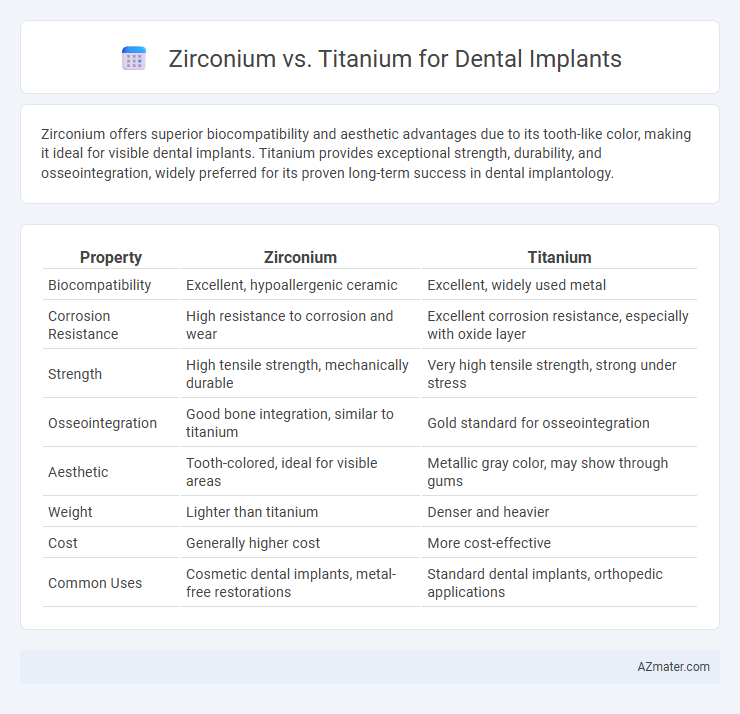
Zirconium offers superior biocompatibility and aesthetic advantages due to its tooth-like color, making it ideal for visible dental implants. Titanium provides exceptional strength, durability, and osseointegration, widely preferred for its proven long-term success in dental implantology.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Zirconium | Titanium |
|---|---|---|
| Biocompatibility | Excellent, hypoallergenic ceramic | Excellent, widely used metal |
| Corrosion Resistance | High resistance to corrosion and wear | Excellent corrosion resistance, especially with oxide layer |
| Strength | High tensile strength, mechanically durable | Very high tensile strength, strong under stress |
| Osseointegration | Good bone integration, similar to titanium | Gold standard for osseointegration |
| Aesthetic | Tooth-colored, ideal for visible areas | Metallic gray color, may show through gums |
| Weight | Lighter than titanium | Denser and heavier |
| Cost | Generally higher cost | More cost-effective |
| Common Uses | Cosmetic dental implants, metal-free restorations | Standard dental implants, orthopedic applications |
Introduction to Dental Implant Materials
Zirconium and titanium are the two primary materials used for dental implants, each offering unique benefits in biocompatibility and mechanical strength. Titanium, known for its excellent osseointegration and durability, remains the gold standard in dental implantology. Zirconium, a ceramic material, provides superior aesthetics due to its tooth-like color and exhibits high resistance to corrosion and metal sensitivity.
Overview of Zirconium and Titanium Implants
Zirconium dental implants are ceramic and biocompatible, offering superior aesthetic outcomes due to their tooth-colored appearance and resistance to corrosion. Titanium implants, made from a strong metal alloy, have a long history of reliable osseointegration and durability in dental restorations. Both materials provide excellent support for prosthetics, but zirconium is preferred for patients with metal sensitivities while titanium remains the gold standard for overall strength and performance.
Biocompatibility: Zirconium vs Titanium
Zirconium and titanium are both highly biocompatible materials widely used in dental implants, minimizing allergic reactions and promoting osseointegration. Zirconium, a ceramic, offers superior aesthetic outcomes due to its white color, which blends better with natural teeth and reduces the risk of gum discoloration. Titanium, a metal, is renowned for its exceptional strength and long-term stability, making it the most common choice for dental implants worldwide.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Zirconium dental implants exhibit exceptional strength due to their ceramic composition, resisting corrosion and wear effectively while maintaining biocompatibility. Titanium implants, known for their superior tensile strength and proven longevity, offer excellent osseointegration, making them highly durable under biting forces. Comparative studies indicate titanium remains the gold standard for strength and long-term durability, though zirconium provides a strong, metal-free alternative with enhanced aesthetics.
Aesthetic Outcomes: Metal-Free vs Metallic Implants
Zirconium dental implants deliver superior aesthetic outcomes due to their metal-free, tooth-colored composition that mimics natural enamel, reducing the risk of visible dark lines at the gum line. Titanium implants, while highly durable and biocompatible, have a metallic appearance that may cause discoloration of the surrounding soft tissue, potentially compromising the smile's aesthetics. Patients seeking a more natural and discreet restoration often prefer zirconium implants for improved visual integration and metal-free assurance.
Osseointegration Efficiency
Zirconium and titanium are both widely used materials for dental implants, with osseointegration efficiency being a critical factor in their performance. Titanium implants exhibit excellent biocompatibility and faster osseointegration due to their ability to form a direct bone-to-implant interface, supported by a stable titanium oxide layer. Zirconium implants offer comparable osseointegration with added benefits of superior aesthetics and corrosion resistance, making them an effective alternative, especially for patients with metal sensitivities.
Allergic Reactions and Sensitivity Risks
Zirconium dental implants exhibit significantly lower allergic reactions and sensitivity risks compared to titanium, making them ideal for patients with metal sensitivities or allergies. Research shows zirconium is biocompatible and inert, minimizing immune responses and inflammation around the implant site. Titanium, although widely used, has a higher incidence of allergic reactions linked to its metal ions, potentially causing peri-implantitis and implant failure in susceptible individuals.
Clinical Performance and Longevity
Zirconium dental implants exhibit superior biocompatibility and lower plaque accumulation compared to titanium, supporting enhanced gum tissue integration and reduced peri-implantitis risk. Titanium implants remain the gold standard due to proven osseointegration strength and long-term clinical success with survival rates above 95% over 10 years. Studies show zirconium implants offer comparable durability and aesthetic benefits, particularly in patients with metal sensitivity or thin gingival biotypes, although long-term data is less extensive than titanium.
Cost Analysis: Zirconium vs Titanium Implants
Zirconium dental implants typically cost 20-30% more than titanium implants due to higher material and manufacturing expenses. Titanium implants benefit from widespread use and established supply chains, allowing for more affordable pricing and greater insurance coverage. Cost differences should be weighed against factors like biocompatibility and aesthetic preferences when selecting between zirconium and titanium for dental implants.
Choosing the Right Material for Dental Implants
Zirconium and titanium are the two primary materials used for dental implants, each offering unique benefits important for patient-specific considerations. Titanium is highly durable, biocompatible, and has a long track record of successful osseointegration, making it the preferred choice for most traditional dental implant cases. Zirconium, a ceramic material, offers excellent aesthetic advantages with a tooth-colored appearance and is a strong alternative for patients with metal sensitivities or allergies.
Infographic: Zirconium vs Titanium for Dental Implant
 azmater.com
azmater.com