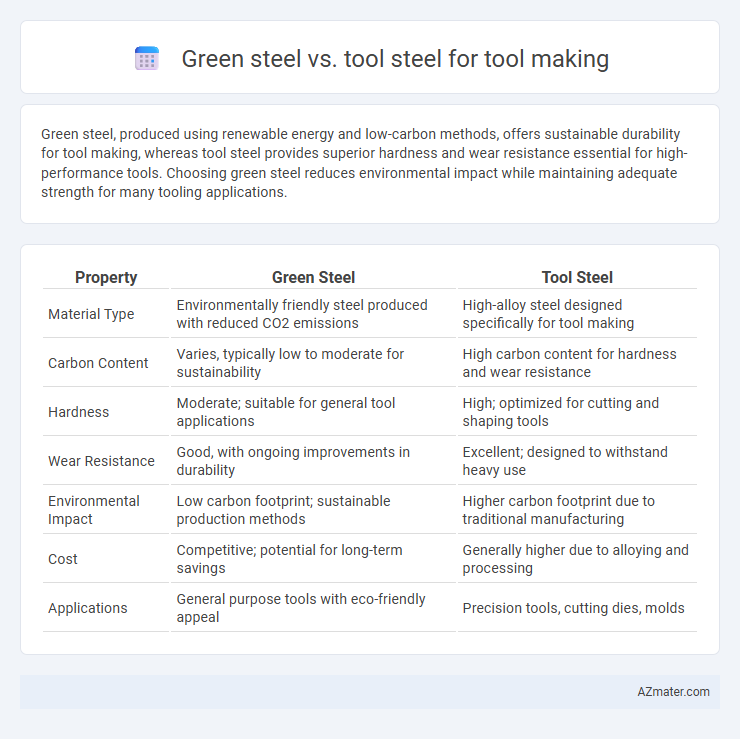
Green steel, produced using renewable energy and low-carbon methods, offers sustainable durability for tool making, whereas tool steel provides superior hardness and wear resistance essential for high-performance tools. Choosing green steel reduces environmental impact while maintaining adequate strength for many tooling applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Green Steel | Tool Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Environmentally friendly steel produced with reduced CO2 emissions | High-alloy steel designed specifically for tool making |
| Carbon Content | Varies, typically low to moderate for sustainability | High carbon content for hardness and wear resistance |
| Hardness | Moderate; suitable for general tool applications | High; optimized for cutting and shaping tools |
| Wear Resistance | Good, with ongoing improvements in durability | Excellent; designed to withstand heavy use |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint; sustainable production methods | Higher carbon footprint due to traditional manufacturing |
| Cost | Competitive; potential for long-term savings | Generally higher due to alloying and processing |
| Applications | General purpose tools with eco-friendly appeal | Precision tools, cutting dies, molds |
Introduction to Green Steel and Tool Steel
Green steel, produced using environmentally friendly methods such as hydrogen-based direct reduction, offers significantly lower carbon emissions compared to traditional steelmaking. Tool steel, characterized by its high hardness, abrasion resistance, and ability to hold a sharp edge, is specifically engineered for manufacturing cutting and shaping tools. The emergence of green steel introduces a sustainable alternative for tool production, maintaining essential mechanical properties while reducing the environmental impact of tool steel manufacturing.
Defining Green Steel: Sustainable Manufacturing Approaches
Green steel in tool making refers to steel produced using sustainable manufacturing approaches that significantly reduce carbon emissions, such as electric arc furnaces powered by renewable energy and hydrogen-based direct reduction methods. This environmentally friendly process minimizes the use of fossil fuels and lowers the carbon footprint compared to traditional tool steel production, which relies heavily on coke and blast furnace operations. Emphasizing sustainability, green steel maintains essential mechanical properties required for tool making while promoting eco-conscious industry practices.
Tool Steel: Composition and Traditional Production
Tool steel is primarily composed of carbon, manganese, chromium, vanadium, and tungsten, elements that contribute to its hardness, wear resistance, and ability to retain a sharp edge at high temperatures. Traditional production of tool steel involves a complex alloying process followed by heat treatment techniques such as quenching and tempering, which enhance its mechanical properties for demanding applications. Unlike green steel, which emphasizes eco-friendly recycling and reduced emissions, tool steel production prioritizes precise chemical composition and thermal processing to meet rigorous performance standards in tool making.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Green steel for tool making offers improved sustainability with mechanical properties such as high tensile strength and good ductility, but generally lower hardness and wear resistance compared to traditional tool steel. Tool steel excels in hardness, toughness, and wear resistance due to its high carbon and alloy content, making it ideal for cutting, shaping, and heavy-duty tooling applications. While green steel provides sufficient mechanical strength for moderate tool use, tool steel remains superior for applications requiring maximum durability and precision under high stress.
Environmental Impact: Emissions and Resource Use
Green steel significantly reduces carbon emissions compared to conventional tool steel by utilizing hydrogen-based direct reduction and renewable energy sources, cutting CO2 emissions by up to 95%. Tool steel production traditionally relies on energy-intensive coal-based blast furnaces, leading to substantial greenhouse gas emissions and high resource consumption. Switching to green steel not only lowers environmental impact but also promotes sustainable resource use by minimizing reliance on virgin iron ore and fossil fuels.
Performance in Tool Making Applications
Green steel offers superior environmental benefits but generally lacks the high hardness and wear resistance required for demanding tool-making applications. Tool steel is specifically designed for exceptional toughness, heat resistance, and durability, making it the preferred choice for cutting, shaping, and forming tools. Performance in tool-making processes heavily favors tool steel due to its ability to maintain sharp cutting edges and withstand repeated mechanical stress under high temperatures.
Cost and Market Availability
Green steel offers a cost advantage due to lower energy consumption and reduced carbon footprint during production, making it increasingly attractive as environmental regulations tighten. Tool steel remains more widely available in the market, benefiting from established supply chains and a broad range of grades tailored for specific tool-making applications. The current market dynamics favor tool steel for immediate use, but rising demand for sustainable materials is gradually enhancing green steel's market presence and cost competitiveness.
Challenges in Adopting Green Steel for Tool Making
Green steel faces significant challenges in tool making due to its variable microstructure and inconsistent mechanical properties compared to traditional tool steel, which offers superior hardness, wear resistance, and heat treatment reliability. The limited availability of green steel grades optimized for high-stress applications and difficulties in achieving precise heat treatment further hinder its widespread adoption in precision tool manufacturing. Manufacturing processes must adapt to overcome issues with durability and performance consistency to meet the stringent demands of industrial tooling applications.
Innovations and Future Trends
Green steel, produced through low-carbon or carbon-free methods like hydrogen-based direct reduction, represents a revolutionary shift in sustainable tool making, reducing carbon emissions by up to 90%. Tool steel remains essential for its high hardness, wear resistance, and machinability, but innovations are integrating green steel alloys with advanced heat treatment processes to enhance durability and environmental performance. Future trends focus on combining green steel production with additive manufacturing and AI-driven design to optimize tool life and reduce ecological impact while maintaining superior mechanical properties.
Choosing the Right Steel for Sustainable Tool Making
Green steel, produced with reduced carbon emissions and sustainable practices, offers an eco-friendly alternative for tool making, emphasizing environmental responsibility without compromising strength. Tool steel, known for its high hardness, wear resistance, and toughness, remains the industry standard for durability and precision in manufacturing tools. Selecting the right steel for sustainable tool making involves balancing performance requirements with carbon footprint, making green steel a compelling choice for companies aiming to reduce environmental impact while maintaining quality.
Infographic: Green steel vs Tool steel for Tool making
 azmater.com
azmater.com