Brass offers superior corrosion resistance and machinability compared to steel, making it ideal for plumbing and decorative pipe applications. Steel provides higher strength and durability, preferred for high-pressure industrial pipes and structural uses.
Table of Comparison
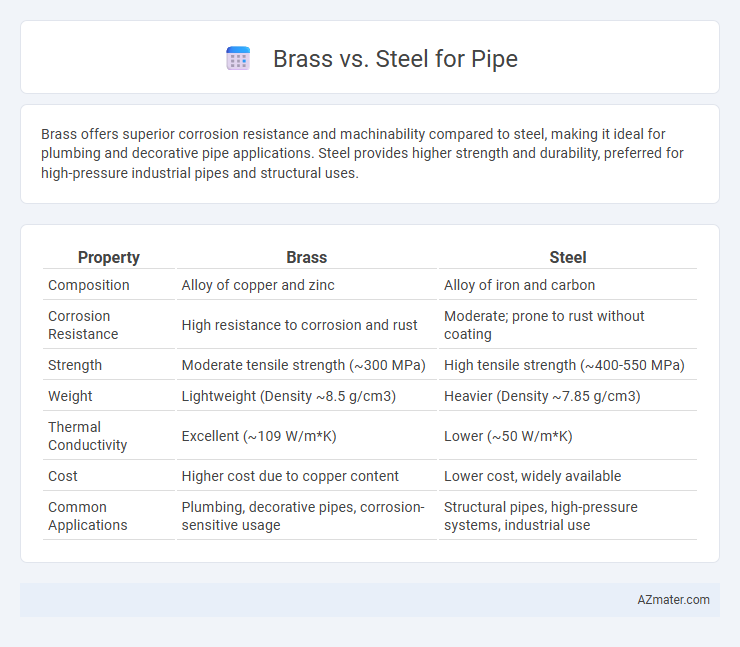
| Property | Brass | Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Alloy of copper and zinc | Alloy of iron and carbon |
| Corrosion Resistance | High resistance to corrosion and rust | Moderate; prone to rust without coating |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength (~300 MPa) | High tensile strength (~400-550 MPa) |
| Weight | Lightweight (Density ~8.5 g/cm3) | Heavier (Density ~7.85 g/cm3) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Excellent (~109 W/m*K) | Lower (~50 W/m*K) |
| Cost | Higher cost due to copper content | Lower cost, widely available |
| Common Applications | Plumbing, decorative pipes, corrosion-sensitive usage | Structural pipes, high-pressure systems, industrial use |
Overview of Brass and Steel Pipes
Brass pipes, composed primarily of copper and zinc, offer excellent corrosion resistance and malleability, making them ideal for plumbing and decorative applications. Steel pipes, available in carbon and stainless varieties, provide superior strength and durability, suitable for structural and high-pressure environments. Both materials serve diverse industrial and residential purposes, with brass favored for resistance to water corrosion and steel preferred for heavy-load and high-temperature conditions.
Key Material Properties: Brass vs Steel
Brass pipes exhibit excellent corrosion resistance, superior machinability, and naturally antimicrobial properties, making them ideal for plumbing applications where water quality is critical. Steel pipes, particularly carbon and stainless steel, offer higher tensile strength and durability, suitable for high-pressure environments and structural use. The choice between brass and steel hinges on factors such as environmental conditions, mechanical requirements, and cost considerations, with brass excelling in corrosion resistance and steel in mechanical resilience.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Brass pipes offer excellent corrosion resistance and moderate strength, making them suitable for plumbing applications that require long-lasting durability without extreme mechanical stress. Steel pipes, especially carbon and stainless steel variants, provide superior tensile strength and high durability under heavy loads and high-pressure conditions, ideal for industrial and structural uses. While brass resists rust and is easier to work with, steel pipes withstand physical impact and high temperatures better, ensuring longer service life in demanding environments.
Corrosion Resistance Performance
Brass pipes exhibit superior corrosion resistance due to their copper and zinc alloy composition, which naturally resists rust and mineral build-up, making them ideal for water supply systems. Steel pipes, particularly carbon steel, are prone to rust and corrosion without protective coatings or galvanization, leading to potential leaks and reduced lifespan in moist environments. Stainless steel pipes provide enhanced corrosion resistance from their chromium content, offering durability in harsh, corrosive conditions where brass may degrade more quickly.
Cost Analysis: Brass vs Steel Pipes
Brass pipes generally have a higher upfront cost compared to steel pipes due to the alloy's copper content and corrosion resistance properties. Steel pipes, particularly carbon steel, offer a more economical option for large-scale projects but may incur higher maintenance costs over time due to rust and corrosion susceptibility. Evaluating total lifecycle expenses, including installation, durability, and maintenance, is essential for accurate cost analysis between brass and steel pipes.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Brass pipes offer superior corrosion resistance and easier joint assembly with soldering, requiring less frequent maintenance and specialized tools during installation. Steel pipes, while robust and cost-effective, demand protective coatings to prevent rust and involve more complex threading or welding processes, increasing installation time and ongoing upkeep. Choosing brass minimizes long-term maintenance costs, whereas steel may require regular inspections and treatment to ensure durability.
Common Applications for Brass and Steel Pipes
Brass pipes are commonly used in plumbing, heating, and water supply systems due to their excellent corrosion resistance and antimicrobial properties, making them ideal for potable water applications. Steel pipes, particularly carbon steel and stainless steel, dominate in industrial environments for transporting gas, oil, and high-pressure fluids because of their superior strength and durability. Both materials serve essential roles, with brass preferred for residential and low-pressure systems, while steel pipes are favored for heavy-duty and industrial applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Brass pipes offer superior corrosion resistance and recyclability, reducing the need for replacement and minimizing environmental waste compared to steel pipes, which are prone to rust and require frequent maintenance. Steel production involves higher carbon emissions due to intensive mining and smelting processes, whereas brass, made primarily from copper and zinc, benefits from established recycling systems that lower overall environmental impact. Choosing brass for piping applications promotes sustainability by extending material lifespan and enhancing recyclability in construction and plumbing industries.
Safety Considerations and Compliance
Brass pipes offer excellent corrosion resistance and natural antimicrobial properties, making them a safer choice for potable water systems compared to steel, which is prone to rust and corrosion over time. Steel pipes require regular maintenance and protective coatings to prevent contamination and ensure compliance with safety standards such as ANSI/NSF 61 for drinking water applications. Ensuring proper material selection and adherence to relevant regulations like ASTM A53 for steel or ASTM B43 for brass is critical for maintaining health safety and regulatory compliance in piping systems.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Brass pipes offer excellent corrosion resistance and superior machinability, making them ideal for plumbing applications involving water. Steel pipes provide higher strength and durability, suitable for high-pressure systems and construction projects requiring robust materials. Selecting between brass and steel depends on project requirements such as environmental exposure, mechanical stress, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Brass vs Steel for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com