Indium offers excellent biocompatibility and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for medical implants in soft tissue applications. Titanium provides superior strength, osseointegration, and durability, making it the preferred choice for load-bearing implants such as orthopedic devices.
Table of Comparison
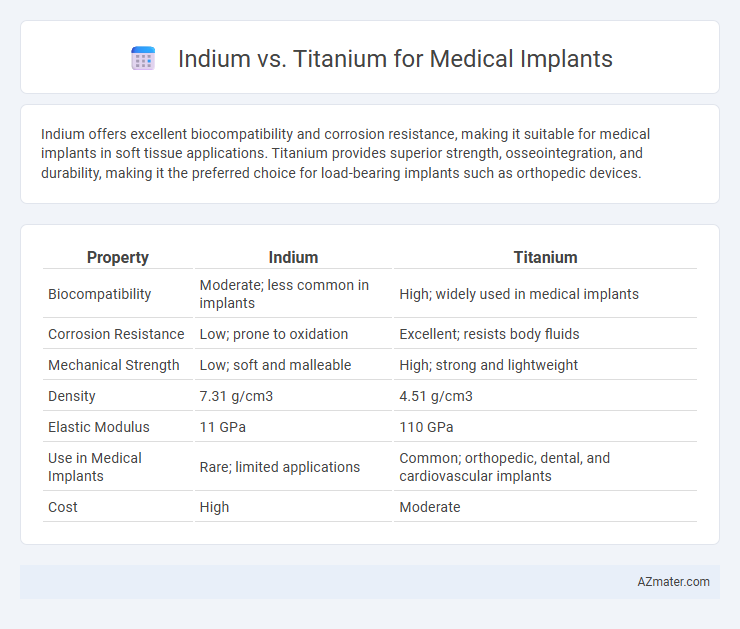
| Property | Indium | Titanium |
|---|---|---|
| Biocompatibility | Moderate; less common in implants | High; widely used in medical implants |
| Corrosion Resistance | Low; prone to oxidation | Excellent; resists body fluids |
| Mechanical Strength | Low; soft and malleable | High; strong and lightweight |
| Density | 7.31 g/cm3 | 4.51 g/cm3 |
| Elastic Modulus | 11 GPa | 110 GPa |
| Use in Medical Implants | Rare; limited applications | Common; orthopedic, dental, and cardiovascular implants |
| Cost | High | Moderate |
Introduction to Indium and Titanium in Medical Implants
Indium and titanium are materials utilized in medical implants due to their biocompatibility and mechanical properties. Titanium is renowned for its strength, corrosion resistance, and ability to bond with bone, making it a preferred choice for orthopedic and dental implants. Indium, less common, offers unique properties such as malleability and biocompatibility that are explored for specialized applications in implant coatings and flexible interfaces.
Material Properties: Indium vs Titanium
Indium offers excellent biocompatibility and corrosion resistance but lacks the mechanical strength and durability of titanium, which is renowned for its high tensile strength, fatigue resistance, and lightweight nature ideal for load-bearing medical implants. Titanium's superior modulus of elasticity closely matches that of human bone, reducing stress shielding and promoting osseointegration, whereas indium's softness limits its application to non-structural implant components. The choice between indium and titanium hinges on balancing biocompatibility with mechanical performance required for specific medical implant applications.
Biocompatibility and Safety Comparison
Indium exhibits excellent biocompatibility with minimal cytotoxicity, but its softness and limited mechanical strength restrict its use in high-stress medical implants. Titanium is widely preferred due to its superior biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and strength, making it ideal for long-term implant stability and osseointegration. Safety comparisons highlight titanium's proven track record in reducing inflammatory responses and implant rejection compared to indium.
Durability and Longevity in the Human Body
Titanium exhibits superior durability and longevity for medical implants due to its exceptional corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, and high strength-to-weight ratio, enabling it to withstand mechanical stress within the human body over extended periods. Indium, while biocompatible, lacks the same mechanical strength and corrosion resistance, making it less suitable for long-term implants subjected to repetitive loading and bodily fluids. Clinical studies consistently demonstrate titanium's reliability in maintaining structural integrity and minimizing adverse tissue reactions compared to indium-based materials.
Corrosion Resistance: Indium vs Titanium
Titanium exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to indium, making it the preferred choice for medical implants exposed to bodily fluids. Indium, while biocompatible, is more prone to oxidation and corrosion under physiological conditions. The stable oxide layer on titanium implants enhances longevity and reduces the risk of adverse reactions in the body.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility
Titanium exhibits superior mechanical strength with a high tensile strength of around 434 MPa and excellent corrosion resistance, making it a preferred choice for load-bearing medical implants. Indium, while offering notable flexibility and biocompatibility, has significantly lower mechanical strength, limiting its use to applications requiring pliability rather than structural support. The balance between titanium's rigidity and indium's flexibility guides implant selection based on specific medical requirements.
Applications in Medical Implants
Indium is rarely used in medical implants due to its softness and limited biocompatibility, whereas titanium is extensively utilized for orthopedic implants, dental devices, and cardiovascular applications because of its exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. Titanium's ability to promote osseointegration makes it ideal for bone implants and joint replacements. Indium's primary medical use remains in diagnostic imaging rather than implantable devices.
Cost and Availability for Healthcare Providers
Indium is rare and expensive, making it less accessible for widespread medical implant use compared to titanium, which is abundant and cost-effective. Titanium offers excellent biocompatibility and strength at a lower price point, supporting broad healthcare provider adoption. The cost-efficiency and high availability of titanium drive its preference over indium in medical implant manufacturing.
Recent Advances and Research Developments
Recent advances in medical implants have highlighted titanium's superior biocompatibility and mechanical strength, making it the gold standard for orthopedic and dental applications. Emerging research on indium-based coatings aims to enhance implant corrosion resistance and antimicrobial properties, potentially reducing post-surgical infections. Studies also explore indium-titanium alloys to combine titanium's durability with indium's unique surface characteristics, offering promising improvements in implant longevity and tissue integration.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Material for Medical Implants
Indium is rarely used for medical implants due to its limited biocompatibility and mechanical strength compared to titanium, which offers exceptional corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, and mechanical durability essential for long-term implant success. Titanium's ability to osseointegrate with bone tissue significantly enhances implant stability and patient outcomes, making it the preferred choice in orthopedic and dental applications. Selecting titanium ensures optimal performance, longevity, and safety in medical implants.
Infographic: Indium vs Titanium for Medical Implant
 azmater.com
azmater.com