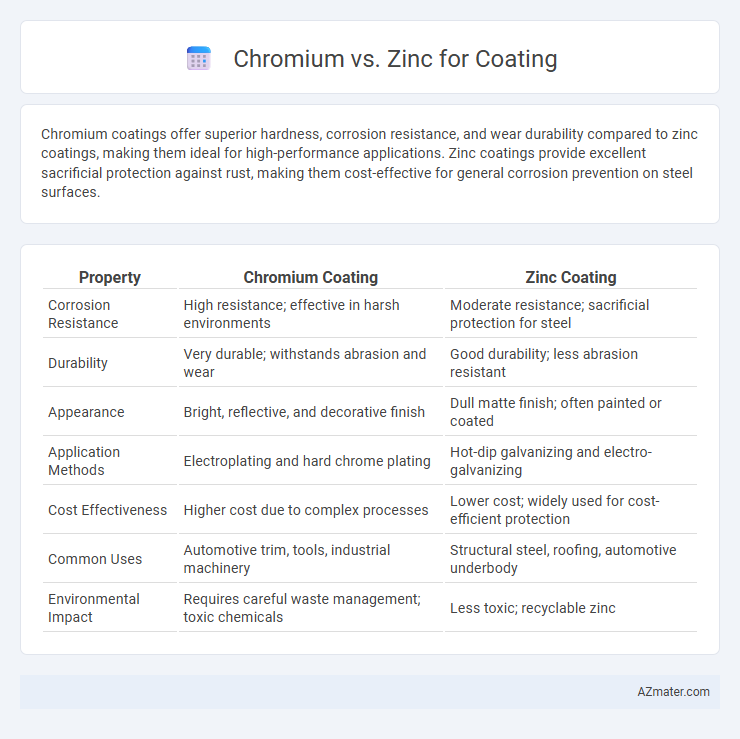
Chromium coatings offer superior hardness, corrosion resistance, and wear durability compared to zinc coatings, making them ideal for high-performance applications. Zinc coatings provide excellent sacrificial protection against rust, making them cost-effective for general corrosion prevention on steel surfaces.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chromium Coating | Zinc Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | High resistance; effective in harsh environments | Moderate resistance; sacrificial protection for steel |
| Durability | Very durable; withstands abrasion and wear | Good durability; less abrasion resistant |
| Appearance | Bright, reflective, and decorative finish | Dull matte finish; often painted or coated |
| Application Methods | Electroplating and hard chrome plating | Hot-dip galvanizing and electro-galvanizing |
| Cost Effectiveness | Higher cost due to complex processes | Lower cost; widely used for cost-efficient protection |
| Common Uses | Automotive trim, tools, industrial machinery | Structural steel, roofing, automotive underbody |
| Environmental Impact | Requires careful waste management; toxic chemicals | Less toxic; recyclable zinc |
Overview of Chromium and Zinc Coatings
Chromium coatings offer exceptional hardness, corrosion resistance, and a bright, reflective finish, making them ideal for automotive parts, aerospace components, and decorative applications. Zinc coatings provide excellent sacrificial protection against rust, commonly used in galvanization for steel structures, automotive bodies, and outdoor equipment. Both metals enhance durability but serve different purposes: chromium emphasizes surface aesthetics and wear resistance, while zinc primarily prevents corrosion through a protective barrier.
Chemical Properties and Composition
Chromium coatings provide exceptional corrosion resistance due to their stable oxide layer, primarily composed of chromium oxide (Cr2O3), which acts as a protective barrier against oxidation and chemical attack. Zinc coatings form a sacrificial anode with a primarily metallic zinc (Zn) composition, offering galvanic protection by corroding preferentially to the underlying metal. The chemical stability of chromium makes it suitable for high-temperature and abrasive environments, whereas zinc's reactivity ensures effective protection in moist and mildly acidic conditions.
Application Methods: Chromium vs Zinc
Chromium coating is commonly applied using electroplating or physical vapor deposition (PVD) methods, providing a hard, corrosion-resistant surface ideal for automotive parts and industrial tools. Zinc coatings are primarily applied through hot-dip galvanizing or electroplating techniques, offering effective protection against rust for steel structures and fasteners in construction and outdoor applications. Both metals utilize distinct application processes tailored to maximize their protective properties on various substrates.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Chromium coatings provide superior corrosion resistance due to their ability to form a dense, passive oxide layer that effectively protects the underlying metal from oxidation and aggressive environmental factors. Zinc coatings offer sacrificial protection by corroding preferentially, which is beneficial for steel structures but generally less durable than chromium in harsh or long-term exposure. Chromium's higher resistance to abrasion and chemical attack makes it the preferred choice for applications requiring prolonged corrosion protection and aesthetic durability.
Durability and Longevity
Chromium coatings exhibit superior durability and corrosion resistance due to their hardness and chemical stability, making them ideal for high-wear applications. Zinc coatings primarily offer sacrificial protection by corroding preferentially, which extends the substrate's lifespan but typically lasts less than chromium coatings. While zinc is cost-effective for long-term rust prevention, chromium ensures greater longevity and maintains surface integrity under extreme conditions.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Chromium coatings, particularly hexavalent chromium, pose significant environmental and health risks due to their toxicity and carcinogenic properties, leading to stringent regulations and costly waste management. Zinc coatings offer a safer and more eco-friendly alternative, with lower toxicity and easier recycling processes, making them preferable for reducing environmental impact. The selection between chromium and zinc coatings heavily depends on balancing performance requirements with compliance to environmental and occupational safety standards.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Chromium coatings typically incur higher material and processing costs compared to zinc due to chromium's complex plating procedures and environmental regulations impacting waste treatment. Zinc coatings offer a more cost-effective solution with lower raw material expenses and simpler application methods, making zinc preferred for large-scale industrial use where budget constraints are critical. Evaluating long-term economic benefits, zinc's corrosion resistance and ease of maintenance often result in reduced total lifecycle costs despite chromium's superior hardness and aesthetic appeal.
Common Industrial Uses
Chromium and zinc are widely used for protective metal coatings in various industries due to their corrosion resistance properties. Chromium coatings are primarily utilized in automotive parts and aerospace components to provide hardness, wear resistance, and aesthetic appeal. Zinc coatings, commonly applied through galvanization, protect steel structures and fasteners in construction and manufacturing by preventing rust formation.
Maintenance and Repair Requirements
Chromium coatings offer superior corrosion resistance and durability, resulting in lower maintenance frequency and reduced repair costs compared to zinc coatings. Zinc coatings may require more frequent inspections and touch-ups due to their sacrificial protection nature, which corrodes to protect the base metal. Maintenance efforts for chromium coatings are often limited to surface cleaning, while zinc coatings might need periodic reapplication to maintain protective properties.
Choosing the Right Coating for Your Needs
Chromium coatings offer superior corrosion resistance, high hardness, and excellent wear protection, making them ideal for industrial machinery and automotive parts exposed to harsh environments. Zinc coatings provide effective sacrificial protection against rust, especially for steel structures like bridges and outdoor equipment, due to zinc's ability to corrode preferentially. Selecting the right coating depends on factors such as environmental exposure, desired durability, and cost considerations, with chromium preferred for heavy-duty applications and zinc favored for economical, long-term corrosion prevention.
Infographic: Chromium vs Zinc for Coating
 azmater.com
azmater.com