Green steel reduces carbon emissions by up to 90% compared to traditional rebar steel used in reinforcement. Its sustainable production process enhances durability and meets stringent environmental standards in construction.
Table of Comparison
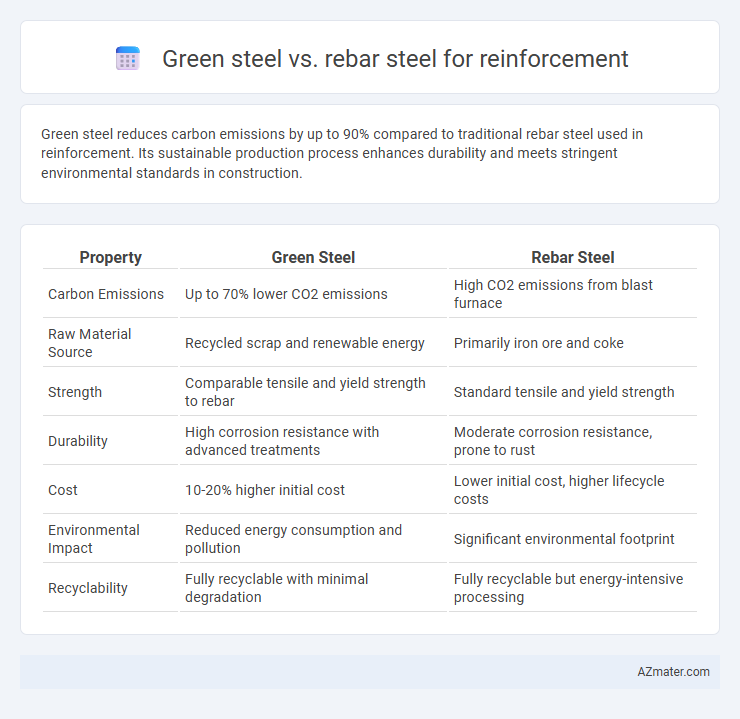
| Property | Green Steel | Rebar Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Emissions | Up to 70% lower CO2 emissions | High CO2 emissions from blast furnace |
| Raw Material Source | Recycled scrap and renewable energy | Primarily iron ore and coke |
| Strength | Comparable tensile and yield strength to rebar | Standard tensile and yield strength |
| Durability | High corrosion resistance with advanced treatments | Moderate corrosion resistance, prone to rust |
| Cost | 10-20% higher initial cost | Lower initial cost, higher lifecycle costs |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced energy consumption and pollution | Significant environmental footprint |
| Recyclability | Fully recyclable with minimal degradation | Fully recyclable but energy-intensive processing |
Introduction to Green Steel and Rebar Steel
Green steel, produced through low-emission methods such as hydrogen-based direct reduction, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional rebar steel used in concrete reinforcement. Rebar steel, typically made from carbon-intensive blast furnace processes, provides essential tensile strength and durability in construction despite higher environmental impacts. Innovations in green steel technology aim to reduce carbon footprints while maintaining the mechanical properties required for effective reinforcement in infrastructure projects.
Understanding the Production Processes
Green steel production utilizes hydrogen-based direct reduction or electric arc furnaces powered by renewable energy, significantly reducing carbon emissions compared to traditional methods. Rebar steel production typically involves blast furnace-basic oxygen furnace (BF-BOF) routes, relying heavily on coal and coke, resulting in higher CO2 footprints. Understanding these processes highlights the environmental benefits of green steel in reinforcing concrete structures while maintaining equivalent mechanical properties.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Green steel production significantly reduces carbon emissions by utilizing renewable energy and hydrogen-based reduction methods instead of traditional coal-fired blast furnaces. Rebar steel manufacturing typically relies on conventional blast furnace techniques, resulting in higher greenhouse gas emissions and greater environmental degradation. Life cycle assessments reveal that green steel reinforcement can lower the carbon footprint of construction projects by up to 70%, promoting sustainable infrastructure development.
Mechanical Properties and Performance
Green steel, produced using low-carbon and sustainable methods, exhibits mechanical properties comparable to traditional rebar steel, including tensile strength and yield strength. Its enhanced corrosion resistance and improved ductility contribute to superior long-term performance in reinforcement applications. Green steel's lower carbon footprint and consistent mechanical behavior make it a viable and eco-friendly alternative for structural reinforcement.
Cost Analysis and Economic Viability
Green steel, produced with reduced carbon emissions using renewable energy or hydrogen, generally incurs higher initial production costs than traditional rebar steel, driven by advanced technology and limited large-scale manufacturing. However, the economic viability of green steel improves with government incentives, carbon pricing mechanisms, and long-term reduction in environmental compliance costs. In contrast, traditional rebar steel remains more cost-effective upfront for reinforcement applications but faces increasing cost risks due to environmental regulations and carbon taxes.
Sustainability and Certification Standards
Green steel for reinforcement prioritizes sustainability by utilizing renewable energy sources and reducing carbon emissions during production, significantly lowering the environmental impact compared to traditional rebar steel. Certification standards such as the ResponsibleSteel(tm) and the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) ensure green steel adheres to rigorous environmental and social criteria, promoting transparency and eco-friendly practices. Rebar steel, while essential for structural integrity, often lacks comprehensive sustainability certification, making green steel a more accountable choice for environmentally conscious construction projects.
Durability and Lifespan in Construction
Green steel, produced using sustainable methods like hydrogen reduction or electric arc furnaces, offers comparable or superior durability to traditional rebar steel due to its reduced impurities and enhanced corrosion resistance. Rebar steel, typically made from conventional blast furnace processes, may be more prone to corrosion over time, especially in harsh environments, potentially compromising structural lifespan. Choosing green steel for reinforcement extends the construction's durability and lifespan while minimizing environmental impact.
Availability and Market Trends
Green steel, produced using low-carbon or renewable energy methods, is gaining traction in the reinforcement market due to increasing environmental regulations and demand for sustainable construction materials. Rebar steel remains widely available and dominates the market because of its established supply chains and cost-effectiveness, though its production is carbon-intensive. Market trends indicate a gradual shift as manufacturers invest in green steel technologies to meet the growing preference for eco-friendly infrastructure development.
Applications in Modern Infrastructure
Green steel offers sustainable reinforcement solutions with lower carbon emissions, making it ideal for eco-friendly infrastructure projects such as green buildings and sustainable urban development. Rebar steel remains the standard choice for conventional concrete reinforcement in bridges, highways, and high-rise buildings due to its high tensile strength and availability. Innovations in green steel production are expanding applications by combining environmental benefits with the mechanical properties required for modern infrastructure demands.
Future Prospects and Industry Innovations
Green steel, produced using low-carbon methods such as hydrogen reduction and electric arc furnaces powered by renewable energy, is gaining traction as the future of sustainable reinforcement materials in construction. Innovations like carbon capture technology and circular steel economy initiatives are accelerating green steel adoption, potentially reducing the reinforcement sector's carbon emissions by up to 70% by 2050. Rebar steel manufacturers are increasingly integrating these green processes to meet stringent environmental regulations and growing demand for eco-friendly infrastructure.
Infographic: Green steel vs Rebar steel for Reinforcement
 azmater.com
azmater.com