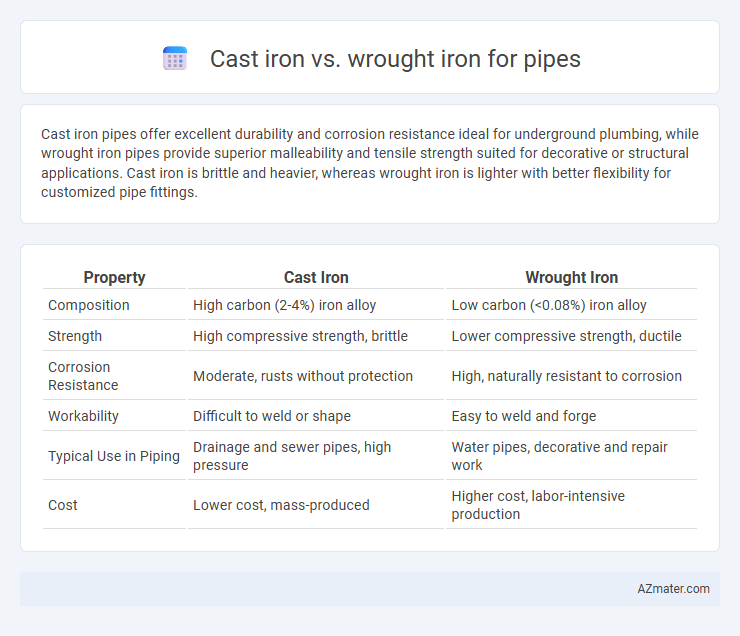
Cast iron pipes offer excellent durability and corrosion resistance ideal for underground plumbing, while wrought iron pipes provide superior malleability and tensile strength suited for decorative or structural applications. Cast iron is brittle and heavier, whereas wrought iron is lighter with better flexibility for customized pipe fittings.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cast Iron | Wrought Iron |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | High carbon (2-4%) iron alloy | Low carbon (<0.08%) iron alloy |
| Strength | High compressive strength, brittle | Lower compressive strength, ductile |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate, rusts without protection | High, naturally resistant to corrosion |
| Workability | Difficult to weld or shape | Easy to weld and forge |
| Typical Use in Piping | Drainage and sewer pipes, high pressure | Water pipes, decorative and repair work |
| Cost | Lower cost, mass-produced | Higher cost, labor-intensive production |
Introduction to Cast Iron and Wrought Iron Pipes
Cast iron pipes, made from molten iron with high carbon content, offer exceptional durability and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for water and sewage systems. Wrought iron pipes, composed primarily of iron with very low carbon content, provide superior ductility and toughness, often used for decorative or specialized piping applications. Both materials have distinct metallurgical properties that influence their performance and suitability in plumbing and infrastructure projects.
Historical Use in Piping Systems
Cast iron pipes, widely used since the 19th century, were favored for their durability and resistance to corrosion in municipal water and sewage systems. Wrought iron pipes, historically prominent in the 18th and early 19th centuries, were valued for their malleability and ability to withstand internal pressure, making them suitable for gas and water distribution before the advent of steel pipes. The transition from wrought iron to cast iron marked a significant advancement in piping technology, enabling longer pipe sections and improved reliability in infrastructure.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Cast iron pipes consist primarily of carbon (2-4%) and silicon, produced through a casting process where molten iron is poured into molds, resulting in a brittle yet corrosion-resistant structure. Wrought iron pipes contain very low carbon content (generally less than 0.08%) and are manufactured by heating iron and mechanically working it through rolling, hammering, or drawing, which imparts ductility and toughness. The manufacturing differences lead to cast iron being rigid and ideal for high-compression applications, while wrought iron offers greater malleability and weldability ideal for customized or restorative pipework.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Cast iron pipes exhibit high compressive strength and excellent wear resistance but tend to be brittle with low tensile strength, making them prone to cracking under tensile stress. Wrought iron pipes offer superior tensile strength, ductility, and impact resistance due to their fibrous grain structure, enhancing durability under dynamic loads and bending. The choice between cast iron and wrought iron pipes depends on specific mechanical demands, with wrought iron preferred for applications requiring toughness and flexibility, while cast iron suits environments needing strong compressive capacity.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Cast iron pipes exhibit moderate corrosion resistance due to their dense, brittle structure but are prone to rust and cracking under prolonged moisture exposure. Wrought iron pipes offer superior corrosion resistance thanks to their fibrous structure and high purity, enhancing durability in moist and aggressive environments. The durability of wrought iron surpasses cast iron, making it preferable for applications requiring longevity and resistance to corrosive elements.
Installation Methods and Ease
Cast iron pipes require heavy-duty equipment for installation due to their brittle nature and weight, often needing mechanical joints or lead and oakum for sealing, making the process labor-intensive. Wrought iron pipes, being more malleable and lighter, allow for easier handling and installation using threaded or welded joints, facilitating quicker assembly and adjustments on-site. The ease of installation for wrought iron pipes typically results in lower labor costs and reduced installation time compared to cast iron pipes.
Cost Analysis: Cast Iron vs Wrought Iron
Cast iron pipes typically cost less upfront due to lower material and manufacturing expenses, making them a budget-friendly option for plumbing and drainage systems. Wrought iron pipes, while more expensive initially, offer superior durability and corrosion resistance, potentially reducing long-term maintenance and replacement costs. Overall, cast iron is advantageous for cost-sensitive projects, whereas wrought iron delivers better value in applications requiring enhanced longevity.
Applications in Modern Plumbing
Cast iron pipes are widely used in modern plumbing for their excellent durability and sound dampening qualities, making them ideal for waste and drainage systems. Wrought iron pipes, though less common today, are prized for their corrosion resistance and strength, often utilized in specialty applications such as historic restoration and decorative water fixtures. Choosing between cast iron and wrought iron depends on factors such as load-bearing requirements, exposure to corrosive elements, and longevity expectations.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Cast iron pipes have a higher carbon footprint due to energy-intensive production processes and the use of coke in smelting, whereas wrought iron pipes involve less energy consumption but are less common in modern applications. Both materials are recyclable; cast iron is typically remelted and repurposed in foundries, maintaining material efficiency and reducing landfill waste. Wrought iron's recyclability is limited as it is often combined with other metals during fabrication, complicating recycling efforts despite its longer lifespan and lower corrosion rate.
Choosing the Right Iron Pipe for Your Project
Choosing between cast iron and wrought iron pipes depends on project requirements like durability, corrosion resistance, and flexibility. Cast iron pipes offer excellent strength and noise reduction, making them ideal for drainage and underground applications, while wrought iron pipes provide superior ductility and resistance to fatigue, suited for decorative and structural uses. Consider the environment, budget, and installation needs to select the best iron pipe material for longevity and performance.
Infographic: Cast iron vs Wrought iron for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com