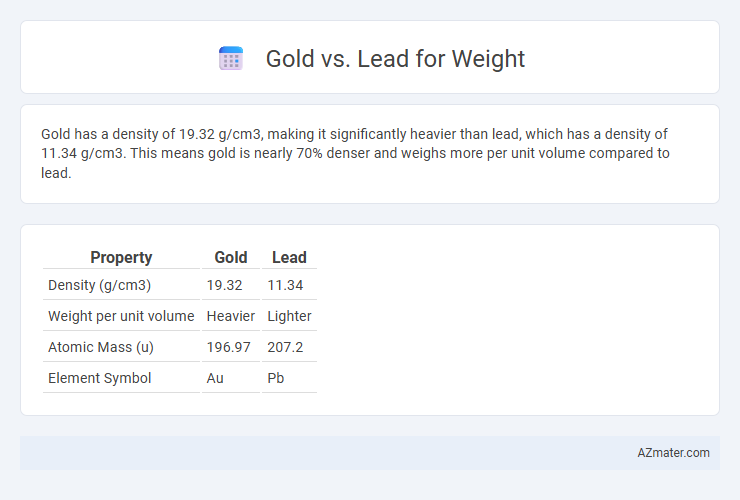
Gold has a density of 19.32 g/cm3, making it significantly heavier than lead, which has a density of 11.34 g/cm3. This means gold is nearly 70% denser and weighs more per unit volume compared to lead.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Gold | Lead |
|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm3) | 19.32 | 11.34 |
| Weight per unit volume | Heavier | Lighter |
| Atomic Mass (u) | 196.97 | 207.2 |
| Element Symbol | Au | Pb |
Introduction to Gold and Lead as Weights
Gold and lead are commonly compared metals when discussing weight due to their distinct densities, with gold having a density of approximately 19.32 g/cm3 and lead approximately 11.34 g/cm3. These differences in density make gold significantly heavier than lead for the same volume, influencing their use in weights and measurement standards. Gold's higher density combined with its resistance to corrosion makes it ideal for precise weights, whereas lead is often used for ballast and counterweights due to its lower cost and malleability.
Physical Properties Comparison
Gold has a density of approximately 19.32 g/cm3, making it significantly heavier than lead, which has a density of about 11.34 g/cm3. This difference means gold weighs nearly 70% more than lead for the same volume. Both metals have malleable properties, but gold's higher density results in a noticeably greater weight when compared at equal sizes.
Density Differences: Gold vs Lead
Gold and lead differ significantly in density, with gold having a density of approximately 19.32 grams per cubic centimeter compared to lead's 11.34 grams per cubic centimeter. This means gold is nearly 1.7 times denser than lead, making it substantially heavier for the same volume. The high density of gold contributes to its value in applications requiring compact weight, such as jewelry and electronics.
Weight-to-Volume Ratio
Gold has a significantly higher weight-to-volume ratio compared to lead, with a density of approximately 19.32 grams per cubic centimeter versus lead's 11.34 grams per cubic centimeter. This means that for the same volume, gold weighs nearly 70% more than lead. The higher density of gold makes it ideal for applications requiring compact, heavy materials, such as in jewelry or precision instruments.
Practical Applications in Industry
Gold's density of 19.32 g/cm3 makes it significantly heavier than lead, which has a density of 11.34 g/cm3, influencing their use in industry. Gold's high weight and resistance to corrosion suit applications in precision balance weights and high-reliability electronics, whereas lead's moderate weight and malleability favor use in radiation shielding, batteries, and soundproofing materials. Industries select gold for weight-critical, durable components, while lead is preferred for cost-effective, heavy-duty protective solutions.
Cost Implications of Using Gold or Lead
Gold is significantly more expensive than lead, with gold prices averaging around $60 per gram compared to lead's price of about $0.002 per gram, impacting overall project budgets substantially. Using gold for weight-related applications increases material costs and requires careful cost-benefit analysis due to its high value and limited availability. Lead's low cost and abundance make it the preferred choice for weight or ballast purposes when budget constraints are critical.
Safety and Toxicity Concerns
Gold offers a safer alternative to lead in weight applications due to its non-toxic and non-reactive properties, minimizing health risks associated with exposure. Lead poses significant toxicity concerns, especially through inhalation or ingestion of dust and fumes, leading to neurological and systemic health issues. Using gold weights eliminates lead's hazardous impact, ensuring safer handling and environmental compatibility.
Durability and Longevity
Gold is denser than lead, making it significantly heavier by volume and highly valued for its enduring weight stability in applications like jewelry and electronics. Its exceptional resistance to corrosion and tarnish ensures long-lasting durability, maintaining integrity over centuries without significant degradation. Lead, although heavier per unit volume in specific forms, is prone to oxidation and environmental wear, reducing its longevity and performance in long-term uses.
Environmental Impact
Gold mining generates significant environmental impacts, including habitat destruction and toxic chemical use, but its high value motivates extensive recycling efforts that reduce waste. Lead, commonly used in batteries and construction, poses serious environmental hazards due to toxic contamination of soil and water during extraction and disposal. The environmental footprint of lead is often more harmful than gold, especially because lead pollutants persist in ecosystems and require careful management to minimize health risks.
Summary: Choosing Between Gold and Lead for Weight
Gold has a density of approximately 19.32 g/cm3, making it significantly heavier than lead, which has a density of about 11.34 g/cm3. This greater density allows gold to provide more weight in a smaller volume, ideal for applications requiring compact mass. Lead is more affordable and easier to work with but delivers less weight compared to gold for the same size.
Infographic: Gold vs Lead for Weight
 azmater.com
azmater.com