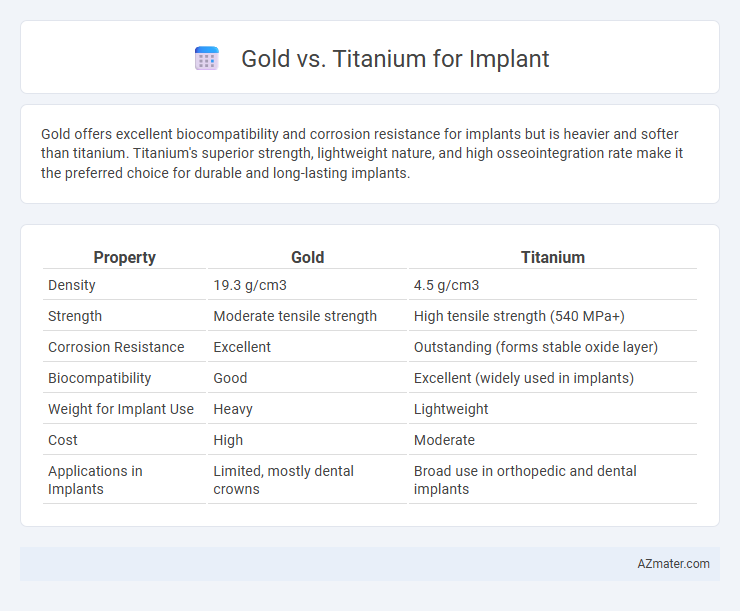
Gold offers excellent biocompatibility and corrosion resistance for implants but is heavier and softer than titanium. Titanium's superior strength, lightweight nature, and high osseointegration rate make it the preferred choice for durable and long-lasting implants.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Gold | Titanium |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 19.3 g/cm3 | 4.5 g/cm3 |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength (540 MPa+) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Outstanding (forms stable oxide layer) |
| Biocompatibility | Good | Excellent (widely used in implants) |
| Weight for Implant Use | Heavy | Lightweight |
| Cost | High | Moderate |
| Applications in Implants | Limited, mostly dental crowns | Broad use in orthopedic and dental implants |
Introduction to Dental Implant Materials
Dental implants commonly utilize materials such as gold and titanium due to their biocompatibility and strength. Titanium's high osseointegration capability makes it the preferred choice for implant fixtures, promoting bone growth and stability. Gold offers excellent corrosion resistance and aesthetic benefits but is less frequently used due to its higher cost and lower integration with bone tissue compared to titanium.
Overview of Gold and Titanium Implants
Gold implants exhibit excellent biocompatibility and corrosion resistance, making them a historically significant choice in dental and orthopedic applications. Titanium implants have become the standard due to their superior osseointegration, lightweight strength, and resistance to corrosion under physiological conditions. Both materials offer durability and compatibility, but titanium's ability to bond directly with bone tissue provides distinct advantages for long-term implant stability.
Biocompatibility: Gold vs Titanium
Titanium exhibits superior biocompatibility compared to gold, as it forms a stable oxide layer that promotes osseointegration and minimizes allergic reactions in dental and medical implants. Gold, while biocompatible and corrosion-resistant, lacks the same level of integration with bone tissue, potentially limiting its effectiveness in long-term implant stability. Clinical studies have consistently favored titanium for implants due to its ability to support bone growth and reduce inflammation around the implant site.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Titanium implants exhibit superior strength-to-weight ratio and higher tensile strength compared to gold, making them more resistant to mechanical stress and deformation. Gold, while corrosion-resistant and biocompatible, is softer and more prone to wear over time, reducing its durability in load-bearing implant applications. Titanium's exceptional fatigue resistance and ability to osseointegrate contribute to longer-lasting, stable implants in medical and dental fields.
Aesthetic Considerations in Implant Selection
Gold implants offer a warm, natural hue that can blend seamlessly with certain skin tones, reducing the risk of metal show-through compared to titanium. Titanium implants, while highly durable and biocompatible, may sometimes cause a grayish tint around the gum line, affecting aesthetic outcomes. Selecting the appropriate material depends on patient-specific factors such as skin tone, gum thickness, and desired visual results for optimal implant aesthetics.
Corrosion Resistance: Gold vs Titanium
Gold exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance due to its inert properties, making it highly stable and biocompatible in oral environments. Titanium also offers excellent corrosion resistance, forming a protective titanium oxide layer that prevents degradation and promotes osseointegration. While gold resists chemical reactions, titanium's passive oxide film provides durability against mechanical wear and corrosive bodily fluids in dental implants.
Cost Analysis of Gold and Titanium Implants
Gold implants typically cost significantly more than titanium implants due to the high price of gold as a raw material and its processing requirements. Titanium implants offer a cost-effective solution, combining durability and biocompatibility with lower manufacturing expenses. The overall cost analysis favors titanium for patients seeking affordability without compromising implant quality and longevity.
Allergic Reactions and Patient Safety
Gold implants have a higher risk of causing allergic reactions due to nickel or other metal alloys commonly mixed with gold, whereas titanium is highly biocompatible and rarely triggers allergies. Titanium's superior corrosion resistance minimizes ion release, further reducing the risk of hypersensitivity and improving patient safety in dental and orthopedic implants. Clinical studies consistently show titanium's excellent performance in promoting osseointegration without adverse immune responses, making it the preferred choice for patients prone to metal allergies.
Longevity and Clinical Success Rates
Gold and titanium implants both demonstrate high clinical success rates, with titanium showing superior osseointegration and longevity due to its biocompatibility and corrosion resistance. Studies report titanium implants have success rates exceeding 95% over 10 years, whereas gold alloys, while biocompatible, often exhibit lower durability and higher risks of mechanical wear. Titanium's ability to withstand mechanical stresses and support bone integration makes it the preferred choice for long-term implant stability and patient outcomes.
Choosing the Right Material for Dental Implants
Gold and titanium are the two primary materials used for dental implants due to their biocompatibility and durability. Titanium is favored for its exceptional strength, lightweight nature, and high osseointegration rate, ensuring stable bone attachment, while gold offers superior corrosion resistance and a natural aesthetic appeal for certain patients. Selecting the right material depends on factors such as patient allergies, implant location, load-bearing requirements, and desired cosmetic outcomes.
Infographic: Gold vs Titanium for Implant
 azmater.com
azmater.com