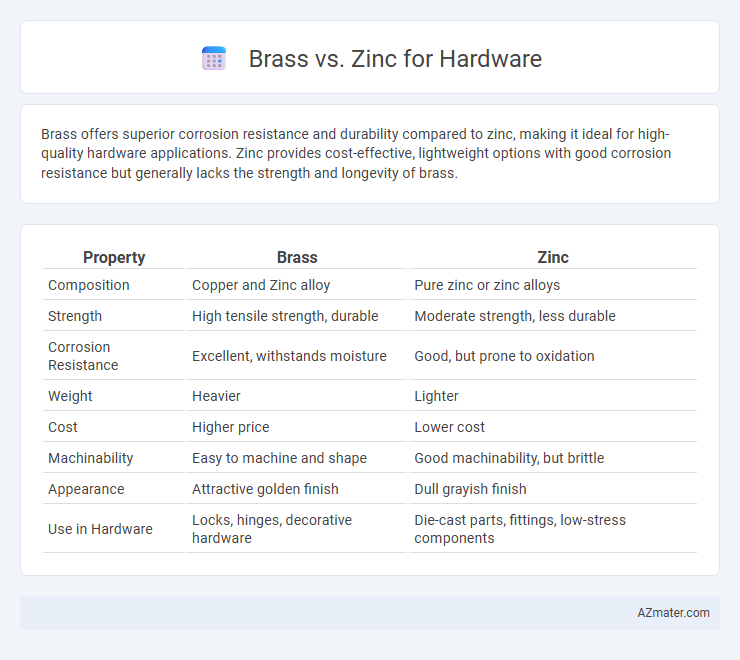
Brass offers superior corrosion resistance and durability compared to zinc, making it ideal for high-quality hardware applications. Zinc provides cost-effective, lightweight options with good corrosion resistance but generally lacks the strength and longevity of brass.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Brass | Zinc |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copper and Zinc alloy | Pure zinc or zinc alloys |
| Strength | High tensile strength, durable | Moderate strength, less durable |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, withstands moisture | Good, but prone to oxidation |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Cost | Higher price | Lower cost |
| Machinability | Easy to machine and shape | Good machinability, but brittle |
| Appearance | Attractive golden finish | Dull grayish finish |
| Use in Hardware | Locks, hinges, decorative hardware | Die-cast parts, fittings, low-stress components |
Introduction to Brass and Zinc Hardware
Brass hardware, composed primarily of copper and zinc, offers high corrosion resistance, durability, and an attractive gold-like appearance, making it ideal for decorative and functional applications. Zinc hardware, predominantly made from zinc alloy, provides cost-effective strength, excellent corrosion resistance through zinc's protective properties, and versatility in casting intricate shapes for various hardware uses. Both materials are essential in hardware manufacturing, with brass favored for aesthetic appeal and zinc valued for economic efficiency and design flexibility.
Composition and Properties of Brass
Brass is primarily an alloy of copper and zinc, typically composed of 60-70% copper combined with 30-40% zinc, which gives it excellent corrosion resistance and malleability for hardware applications. Its properties include high tensile strength, good machinability, and an attractive gold-like appearance, making it ideal for decorative and functional hardware components. Compared to zinc, brass offers superior durability and resistance to wear, making it preferable for high-stress mechanical parts and long-lasting fixtures.
Composition and Properties of Zinc
Zinc, primarily composed of a bluish-silver metal, exhibits excellent corrosion resistance and moderate strength, making it a popular choice for hardware components exposed to moisture. Unlike brass, which is an alloy of copper and zinc offering higher ductility and electrical conductivity, zinc's natural properties contribute to its durability and cost-effectiveness in protective coatings and die-cast applications. Zinc's ability to form a protective oxide layer ensures prolonged hardware lifespan, especially in outdoor or industrial environments.
Durability: Brass vs Zinc
Brass hardware demonstrates superior durability due to its corrosion resistance and ability to withstand high tensile stress without deforming, making it ideal for long-term use in harsh environments. Zinc hardware, while cost-effective and resistant to rust through galvanization, typically has lower mechanical strength and is more prone to wear and cracking under heavy or frequent stress. Choosing brass over zinc ensures enhanced longevity and reliability in demanding applications such as door handles, locks, and plumbing fittings.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Brass exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to zinc, making it ideal for hardware exposed to moisture and harsh environments. Zinc tends to corrode more quickly, especially in acidic or saline conditions, leading to potential hardware failure. The natural patina of brass also provides a protective barrier that extends the lifespan of hardware components.
Aesthetic Appeal and Finishing Options
Brass hardware offers a warm, golden tone that enhances traditional and vintage aesthetics, with natural corrosion resistance that develops an attractive patina over time, adding character to fixtures. Zinc hardware provides versatile finishing options, including matte, polished, and plated surfaces, allowing for a wide range of contemporary designs and colors, often at a more cost-effective price point. Both metals support plating techniques such as chrome or nickel, but brass's inherent luster and ability to age gracefully often make it the preferred choice for premium, long-lasting aesthetic appeal in hardware applications.
Cost Considerations: Brass vs Zinc
Brass hardware generally costs more than zinc due to its superior durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal, making it a preferred choice for long-term applications despite the higher price. Zinc hardware offers a more budget-friendly option with adequate strength and corrosion resistance, suitable for projects requiring cost efficiency and moderate wear. When comparing brass vs zinc, factors such as initial investment, lifespan, and maintenance expenses are critical to determining overall cost-effectiveness.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Brass offers superior environmental benefits due to its high recyclability and long lifespan, significantly reducing waste and resource consumption in hardware applications. Zinc, while also recyclable, generally requires more energy-intensive extraction processes that contribute to higher carbon emissions and environmental degradation. Choosing brass hardware aligns better with sustainability goals by promoting durability and minimizing ecological footprints throughout the product lifecycle.
Common Applications in Hardware Industry
Brass is widely used in hardware for decorative fixtures, plumbing fittings, and musical instrument components due to its corrosion resistance and attractive gold-like appearance. Zinc is commonly found in die-cast hardware parts, automotive components, and fasteners because of its excellent casting properties and cost-effectiveness. Both metals serve essential roles, with brass preferred for durability and aesthetics, while zinc offers lightweight strength and versatility in mass production.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Brass offers high corrosion resistance, durability, and an attractive gold-like appearance, making it ideal for hardware in marine or decorative applications. Zinc is cost-effective, provides good corrosion protection through galvanization, and suits hardware projects requiring lightweight strength and budget-friendly materials. Selecting the right material depends on environmental exposure, aesthetic preference, and functional requirements such as load-bearing capacity and longevity.
Infographic: Brass vs Zinc for Hardware
 azmater.com
azmater.com