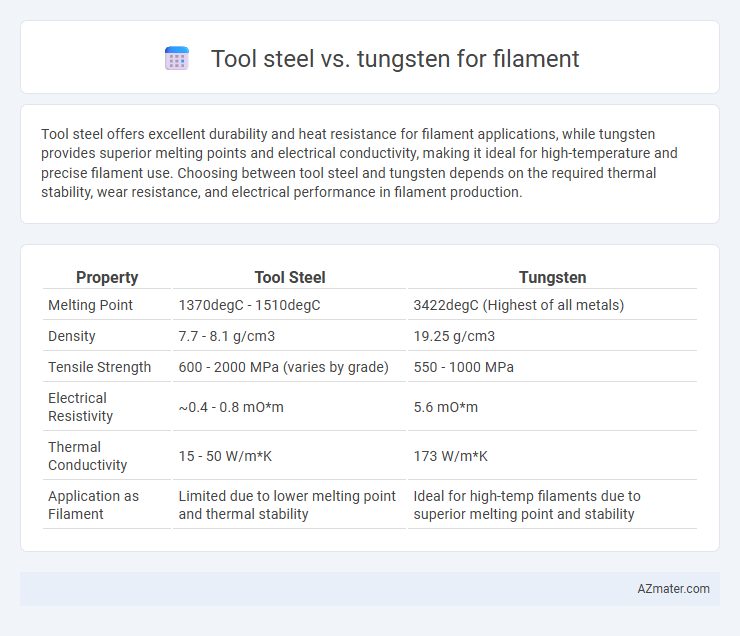
Tool steel offers excellent durability and heat resistance for filament applications, while tungsten provides superior melting points and electrical conductivity, making it ideal for high-temperature and precise filament use. Choosing between tool steel and tungsten depends on the required thermal stability, wear resistance, and electrical performance in filament production.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tool Steel | Tungsten |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | 1370degC - 1510degC | 3422degC (Highest of all metals) |
| Density | 7.7 - 8.1 g/cm3 | 19.25 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 600 - 2000 MPa (varies by grade) | 550 - 1000 MPa |
| Electrical Resistivity | ~0.4 - 0.8 mO*m | 5.6 mO*m |
| Thermal Conductivity | 15 - 50 W/m*K | 173 W/m*K |
| Application as Filament | Limited due to lower melting point and thermal stability | Ideal for high-temp filaments due to superior melting point and stability |
Introduction to Tool Steel and Tungsten
Tool steel, characterized by its high hardness, abrasion resistance, and ability to retain a sharp edge under high temperatures, is commonly used in precision cutting and forming tools. Tungsten, known for its exceptional melting point of 3422degC and superior density, provides unparalleled durability and thermal stability in filament applications. Choosing between tool steel and tungsten filaments depends on factors like wear resistance, temperature tolerance, and specific use-case requirements in manufacturing or 3D printing processes.
Overview of Filament Materials
Tool steel filaments offer high hardness, wear resistance, and excellent toughness, making them ideal for durable, precision 3D printing applications requiring strength and heat resistance. Tungsten filaments excel with exceptional melting points, superior heat conductivity, and density, suited for high-temperature and wear-intensive environments. Selecting between tool steel and tungsten depends on balancing mechanical strength and thermal performance to meet specific industrial filament material needs.
Composition of Tool Steel Filaments
Tool steel filaments are primarily composed of iron alloys with carbon content ranging from 0.5% to 1.5%, enhanced by elements such as chromium, vanadium, molybdenum, and tungsten to improve hardness, wear resistance, and heat tolerance. Unlike pure tungsten filaments known for their extremely high melting point (3422degC), tool steel offers balanced mechanical properties attributable to its alloying elements, making it suitable for applications requiring toughness and thermal resilience. The presence of carbide-forming elements in tool steel filaments contributes to a microstructure optimized for durability under cyclic thermal and mechanical stress.
Properties of Tungsten Filaments
Tungsten filaments exhibit exceptional properties such as a high melting point of 3422degC, excellent tensile strength, and superior resistance to oxidation at elevated temperatures, making them ideal for high-temperature applications. Their low vapor pressure ensures prolonged filament life and consistent luminosity in lighting and industrial devices. Compared to tool steel, tungsten offers unmatched thermal stability and durability in filament use, enhancing performance in extreme thermal environments.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Tool steel offers high tensile strength and excellent resistance to wear, making it a durable choice for filament applications subject to mechanical stress. Tungsten surpasses tool steel in hardness and can withstand extreme temperatures without deformation, providing superior durability in high-heat conditions. While tool steel excels in toughness and flexibility, tungsten filament ensures longer lifespan and reliability under intense thermal and abrasive environments.
Heat Resistance: Tool Steel vs Tungsten
Tungsten exhibits superior heat resistance compared to tool steel, with a melting point around 3,422degC, making it ideal for high-temperature filament applications. Tool steel typically melts between 1,370degC and 1,530degC, limiting its effectiveness under extreme heat conditions. This significant difference in thermal stability ensures tungsten filaments maintain structural integrity and performance in environments where tool steel would degrade or fail.
Conductivity and Performance in Filaments
Tool steel offers moderate electrical conductivity and excellent wear resistance, making it suitable for filaments requiring durability under high mechanical stress. Tungsten exhibits superior electrical conductivity and exceptional melting point, ensuring consistent performance and longer lifespan in high-temperature filament applications. The choice between tool steel and tungsten filaments depends on balancing conductivity needs with thermal and mechanical stability in the intended use case.
Cost Analysis of Tool Steel and Tungsten
Tool steel offers a significantly lower initial cost compared to tungsten, making it more budget-friendly for filament applications. Tungsten's higher raw material and processing expenses drive up its price, though it provides superior wear resistance and heat tolerance. When analyzing long-term cost efficiency, tool steel may require more frequent replacements, while tungsten's durability can reduce overall lifecycle expenses despite the upfront investment.
Best Applications for Each Filament Material
Tool steel filaments excel in applications requiring high wear resistance and durability, making them ideal for manufacturing functional prototypes, mechanical parts, and tools exposed to abrasion. Tungsten filaments are best suited for advanced applications demanding exceptional heat resistance and high melting points, such as aerospace components and high-temperature mold inserts. Choosing between tool steel and tungsten depends on balancing mechanical strength with thermal stability for the specific industrial use case.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Filament Material
Tool steel offers superior durability and heat resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring high strength and wear resistance. Tungsten filament excels in high-temperature environments due to its exceptional melting point and electrical conductivity, suitable for specialized industrial uses. Selecting the right filament material depends on the specific application requirements, balancing factors such as tensile strength, heat tolerance, and machining properties to optimize performance and longevity.
Infographic: Tool steel vs Tungsten for Filament
 azmater.com
azmater.com