frequency |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly production, recyclable | Moderate impact, zinc runoff concerns |
Introduction to Galvanizing: Purpose and Processes
Galvanizing involves coating iron or steel with a protective layer of zinc to prevent corrosion and extend material lifespan. Smart metal technologies enhance traditional zinc galvanizing by incorporating advanced coatings or alloy compositions that improve durability and environmental resistance. The galvanizing process typically includes surface preparation, zinc application through hot-dip or electro-galvanizing, and quality assurance to ensure optimal adhesion and corrosion protection.
What is Smart Metal? An Overview
Smart Metal refers to advanced zinc-aluminum-magnesium alloy coatings designed for galvanized steel, offering superior corrosion resistance compared to traditional zinc coatings. It enhances durability by forming a protective layer that self-heals minor scratches and resists harsh environmental conditions, extending the lifespan of galvanized products. This innovative technology reduces maintenance costs and improves structural performance in industrial, automotive, and construction applications.
Understanding Zinc: Properties and Uses in Galvanizing
Zinc is a corrosion-resistant metal widely used in galvanizing due to its excellent sacrificial protection properties, forming a stable oxide layer that prevents rust. Its melting point of 419.5degC and ability to bond well with steel make zinc ideal for coating applications, enhancing durability in outdoor and industrial environments. Zinc's affordability, availability, and effectiveness in extending the lifespan of steel structures drive its predominant use in galvanizing compared to other metals.
Durability Comparison: Smart Metal vs Zinc
Smart metal coatings exhibit superior durability compared to traditional zinc galvanizing, offering enhanced resistance to corrosion, abrasion, and environmental degradation. Zinc coatings typically provide effective sacrificial protection for steel but can degrade faster in harsh environments, leading to shorter service life. Advanced smart metal solutions incorporate alloying elements and protective layers that extend lifespan and maintain structural integrity under extreme conditions.
Corrosion Resistance: Which Material Performs Better?
Smart metal alloys designed for galvanizing often exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to traditional zinc coatings due to their enhanced protective properties and ability to form more stable oxide layers. Zinc remains a widely used material for galvanizing due to its effective sacrificial protection against rust and cost efficiency, but its corrosion resistance can diminish faster in highly acidic or saline environments. Studies indicate that smart metal coatings extend the lifespan of galvanized surfaces by up to 30% under severe weather conditions, making them a better choice for long-term durability.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability of Smart Metal and Zinc
Smart metal offers enhanced environmental benefits over traditional zinc for galvanizing due to its longer lifespan and superior corrosion resistance, reducing the frequency of reapplication and metal waste. Zinc, while widely used for galvanizing, can contribute to environmental pollution through runoff and mining processes that affect ecosystems. Choosing smart metal supports sustainability goals by minimizing resource extraction and lowering the carbon footprint associated with maintenance and material replacement.
Cost Analysis: Smart Metal vs Zinc for Galvanization
Smart metal offers a cost-effective alternative to traditional zinc for galvanization, as it typically requires lower material expenses and reduced energy consumption during application. Zinc remains widely used due to its proven corrosion resistance and availability, but fluctuating market prices can increase overall project costs. Evaluating lifecycle costs reveals smart metal's potential for long-term savings despite initial adoption challenges in galvanizing processes.
Application Suitability: Industrial and Commercial Uses
Smart metal offers enhanced corrosion resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for industrial applications that demand long-term durability and exposure to harsh environments. Zinc galvanizing remains a cost-effective choice widely used in commercial construction and automotive sectors, providing reliable protection against rust and wear. Both materials suit different industrial and commercial needs based on factors like environmental exposure, budget, and specific performance requirements.
Maintenance and Longevity: What to Expect
Smart metal galvanizing offers enhanced corrosion resistance and significantly reduces maintenance frequency compared to traditional zinc coatings, extending the lifespan of metal structures in harsh environments. Zinc galvanizing provides good protection but may require more frequent inspections and touch-ups to prevent rust and degradation over time. Expect smart metal coatings to deliver superior longevity and lower long-term maintenance costs for industrial applications.
Future Trends in Galvanizing Materials
Smart metals in galvanizing showcase enhanced corrosion resistance and self-healing properties, offering significant advancements over traditional zinc coatings. Innovations in nano-coatings and alloyed metals are driving the future trends, enabling longer lifespan and reduced maintenance costs in industrial applications. The integration of eco-friendly and sustainable materials within galvanizing processes aligns with increasing environmental regulations and market demand.
Infographic: Smart metal vs Zinc for Galvanizing
 azmater.com
azmater.com