Iridium offers superior corrosion resistance and conductivity for electrical contacts compared to aluminum, making it ideal for high-reliability applications. Aluminum is lightweight and cost-effective but prone to oxidation, reducing long-term contact performance.
Table of Comparison
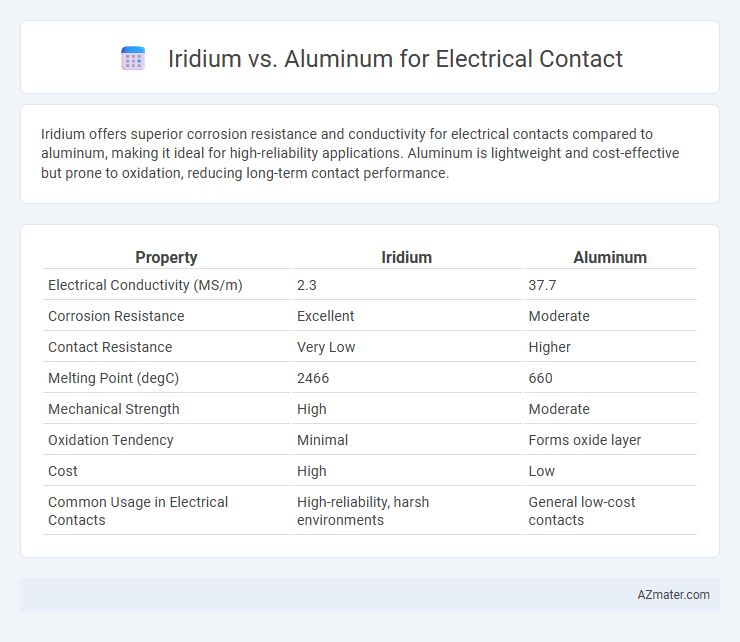
| Property | Iridium | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity (MS/m) | 2.3 | 37.7 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
| Contact Resistance | Very Low | Higher |
| Melting Point (degC) | 2466 | 660 |
| Mechanical Strength | High | Moderate |
| Oxidation Tendency | Minimal | Forms oxide layer |
| Cost | High | Low |
| Common Usage in Electrical Contacts | High-reliability, harsh environments | General low-cost contacts |
Introduction to Electrical Contact Materials
Iridium and aluminum serve distinct roles in electrical contact materials due to their unique conductivity and corrosion resistance properties. Iridium offers exceptional durability and resistance to oxidation, making it ideal for high-performance, high-reliability electrical contacts in harsh environments. Aluminum provides excellent electrical conductivity and cost-effectiveness, primarily used in applications where weight and budget are critical factors.
Properties of Iridium for Electrical Contacts
Iridium exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance and high melting point, making it ideal for electrical contacts in harsh environments. Its excellent conductivity combined with outstanding wear resistance ensures reliable performance in high-current applications. The metal's durability minimizes contact degradation, enhancing the longevity and stability of electrical connections compared to aluminum.
Properties of Aluminum for Electrical Contacts
Aluminum is widely used for electrical contacts due to its excellent electrical conductivity, lightweight nature, and cost-effectiveness compared to precious metals like iridium. Its high thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance make it suitable for applications where heat dissipation and durability are critical. However, aluminum's tendency to form an insulating oxide layer on its surface can affect contact reliability, requiring special coatings or treatments to enhance performance.
Electrical Conductivity: Iridium vs Aluminum
Iridium exhibits significantly lower electrical conductivity compared to aluminum, with conductivity values around 1.3 x 10^6 S/m versus aluminum's 3.5 x 10^7 S/m, making aluminum a superior choice for efficient electrical current flow. Despite iridium's lower conductivity, its exceptional corrosion resistance and mechanical durability provide advantages in high-temperature or harsh environment applications. Aluminum's lightweight nature and high conductivity make it optimal for general electrical wiring, while iridium is preferred for specialized electrical contacts requiring longevity and stability under extreme conditions.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Iridium exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to aluminum in electrical contacts due to its high resistance to oxidation and chemical degradation, ensuring long-term durability in harsh environments. Aluminum is prone to forming an insulating oxide layer that can hinder electrical conductivity and degrade contact performance over time. Iridium's ability to maintain stable electrical conductivity under extreme conditions makes it a preferred choice for critical applications requiring reliable corrosion protection.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Iridium exhibits superior durability and wear resistance compared to aluminum when used in electrical contacts, maintaining performance under high current and corrosive environments. Its high melting point and excellent hardness allow iridium contacts to withstand repeated arcing and mechanical stress without significant degradation. Aluminum, while lightweight and conductive, tends to oxidize rapidly and wear down faster, leading to reduced contact reliability over time.
Cost Analysis: Iridium vs Aluminum
Iridium offers superior corrosion resistance and conductivity compared to aluminum, but its significantly higher raw material and processing costs impact overall expenses. Aluminum provides a cost-effective solution with lower material prices and easier machinability, suitable for applications where budget constraints outweigh extreme durability requirements. Evaluating total lifecycle costs, including maintenance and replacement, is crucial to determining the most economical choice between iridium and aluminum electrical contacts.
Application Suitability in Electrical Devices
Iridium offers exceptional corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability, making it ideal for use in electrical contacts within harsh environments such as aerospace and industrial equipment. Aluminum, valued for its lightweight and excellent electrical conductivity, is well-suited for low-cost, high-volume applications like consumer electronics and power distribution systems. The choice between iridium and aluminum depends on the specific electrical device requirements, balancing durability and conductivity against cost and environmental conditions.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Iridium offers superior corrosion resistance and is highly stable under extreme environmental conditions, reducing the risk of hazardous degradation compared to aluminum, which oxidizes easily and forms insulating oxide layers that can impair electrical conductivity. Aluminum's lighter weight and abundant availability contribute to lower environmental impact during extraction but require protective coatings or treatments to ensure safety and performance in electrical contacts. Iridium's higher toxicity during mining and higher cost are offset by its longevity and reliability, minimizing maintenance-related environmental risks and enhancing overall safety in critical applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material
Iridium offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent conductivity for electrical contacts in extreme environments, making it ideal for high-performance applications despite its higher cost. Aluminum provides good conductivity and cost-effectiveness for general use but is prone to oxidation, requiring protective coatings to ensure reliability. Selecting between iridium and aluminum depends on balancing durability, conductivity, and budget requirements specific to the electrical application.
Infographic: Iridium vs Aluminum for Electrical Contact
 azmater.com
azmater.com